Opposing counsel plays a critical role in legal proceedings by representing the interests of the opposing party and challenging your case. Understanding their strategies and tactics can help you better prepare and strengthen your position. Dive into the rest of the article to learn how to effectively navigate interactions with opposing counsel.
Table of Comparison
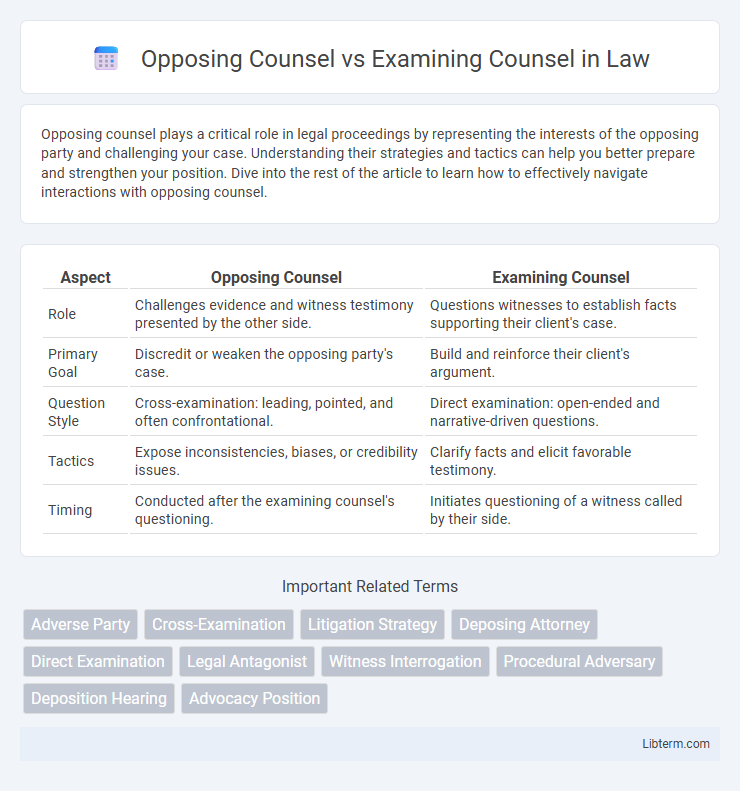
| Aspect | Opposing Counsel | Examining Counsel |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Challenges evidence and witness testimony presented by the other side. | Questions witnesses to establish facts supporting their client's case. |
| Primary Goal | Discredit or weaken the opposing party's case. | Build and reinforce their client's argument. |
| Question Style | Cross-examination: leading, pointed, and often confrontational. | Direct examination: open-ended and narrative-driven questions. |
| Tactics | Expose inconsistencies, biases, or credibility issues. | Clarify facts and elicit favorable testimony. |
| Timing | Conducted after the examining counsel's questioning. | Initiates questioning of a witness called by their side. |
Introduction to Opposing Counsel and Examining Counsel
Opposing Counsel represents the adverse party in legal proceedings, responsible for challenging evidence and advocating against the opposing side's claims. Examining Counsel conducts direct examination of witnesses to elicit favorable testimony supporting their client's case. Both roles require strategic questioning techniques to effectively present or dispute facts within the courtroom.
Defining Opposing Counsel
Opposing Counsel refers to the attorney representing the adverse party in a legal proceeding, responsible for challenging the statements and evidence presented by the opposing side. This role involves cross-examining witnesses, disputing facts, and advocating against the interests of the Examining Counsel, who is the lawyer conducting the direct examination of a witness. Understanding Opposing Counsel is crucial for anticipating objections and strategies during litigation or depositions.
Understanding Examining Counsel
Examining counsel are responsible for questioning witnesses during a trial or deposition to clarify facts and elicit truthful, detailed testimony. Unlike opposing counsel, who focus on challenging the credibility and arguments of the other side, examining counsel aim to present a coherent narrative that supports their client's case. Their role requires deep understanding of legal procedures and strategic questioning techniques to effectively guide witness responses.
Key Differences Between Opposing and Examining Counsel
Opposing counsel represents the adversary party in a legal proceeding, tasked with challenging the case against their client by cross-examining witnesses and presenting counterarguments. Examining counsel, often the lawyer who called the witness, conducts direct examination to elicit favorable testimony supporting their client's position. The key difference lies in their objectives: opposing counsel seeks to dispute and undermine evidence, while examining counsel aims to establish and clarify facts through witness testimony.
Roles and Responsibilities in Legal Proceedings
Opposing Counsel represents the adversarial party in legal proceedings, tasked with challenging the evidence, questioning the credibility of witnesses, and advocating for their client's interests. Examining Counsel conducts direct examination of witnesses they have called, aiming to elicit strong, favorable testimony and establish facts supporting their case. Both roles require strategic questioning and thorough understanding of courtroom procedures to influence the judge or jury effectively.
Legal Strategies: Opposing vs Examining Counsel
Opposing counsel employs legal strategies centered on challenging the credibility of witnesses, undermining the opposing party's case, and protecting their client's interests through aggressive cross-examination and objections. Examining counsel focuses on eliciting favorable testimony, establishing facts, and constructing a coherent narrative by asking clear, open-ended questions and presenting evidence in a logical sequence. Strategic differences revolve around examination techniques, control over witness testimony, and the balance between offensive and defensive advocacy in trial proceedings.
Skills Required for Each Counsel Type
Opposing Counsel requires strong adversarial skills, including effective cross-examination, strategic argumentation, and keen negotiation capabilities to challenge the opposing party's case. Examining Counsel must excel in thorough witness examination, precise questioning techniques, and the ability to elicit clear, relevant testimony to support their client's position. Both roles demand a deep understanding of legal procedures, persuasive communication, and analytical thinking tailored to courtroom dynamics.
Common Challenges Faced by Each Counsel
Opposing Counsel often faces challenges such as anticipating the examination strategy, overcoming witness bias, and managing limited access to information. Examining Counsel struggles with eliciting truthful and precise testimony, maintaining witness composure, and avoiding contradictions that opposing counsel can exploit. Both roles require strategic questioning and adaptability to navigate the complexities of witness behavior and case dynamics effectively.
Impact on Case Outcomes
Opposing counsel and examining counsel play distinct roles that significantly influence case outcomes through their strategies and questioning techniques. Opposing counsel aims to challenge the credibility and evidence presented, often highlighting inconsistencies to weaken the case. Examining counsel focuses on establishing facts and supporting their client's narrative, shaping the judge or jury's perception to strengthen the case's overall argument.
Choosing the Right Legal Representation
Choosing the right legal representation requires understanding the distinct roles of opposing counsel and examining counsel in litigation. Opposing counsel advocates for the adverse party, aiming to challenge and dispute claims, while examining counsel focuses on questioning witnesses to clarify facts and build their client's case. Selecting a lawyer skilled in handling cross-examinations and anticipating opposing counsel's tactics ensures stronger advocacy and strategic advantage in court.
Opposing Counsel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com