Burglary involves unlawfully entering a building or property with the intent to commit theft or another crime, often causing significant emotional and financial distress to victims. Understanding the legal definitions, prevention strategies, and potential consequences can help you better protect your home and assets. Explore the rest of the article to learn effective ways to safeguard your property and respond if a burglary occurs.
Table of Comparison
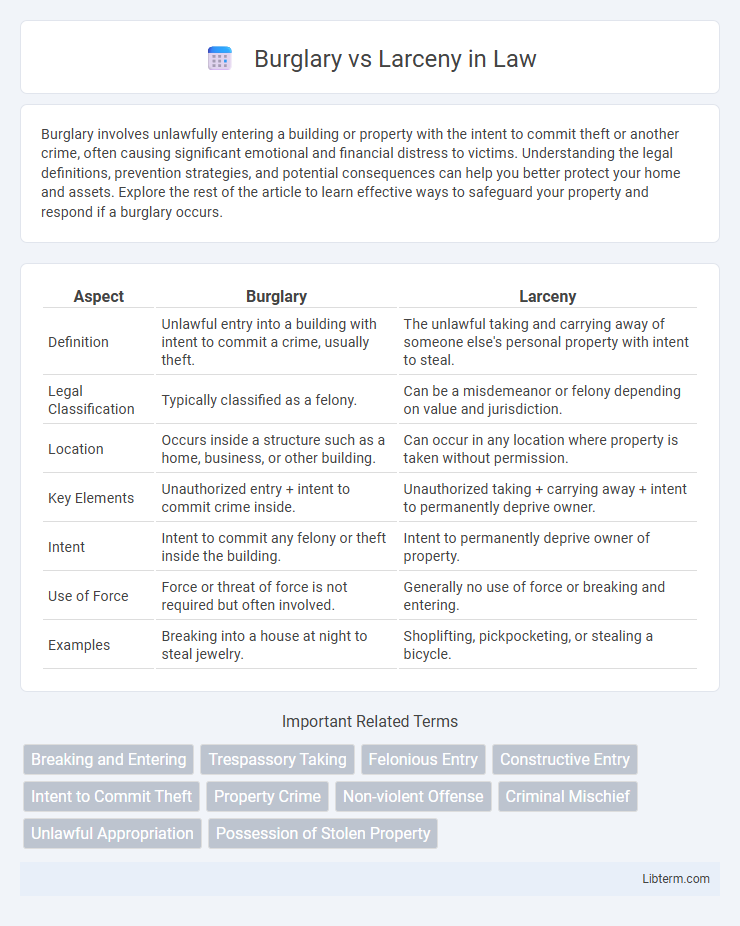
| Aspect | Burglary | Larceny |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unlawful entry into a building with intent to commit a crime, usually theft. | The unlawful taking and carrying away of someone else's personal property with intent to steal. |
| Legal Classification | Typically classified as a felony. | Can be a misdemeanor or felony depending on value and jurisdiction. |
| Location | Occurs inside a structure such as a home, business, or other building. | Can occur in any location where property is taken without permission. |
| Key Elements | Unauthorized entry + intent to commit crime inside. | Unauthorized taking + carrying away + intent to permanently deprive owner. |
| Intent | Intent to commit any felony or theft inside the building. | Intent to permanently deprive owner of property. |
| Use of Force | Force or threat of force is not required but often involved. | Generally no use of force or breaking and entering. |
| Examples | Breaking into a house at night to steal jewelry. | Shoplifting, pickpocketing, or stealing a bicycle. |
Understanding Burglary: Definition and Key Elements
Burglary involves unlawful entry into a building or structure with the intent to commit a crime, typically theft, inside. Key elements include trespassing, intent to commit a felony or theft, and occurrence within a dwelling or commercial premises. Unlike larceny, which is the act of stealing property without breaking into a space, burglary emphasizes the illegal entry aspect paired with criminal intent.
Defining Larceny: Core Characteristics
Larceny is defined as the unlawful taking and carrying away of someone else's personal property with the intent to permanently deprive the owner of it. Unlike burglary, which involves illegal entry into a structure to commit a crime, larceny centers solely on the theft aspect without the necessity of trespassing. Core characteristics of larceny include the absence of force or breaking and entering and the focus on physical possession of the stolen property.
Burglary vs Larceny: Main Differences Explored
Burglary involves unlawfully entering a building or structure with the intent to commit a crime, typically theft, whereas larceny specifically refers to the unlawful taking and carrying away of someone else's personal property with the intent to permanently deprive the owner. Burglary is classified as a felony and may involve damage to property or threats to occupants, while larceny can range from petty theft to grand theft depending on the property value. Legal definitions and penalties for burglary versus larceny vary by jurisdiction, emphasizing unauthorized entry in burglary versus unauthorized taking in larceny.
Legal Consequences: Burglary vs Larceny Penalties
Burglary penalties typically involve harsher legal consequences due to the crime's nature of unlawful entry with intent to commit a felony or theft, often resulting in felony charges and significant prison time. Larceny penalties vary based on the value of stolen property, ranging from misdemeanors for petty theft to felony charges for grand larceny, with corresponding fines and incarceration periods. Courts consider factors such as prior offenses and the presence of aggravating circumstances when determining the severity of sentencing for both crimes.
Common Examples of Burglary
Burglary commonly involves unlawful entry into homes, businesses, or other structures to commit theft, vandalism, or another felony, such as breaking into a residence at night to steal valuables or entering a commercial building after hours to pilfer equipment. Unlike larceny, which simply refers to the unlawful taking of property without breaking and entering, burglary emphasizes the trespass element. Typical examples include breaking a window to gain access, picking locked doors, or using force to enter a property with the intent to commit theft or another crime inside.
Typical Scenarios of Larceny
Typical scenarios of larceny involve the unlawful taking of someone else's personal property without their consent, often occurring in settings such as retail stores, where shoplifting is common. Street theft, including pickpocketing and purse snatching, represents frequent larceny cases targeting individuals in public spaces. Unlike burglary, larceny does not involve unlawful entry into a building but centers on the direct appropriation of movable property.
Proving Burglary in Court: Essential Evidence
Proving burglary in court requires establishing unlawful entry into a building with intent to commit a crime, typically theft or vandalism. Essential evidence includes surveillance footage, eyewitness testimony, physical signs of forced entry, and the presence of stolen property linked to the accused. Forensic evidence like fingerprints, DNA, and tool marks can further strengthen the prosecution's case by directly tying the defendant to the burglary scene.
Establishing Larceny: Legal Requirements
Establishing larceny requires proving the unlawful taking and carrying away of someone else's personal property with the intent to permanently deprive the owner of its possession. The prosecution must demonstrate the defendant's specific intent to steal at the time of the act, alongside the absence of consent from the property owner. Unlike burglary, which involves unlawful entry into a structure, larceny focuses solely on the wrongful appropriation of movable goods.
Preventing Burglary and Larceny: Practical Tips
Effective prevention of burglary and larceny involves securing entry points with high-quality locks and installing visible security cameras to deter potential intruders. Maintaining clear visibility around your property by trimming shrubs and using adequate lighting reduces hiding spots for criminals, while neighborhood watch programs enhance community vigilance. Regularly safeguarding valuables, avoiding public disclosure of travel plans, and promptly reporting suspicious activities reinforce a proactive approach to minimizing risks of theft and break-ins.
When to Seek Legal Help for Burglary or Larceny Charges
Seek legal help immediately after being charged with burglary or larceny to protect your rights and build a strong defense. Burglary, involving unlawful entry with intent to commit a crime, typically carries more severe penalties than larceny, which focuses on theft without unlawful entry. Early consultation with a criminal defense attorney specializing in property crimes can clarify charges, navigate complex legal procedures, and potentially reduce or dismiss the accusations.
Burglary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com