Forcible entry involves breaching secured doors, windows, or barriers using specialized tools and techniques to gain access during emergencies or law enforcement operations. Mastery of forcible entry methods ensures rapid, safe, and effective entry while minimizing damage to property and risk to personnel. Discover essential strategies and tools to enhance your forcible entry skills in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
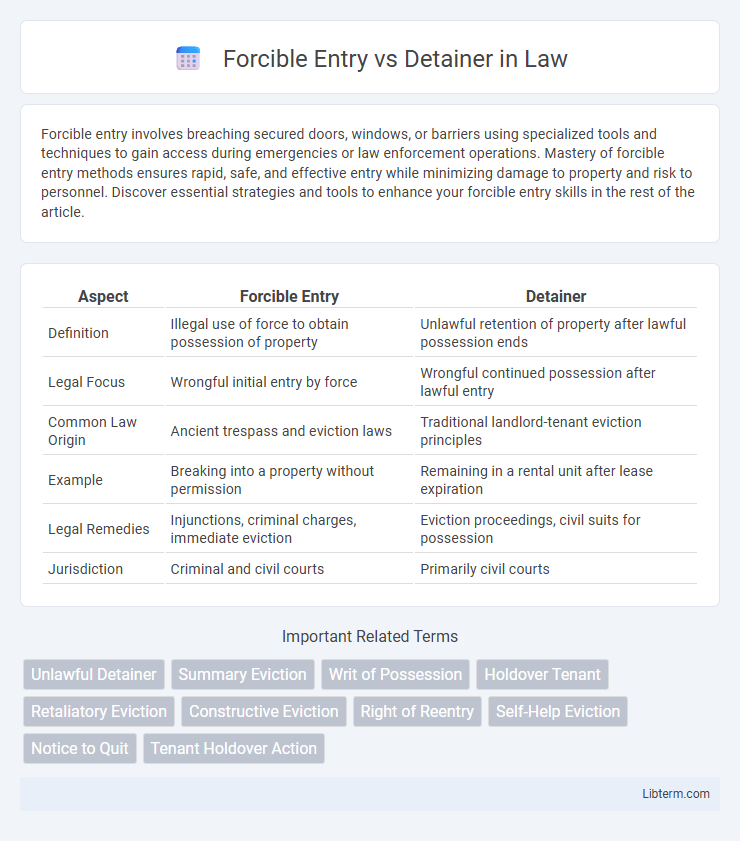
| Aspect | Forcible Entry | Detainer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Illegal use of force to obtain possession of property | Unlawful retention of property after lawful possession ends |
| Legal Focus | Wrongful initial entry by force | Wrongful continued possession after lawful entry |
| Common Law Origin | Ancient trespass and eviction laws | Traditional landlord-tenant eviction principles |
| Example | Breaking into a property without permission | Remaining in a rental unit after lease expiration |
| Legal Remedies | Injunctions, criminal charges, immediate eviction | Eviction proceedings, civil suits for possession |
| Jurisdiction | Criminal and civil courts | Primarily civil courts |
Understanding Forcible Entry and Detainer
Forcible entry and detainer involve legal actions related to property possession disputes. Understanding forcible entry refers to the unlawful entry onto a property by using force or threats without permission, while detainer pertains to unlawfully holding possession after one's right has expired or been terminated. Accurate knowledge of these terms is essential for landlords and tenants to navigate eviction processes and property rights effectively.
Legal Definitions of Forcible Entry
Forcible entry refers to the illegal act of physically entering or taking possession of a property by using force, threats, or other unlawful means without the consent of the rightful occupant. It is distinct from detainer, which involves the refusal to vacate a property after legal possession has been established. Legal definitions of forcible entry often emphasize the presence of violence, intimidation, or breaking and entering as critical elements to differentiate it from other property disputes.
What Constitutes a Detainer
A detainer occurs when a tenant unlawfully remains in possession of a property after the lease term has expired or after proper notice to vacate has been given, without the landlord's consent. This unauthorized retention of possession distinguishes detainer from a forcible entry, which involves the illegal act of physically entering property without permission. Understanding the precise legal definition of detainer is critical in landlord-tenant disputes and eviction proceedings.
Key Differences Between Forcible Entry and Detainer
Forcible entry involves taking possession of property by force or without legal right, often through unlawful means such as breaking locks or barriers. Detainer refers to the wrongful withholding of property or premises by a tenant or occupant after their legal right to possession has expired. The key difference lies in forcible entry being the act of gaining possession unlawfully, while detainer is the refusal to surrender possession after a legal tenancy or right has ended.
Grounds for Filing Forcible Entry Cases
Forcible entry cases are primarily filed when an individual unlawfully enters or re-enters property without a legal right or title, often by force or threat. Grounds for filing include the absence of consent from the lawful owner or rightful possessor, removal of occupants without due legal process, and violation of possession rights after eviction. These cases emphasize the protection of possession rather than ownership, distinguishing them from detainer actions that focus on continued unlawful possession after a lawful entry.
Grounds for Filing Detainer Cases
Detainer cases are typically filed on grounds such as failure to pay rent, violation of lease terms, or illegal occupancy, whereas forcible entry often involves unlawful entry or possession without rightful claim. The primary basis for detainer is the tenant's breach of contractual obligations or statutory duties, enabling landlords to seek eviction through legal channels. Remedies in detainer actions focus on regaining possession and recovering unpaid rent or damages.
Legal Procedures and Timelines
Forcible entry involves unlawfully entering or remaining on property without legal right, whereas detainer pertains to holding possession after lawful entry, often due to lease expiration or nonpayment. Legal procedures for forcible entry require prompt filing of a complaint, typically within days of the incident, with strict adherence to eviction notices and court hearings to prevent self-help evictions. Detainer actions usually follow specific timelines mandated by state laws, including notice periods ranging from three to thirty days before filing for eviction, ensuring due process and lawful repossession.
Rights of Landlords and Tenants
Forcible entry involves taking possession of property without legal right or due process, often leading to immediate conflict between landlords and tenants. Detainer actions are formal legal processes landlords use to regain possession following a tenant's unlawful holdover after lease expiration, protecting landlords' property rights under state eviction laws. Tenants have rights to proper notice and due process during these proceedings, ensuring protection against illegal eviction and the right to contest claims in court.
Common Defenses in Forcible Entry and Detainer Cases
Common defenses in forcible entry and detainer cases include proving lawful possession through valid lease agreements or ownership documents, demonstrating that proper notice to vacate was not provided as required by law, and showing procedural errors made by the landlord during the eviction process. Tenants may also argue that the eviction was retaliatory or based on discrimination, violating local housing ordinances and civil rights protections. Evidence of repairs made despite landlord neglect or proof of rent payment in case of alleged nonpayment can further strengthen tenant defenses.
Remedies and Enforcement of Judgments
Forcible entry and detainer actions provide distinct remedies for landlords seeking possession of property in cases of unlawful entry or unlawful detention by tenants. Remedies for forcible entry typically include immediate eviction and restoration of possession, while detainer actions emphasize recovery of possession following a tenant's holdover after lease expiration. Enforcement of judgments often involves writs of possession issued by courts, enabling law enforcement to physically remove occupants and prevent further trespass or unauthorized retention, ensuring swift resolution and protection of property rights.
Forcible Entry Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com