Equity interpretation involves analyzing the true value and ownership rights within a company or legal agreement. Understanding how equity is distributed can impact financial decisions and long-term investments. Explore this article to learn how equity interpretation affects your financial strategy and business outcomes.
Table of Comparison
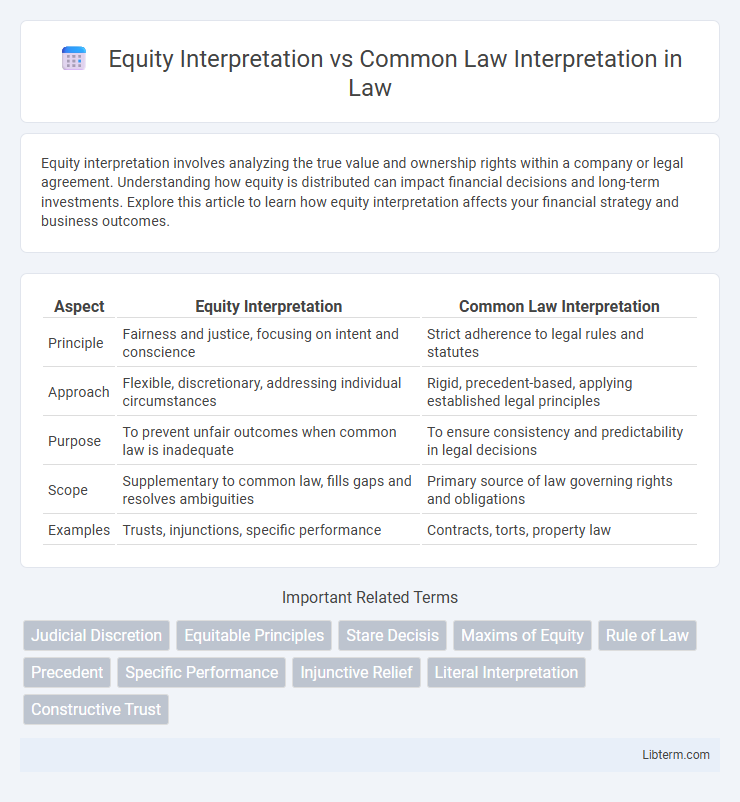
| Aspect | Equity Interpretation | Common Law Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Principle | Fairness and justice, focusing on intent and conscience | Strict adherence to legal rules and statutes |
| Approach | Flexible, discretionary, addressing individual circumstances | Rigid, precedent-based, applying established legal principles |
| Purpose | To prevent unfair outcomes when common law is inadequate | To ensure consistency and predictability in legal decisions |
| Scope | Supplementary to common law, fills gaps and resolves ambiguities | Primary source of law governing rights and obligations |
| Examples | Trusts, injunctions, specific performance | Contracts, torts, property law |
Introduction to Equity and Common Law Interpretation
Equity Interpretation arises from principles developed in the Court of Chancery to provide fairness and justice where common law remedies fall short, emphasizing flexibility and conscience. Common Law Interpretation strictly adheres to statutory text and precedent, prioritizing consistency and predictability in legal rulings. Understanding these foundational approaches highlights the contrast between equitable relief's discretionary nature and common law's rigid application of rules.
Historical Origins of Equity and Common Law
Equity interpretation originated from the English Court of Chancery in the 14th century to address the rigidity and limitations of common law, providing fairness through principles like conscience and good faith. Common law interpretation evolved from medieval English royal courts that emphasized precedent and strict application of statutes and legal rules. The historical divergence stems from equity's role as a corrective system to common law's formalism, shaping distinct interpretative approaches within the legal tradition.
Key Principles of Equity Interpretation
Equity interpretation prioritizes fairness and justice by considering the intent and circumstances surrounding a contract, allowing courts to apply flexible remedies when strict legal rules under common law lead to unjust outcomes. Key principles of equity interpretation include the doctrines of unconscionability, estoppel, and good faith, which ensure equitable relief by preventing unfair advantage and enforcing moral obligations beyond rigid legal formalities. Unlike common law interpretation that relies heavily on literal and precedent-based analysis, equity focuses on substance over form to achieve equitable results in contractual disputes.
Fundamental Doctrines of Common Law Interpretation
Fundamental doctrines of common law interpretation emphasize the plain meaning rule, the presumption against absurdity, and the importance of context within the statutory framework to discern legislative intent. Equity interpretation, contrastingly, prioritizes fairness and justice, allowing courts to mitigate harsh outcomes from rigid application of common law principles. The common law's strict adherence to textual analysis often limits judicial discretion, whereas equity ensures flexibility to uphold substantive justice in ambiguous or unforeseen cases.
Distinctive Features: Equity vs. Common Law
Equity Interpretation prioritizes fairness and moral justice, applying flexible principles that adapt to individual circumstances, unlike Common Law Interpretation which relies on strict legal rules and precedent-based reasoning. Equity courts focus on remedies such as injunctions and specific performance, whereas Common Law courts primarily award monetary damages. The core distinction lies in equity's discretionary power to mitigate rigid common law outcomes, ensuring just results when legal rules prove inadequate.
Judicial Discretion in Equity Interpretation
Equity interpretation grants judges broader discretionary powers to achieve fairness and justice beyond the rigid application of common law rules. Judicial discretion in equity allows courts to consider the spirit and intent of agreements, prioritizing equitable principles such as fairness, good faith, and conscience. This flexible approach contrasts with the more literal and precedent-driven nature of common law interpretation, emphasizing strict adherence to statutory language and established case law.
Precedent and Predictability in Common Law Interpretation
Common law interpretation relies heavily on precedent, ensuring consistency and predictability by following prior judicial decisions to resolve similar legal issues. This adherence to stare decisis allows courts to apply established legal principles uniformly, fostering stability and reliable expectations in the law. In contrast, equity interpretation offers flexibility by focusing on fairness and justice, often overriding rigid common law rules when strict application would result in undue hardship.
Remedies Available Under Equity and Common Law
Equity interpretation offers remedies such as injunctions, specific performance, and rescission, which focus on fairness and preventing unjust enrichment when legal remedies are inadequate. Common law interpretation primarily provides remedies like monetary damages and compensatory awards, aiming to restore the injured party financially. Equity remedies are discretionary and tailored to the circumstances, whereas common law remedies are generally awarded as a matter of right based on established legal principles.
Modern Integration and Conflicts Between Equity and Common Law
Modern legal systems often integrate equity and common law to achieve fair and just outcomes, with courts applying equitable principles to supplement rigid common law rules. Conflicts arise when strict common law doctrines produce harsh results, prompting courts to invoke equitable remedies such as injunctions, specific performance, or rescission to balance interests. This integration enhances legal flexibility, ensuring that justice prevails while maintaining the predictability of common law precedents.
Future Trends in Legal Interpretation: Equity vs. Common Law
Future trends in legal interpretation indicate a growing emphasis on equitable principles to address gaps left by rigid common law rules, promoting fairness and flexibility in judicial decisions. The integration of technology and artificial intelligence is expected to enhance the precision and adaptability of equity interpretation, allowing courts to consider broader contextual factors. This evolution suggests a shift toward a more balanced approach that harmonizes common law's predictability with equity's responsiveness to evolving societal values.
Equity Interpretation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com