Rectification involves correcting errors or inaccuracies in data, documents, or processes to ensure accuracy and compliance with regulations. It is crucial for maintaining the integrity of information systems and legal records, reducing risks, and preventing future discrepancies. Explore the rest of the article to understand how rectification can safeguard your operations and improve overall accuracy.
Table of Comparison
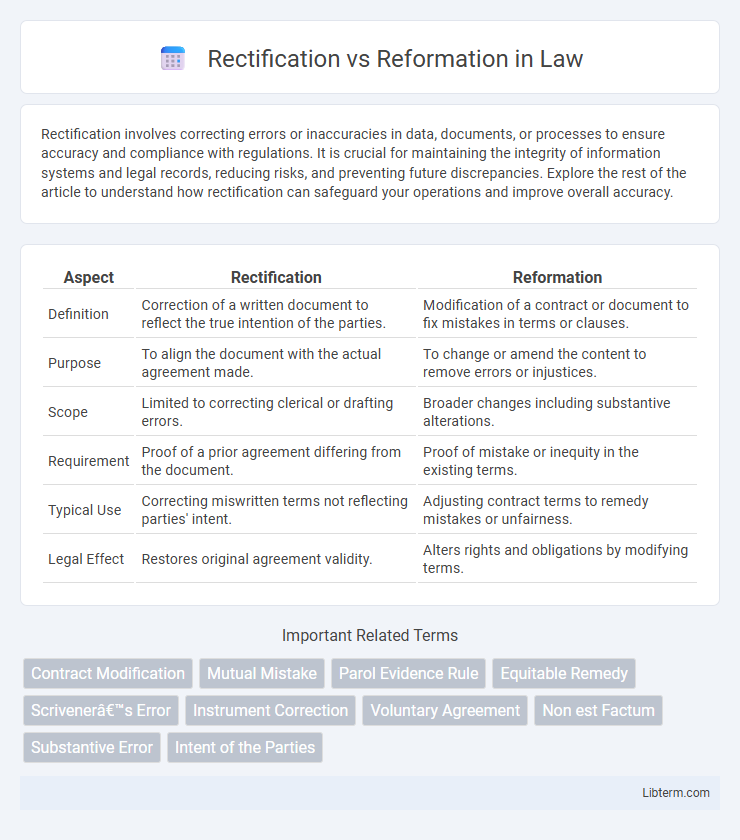
| Aspect | Rectification | Reformation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Correction of a written document to reflect the true intention of the parties. | Modification of a contract or document to fix mistakes in terms or clauses. |
| Purpose | To align the document with the actual agreement made. | To change or amend the content to remove errors or injustices. |
| Scope | Limited to correcting clerical or drafting errors. | Broader changes including substantive alterations. |
| Requirement | Proof of a prior agreement differing from the document. | Proof of mistake or inequity in the existing terms. |
| Typical Use | Correcting miswritten terms not reflecting parties' intent. | Adjusting contract terms to remedy mistakes or unfairness. |
| Legal Effect | Restores original agreement validity. | Alters rights and obligations by modifying terms. |
Understanding Rectification: Definition and Concept
Rectification refers to the legal process of correcting errors or mistakes in a written contract or document to reflect the true intention of the parties involved. It is applied when the written agreement does not accurately capture the agreed terms due to fraud, mistake, or clerical error. Understanding rectification involves recognizing its purpose to align the document with the original agreement, ensuring fairness and preventing unjust enrichment.
What Is Reformation in Legal Contexts?
Reformation in legal contexts refers to the court-ordered modification of a written contract to accurately reflect the true intent of the parties when a mistake, fraud, or misrepresentation has occurred. This equitable remedy corrects errors in the documentation without altering the substance of the agreement, ensuring fairness and preventing unjust enrichment. Reformation differs from rectification by emphasizing the intent and fairness behind contractual terms rather than simply fixing clerical or drafting errors.
Key Differences Between Rectification and Reformation
Rectification involves correcting errors in a written contract to reflect the parties' original intention, typically when the document contains a mutual mistake. Reformation, a broader equitable remedy, modifies or reforms the terms of a contract to address unfairness or misunderstanding, ensuring the agreement aligns with the parties' actual agreement. The key difference lies in rectification correcting a drafting error, whereas reformation adjusts contractual terms to prevent unjust outcomes.
Legal Grounds for Rectification
Rectification is a legal remedy available when a written contract or document fails to reflect the true intention of the parties due to a mutual mistake, fraud, or misrepresentation. The key legal grounds for rectification include proof of a prior agreement that accurately expresses the parties' intentions and evidence that the document does not conform to that agreement. Courts require clear and convincing evidence that the mistake was mutual and that rectification will correct the document to reflect the true contract terms.
Legal Principles Governing Reformation
Reformation is governed by legal principles that focus on correcting errors in written contracts to reflect the true intention of the parties, requiring clear and convincing evidence of mutual mistake or fraud. Unlike rectification, which typically addresses clerical errors or omissions, reformation involves judicial modification of the contract's terms to align with the original agreement. Courts applying reformation principles ensure equitable relief by preventing unjust enrichment and upholding contractual fairness.
Common Scenarios Requiring Rectification
Common scenarios requiring rectification typically involve errors in legal documents such as contracts, deeds, or wills where the written terms do not accurately reflect the parties' original intent. Rectification is often sought when there is a mutual mistake or a clerical error that leads to discrepancies between the agreed terms and the documented agreement. Courts grant rectification to amend the document, ensuring it aligns precisely with the parties' true agreement to avoid unjust outcomes.
Situations Where Reformation Is Applied
Reformation is applied primarily in contractual disputes where the written agreement does not accurately reflect the true intentions of the parties due to mutual mistake, fraud, or misrepresentation. Courts grant reformation to correct the document, ensuring it aligns with the original agreement rather than creating new terms. This remedy is common in real estate transactions, insurance policies, and partnership agreements where precise, intended terms are crucial.
Judicial Approach: Rectification vs. Reformation
Judicial approach to rectification involves correcting errors in written contracts that fail to reflect the true intention of the parties, typically requiring clear proof of the prior agreement. Reformation, on the other hand, allows courts to modify the terms of a contract to align with the parties' original intent when mutual mistake or fraud affects the written document. Courts scrutinize evidence such as parol testimony and prior drafts to distinguish between rectification and reformation, ensuring that contractual obligations correspond to the genuine agreement.
Practical Implications and Outcomes
Rectification corrects clerical or accidental errors in legal documents, ensuring accuracy without altering the original intent, which is crucial for maintaining contractual clarity and enforceability. Reformation modifies the terms of an agreement to reflect the true intent of the parties when a mistake or misrepresentation has led to discrepancies, directly impacting the rights and obligations of the parties involved. Practically, rectification preserves legal certainty by fixing minor mistakes, while reformation addresses substantive errors, often resulting in significant changes to contractual duties and potential remedies.
Choosing the Right Remedy: Rectification or Reformation?
Rectification and reformation are legal remedies used to correct contracts but serve distinct purposes: rectification addresses errors in drafting that misrepresent the parties' true agreement, while reformation modifies terms to reflect the parties' actual intent when the written contract is inaccurate. Choosing the right remedy depends on demonstrating a clear mutual mistake for rectification or a unilateral mistake with inequitable conduct for reformation. Courts require strong evidence of the parties' original intent and the nature of the mistake to grant the appropriate correction, ensuring the contract accurately reflects the agreed terms.
Rectification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com