Estoppel prevents a party from asserting something contrary to what is implied by their previous actions or statements, ensuring fairness and consistency in legal matters. This doctrine plays a critical role in contract law and property disputes by stopping individuals from reneging on promises that others have relied upon. Explore the rest of this article to understand how estoppel can affect your rights and obligations.
Table of Comparison
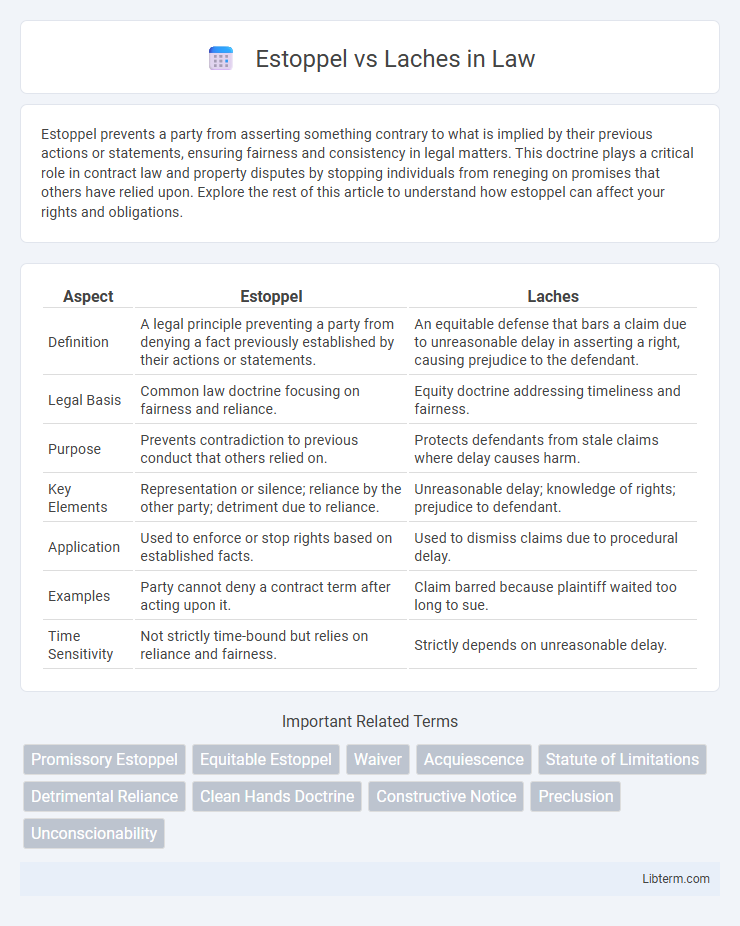
| Aspect | Estoppel | Laches |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A legal principle preventing a party from denying a fact previously established by their actions or statements. | An equitable defense that bars a claim due to unreasonable delay in asserting a right, causing prejudice to the defendant. |
| Legal Basis | Common law doctrine focusing on fairness and reliance. | Equity doctrine addressing timeliness and fairness. |
| Purpose | Prevents contradiction to previous conduct that others relied on. | Protects defendants from stale claims where delay causes harm. |
| Key Elements | Representation or silence; reliance by the other party; detriment due to reliance. | Unreasonable delay; knowledge of rights; prejudice to defendant. |
| Application | Used to enforce or stop rights based on established facts. | Used to dismiss claims due to procedural delay. |
| Examples | Party cannot deny a contract term after acting upon it. | Claim barred because plaintiff waited too long to sue. |
| Time Sensitivity | Not strictly time-bound but relies on reliance and fairness. | Strictly depends on unreasonable delay. |
Understanding Estoppel: A Legal Overview
Estoppel is a legal doctrine preventing a party from asserting a claim or right that contradicts their previous actions or statements when another party has relied on those actions to their detriment. It ensures fairness by holding parties accountable for their representations, promoting consistency in legal dealings. Unlike laches, which is an equitable defense based on unreasonable delay in asserting a right, estoppel focuses on the principle of preventing contradiction and protecting justified reliance.
Laches Explained: The Doctrine of Delay
Laches is a legal doctrine that prevents a party from asserting a claim due to an unreasonable delay in pursuing it, causing prejudice to the opposing party. It is grounded in equity and hinges on the principle that justice requires timely action to protect rights and interests. Courts apply laches by evaluating the length of the delay, the reasons for it, and the resulting harm to ensure fairness in legal proceedings.
Key Differences Between Estoppel and Laches
Estoppel prevents a party from contradicting previous statements or conduct that others have relied on, emphasizing fairness and consistency in legal relationships. Laches addresses unreasonable delay in asserting a right, causing prejudice to the opposing party, and is a defense rooted in equity to bar stale claims. The key difference lies in estoppel focusing on representation and reliance, while laches centers on the timing of the claim and resulting harm.
Historical Origins of Estoppel and Laches
Estoppel originated in English common law during the medieval period as a doctrine preventing a party from contradicting previous statements or behaviors that others relied upon, ensuring fairness and consistency in legal dealings. Laches, derived from the French word "lache," meaning slackness, emerged similarly as an equitable defense designed to prevent claims brought after unreasonable delay that prejudices the opposing party. Both doctrines trace back to equity courts, shaping the balance between legal rights and timely enforcement in Anglo-American jurisprudence.
Essential Elements of Estoppel
Estoppel requires a clear representation or conduct by one party that leads another party to reasonably rely on it to their detriment, establishing a legal obligation to prevent reneging on the initial stance. Essential elements include a definite and unambiguous promise or representation, reliance that is both reasonable and foreseeable, and resulting prejudice or harm to the party relying on that statement. Unlike laches, which focuses on unreasonable delay in asserting a right, estoppel centers on the prevention of injustice by enforcing the original position taken by a party.
Essential Elements of Laches
Laches requires an unreasonable delay in asserting a right or claim combined with prejudice to the opposing party, emphasizing the importance of timely action to prevent injustice. The essential elements include a lack of diligence by the plaintiff in enforcing their rights and resulting harm or disadvantage to the defendant due to the delay. Unlike estoppel, which is based on misleading conduct and reliance, laches centers on equitable principles addressing stale claims.
Practical Applications in Modern Law
Estoppel prevents a party from contradicting previous statements or behaviors that were relied upon by others, ensuring fairness in contractual and property disputes. Laches bars claims where undue delay in asserting a right causes prejudice to the opposing party, commonly applied in equity cases such as intellectual property and real estate. Practical application requires careful assessment of reliance, timing, and prejudice to determine the appropriate defense in modern litigation.
Notable Case Studies: Estoppel vs Laches
In the landmark case *Central London Property Trust Ltd v High Trees House Ltd* (1947), estoppel was firmly established to prevent a party from reneging on a promise, highlighting its role in contract law. Conversely, *Beacon Theatres, Inc. v. Westover* (1959) illustrated laches, where unreasonable delay in asserting a right led to dismissal, emphasizing equitable relief's reliance on timeliness. These cases underscore the critical distinctions: estoppel enforces consistency in representations, while laches bars claims due to prejudicial delay.
Common Misunderstandings and Pitfalls
Estoppel prevents a party from contradicting previous statements or actions that others relied upon, while laches bars claims due to unreasonable delay causing prejudice. A common misunderstanding is treating laches as a strict statute of limitations, although it depends on equity and fairness rather than fixed time. Pitfalls include confusing reliance in estoppel with delay in laches, leading to incorrect defenses or missed deadlines in litigation.
Choosing the Right Doctrine: Legal Strategies
Choosing between estoppel and laches depends on the specific facts and timing of the case, where estoppel prevents a party from contradicting previous statements or actions that the other party relied on, while laches bars claims due to unreasonable delay causing prejudice. Legal strategies favor estoppel when demonstrating clear inducement and reliance, making it crucial to document any promises or conduct influencing the opposing party's decisions. Laches is strategically employed by showing excessive delay in asserting a right or claim, emphasizing the harm or disadvantage caused by such delay to strengthen the defense.
Estoppel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com