A confidentiality agreement legally protects sensitive information shared between parties, ensuring your trade secrets and private data remain secure. Enforcing this agreement helps prevent unauthorized disclosure, maintaining trust and competitive advantage. Explore the full article to understand how confidentiality agreements safeguard your business interests effectively.
Table of Comparison
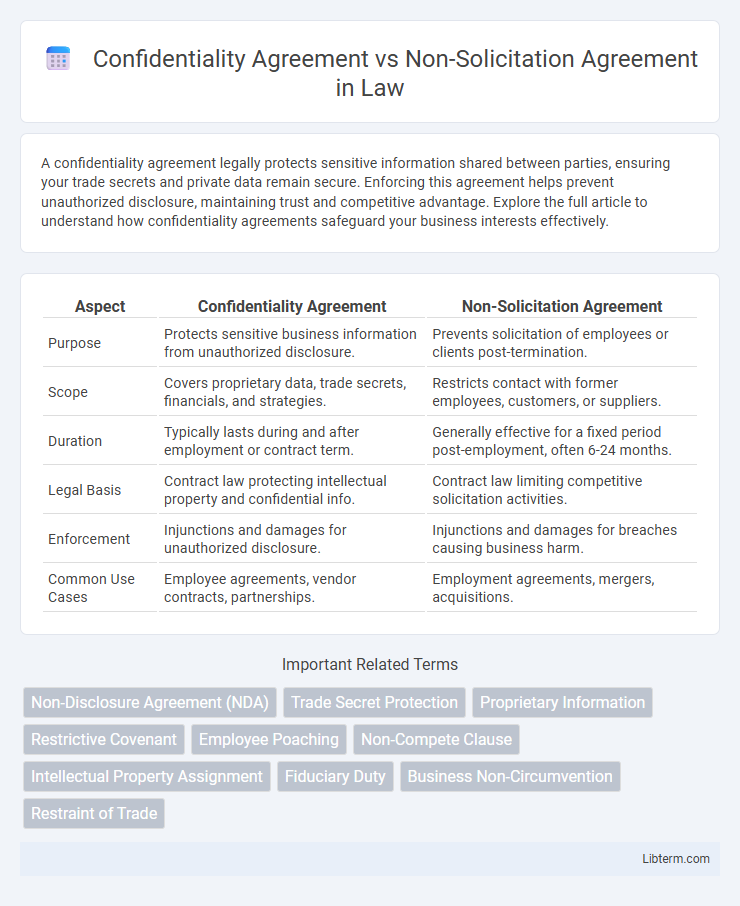
| Aspect | Confidentiality Agreement | Non-Solicitation Agreement |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects sensitive business information from unauthorized disclosure. | Prevents solicitation of employees or clients post-termination. |
| Scope | Covers proprietary data, trade secrets, financials, and strategies. | Restricts contact with former employees, customers, or suppliers. |
| Duration | Typically lasts during and after employment or contract term. | Generally effective for a fixed period post-employment, often 6-24 months. |
| Legal Basis | Contract law protecting intellectual property and confidential info. | Contract law limiting competitive solicitation activities. |
| Enforcement | Injunctions and damages for unauthorized disclosure. | Injunctions and damages for breaches causing business harm. |
| Common Use Cases | Employee agreements, vendor contracts, partnerships. | Employment agreements, mergers, acquisitions. |
Introduction to Confidentiality and Non-Solicitation Agreements
Confidentiality agreements protect sensitive information by legally binding parties to keep proprietary data private, preventing unauthorized disclosure. Non-solicitation agreements restrict parties from directly or indirectly soliciting employees or clients, preserving business relationships and workforce stability. Both agreements serve distinct functions in safeguarding business interests during and after partnerships or employment.
Defining Confidentiality Agreements
Confidentiality Agreements, also known as Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs), are legal contracts that protect sensitive information from being disclosed to unauthorized parties. These agreements define the scope of confidential material, outline the obligations of the parties to maintain secrecy, and specify the duration of confidentiality. Unlike Non-Solicitation Agreements which restrict poaching employees or clients, Confidentiality Agreements primarily focus on safeguarding proprietary information, trade secrets, and business strategies.
Understanding Non-Solicitation Agreements
Non-Solicitation Agreements specifically restrict individuals or entities from directly or indirectly encouraging employees, clients, or customers to leave their current business relationships, safeguarding company interests and workforce stability. These agreements are essential in employment and business contracts to prevent unfair competition and protect proprietary client or employee relationships. Unlike Confidentiality Agreements that focus on protecting sensitive information, Non-Solicitation Agreements emphasize maintaining existing business connections and employee retention.
Key Differences Between Confidentiality and Non-Solicitation Agreements
Confidentiality Agreements primarily protect sensitive information from being disclosed to unauthorized parties, ensuring trade secrets and proprietary data remain secure. Non-Solicitation Agreements restrict former employees or partners from soliciting clients, customers, or employees, preventing competitive poaching and business disruption. The key difference lies in confidentiality focusing on information protection, whereas non-solicitation targets relationship and business interference.
Common Clauses in Confidentiality Agreements
Confidentiality agreements commonly include clauses such as definition of confidential information, obligations of the receiving party to protect the information, and limitations on use and disclosure. These agreements also specify the duration of confidentiality, exclusions from confidentiality obligations, and remedies for breach. Non-solicitation agreements, by contrast, primarily focus on restricting solicitation of clients or employees, but do not typically address the protection of sensitive information in the same detail as confidentiality agreements.
Critical Provisions in Non-Solicitation Agreements
Non-solicitation agreements focus on critical provisions such as defining the scope of restricted activities, including solicitation of clients, employees, and contractors, and specifying the duration and geographic limitations of the restrictions. Key clauses include the identification of protected parties, explicit prohibitions against direct or indirect solicitation, and remedies for breaches such as injunctive relief or monetary damages. These provisions ensure protection of business relationships and workforce stability following termination or partnership changes.
Legal Enforceability: Confidentiality vs Non-Solicitation
Confidentiality agreements protect sensitive information by legally prohibiting parties from disclosing proprietary data, typically enjoying broad enforceability when clearly defined and reasonable in scope. Non-solicitation agreements restrict parties from poaching employees or clients, but their enforceability can vary significantly depending on jurisdiction, often requiring reasonable time limits and geographic scope. Courts generally scrutinize non-solicitation clauses more strictly to ensure they do not unduly restrict trade or employment opportunities.
When to Use a Confidentiality Agreement
A Confidentiality Agreement is essential when sensitive information such as trade secrets, business strategies, or intellectual property needs protection during business negotiations or partnerships. This agreement ensures that parties involved cannot disclose or misuse proprietary information, safeguarding competitive advantage. Use a Confidentiality Agreement anytime proprietary data, client lists, or financial details are shared outside your organization to maintain privacy and prevent unauthorized access.
When to Use a Non-Solicitation Agreement
A Non-Solicitation Agreement is used when a company wants to protect its relationships with clients, employees, or contractors by preventing former employees or business partners from soliciting or recruiting these individuals after separation. It is particularly useful during mergers, acquisitions, or when sensitive client information is at risk of being exploited for competitive advantage. Unlike a Confidentiality Agreement, which safeguards proprietary information, a Non-Solicitation Agreement specifically restricts targeted poaching or solicitation activities to maintain business stability.
Choosing the Right Agreement for Your Business Needs
Choosing the right agreement for your business needs depends on the specific protection required: a Confidentiality Agreement safeguards sensitive information like trade secrets and proprietary data from unauthorized disclosure, while a Non-Solicitation Agreement prevents former employees or partners from poaching clients or staff. Businesses prioritizing intellectual property protection should opt for a robust Confidentiality Agreement, whereas those concerned with retaining client relationships and workforce stability benefit more from a Non-Solicitation Agreement. Evaluating the nature of your business risks and desired protections is essential for selecting the most effective legal instrument.
Confidentiality Agreement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com