Fee Simple Absolute represents the most complete ownership interest one can have in real property, granting unlimited rights to use, sell, or transfer the land indefinitely. This estate is not subject to any conditions or limitations, providing maximum control and security to the owner. Discover how understanding Fee Simple Absolute can protect Your property rights by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
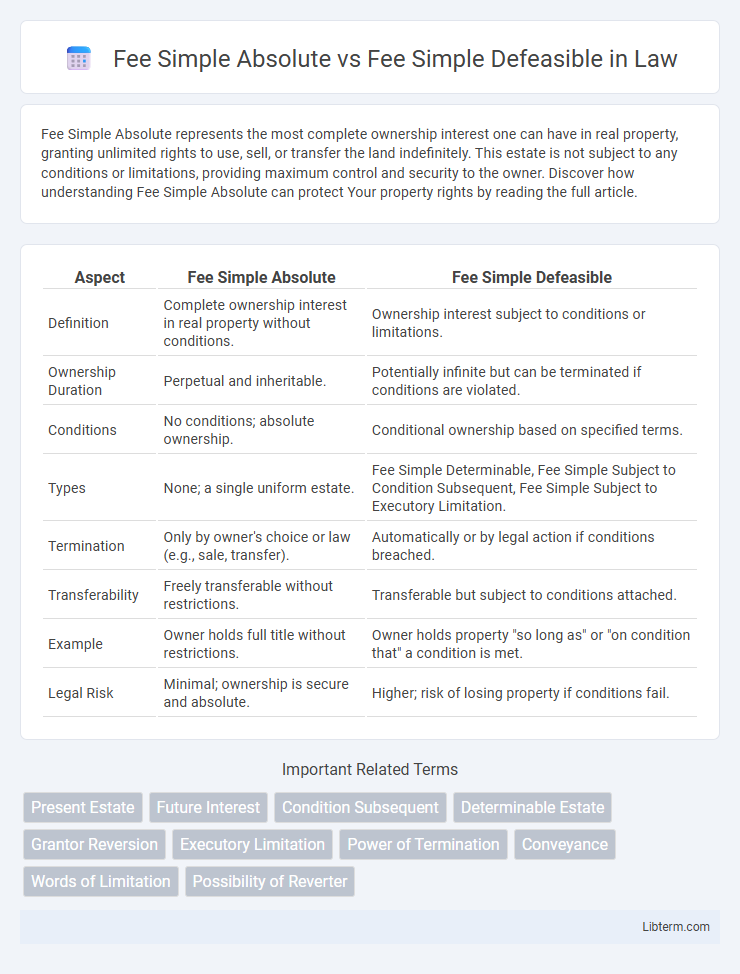
| Aspect | Fee Simple Absolute | Fee Simple Defeasible |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Complete ownership interest in real property without conditions. | Ownership interest subject to conditions or limitations. |
| Ownership Duration | Perpetual and inheritable. | Potentially infinite but can be terminated if conditions are violated. |
| Conditions | No conditions; absolute ownership. | Conditional ownership based on specified terms. |
| Types | None; a single uniform estate. | Fee Simple Determinable, Fee Simple Subject to Condition Subsequent, Fee Simple Subject to Executory Limitation. |
| Termination | Only by owner's choice or law (e.g., sale, transfer). | Automatically or by legal action if conditions breached. |
| Transferability | Freely transferable without restrictions. | Transferable but subject to conditions attached. |
| Example | Owner holds full title without restrictions. | Owner holds property "so long as" or "on condition that" a condition is met. |
| Legal Risk | Minimal; ownership is secure and absolute. | Higher; risk of losing property if conditions fail. |
Introduction to Fee Simple Estates
Fee simple absolute represents the most complete ownership interest in real property, granting the holder unlimited rights to possess, use, and transfer the land without conditions or limitations. In contrast, fee simple defeasible includes conditions or restrictions that may cause the estate to revert to the grantor if violated. Understanding these distinctions is essential in real estate law, as fee simple estates form the foundation of property ownership and affect rights, duration, and potential forfeiture.
Defining Fee Simple Absolute
Fee Simple Absolute is the most complete form of property ownership, granting the owner unlimited rights to use, sell, or transfer the property without restrictions or conditions. This estate is perpetual and cannot be voided by any event, providing absolute control over the property. In contrast, Fee Simple Defeasible includes conditions that, if violated, may cause the property to revert to the original owner or a designated party.
Key Characteristics of Fee Simple Absolute
Fee Simple Absolute is the most complete ownership interest in real estate, granting the owner unlimited duration, unconditional rights, and the ability to freely transfer or bequeath the property. Unlike Fee Simple Defeasible, Fee Simple Absolute does not contain any conditions or restrictions that could result in forfeiture of the estate. This ownership type provides the highest level of security and control, ensuring the owner's property rights are perpetual and unencumbered.
Defining Fee Simple Defeasible
Fee Simple Defeasible is a type of freehold estate in real property that can be terminated upon the occurrence or non-occurrence of a specified event, distinguishing it from Fee Simple Absolute which is unconditional and perpetual. It includes subclasses such as Fee Simple Determinable, which automatically ends when a condition is violated, and Fee Simple Subject to Condition Subsequent, which requires action to reclaim ownership. Property owners with Fee Simple Defeasible hold title with qualifications that embed potential future interests, creating legal contingencies tied to property use or ownership criteria.
Types of Fee Simple Defeasible Estates
Fee Simple Defeasible estates include Fee Simple Determinable, Fee Simple Subject to Condition Subsequent, and Fee Simple Subject to Executory Limitation, each imposing specific conditions or limitations on ownership. Fee Simple Determinable automatically terminates upon the occurrence of a stated event, reverting ownership to the grantor, while Fee Simple Subject to Condition Subsequent requires the grantor to take action to reclaim the estate after a condition is breached. Fee Simple Subject to Executory Limitation transfers ownership to a third party if the condition is violated, distinguishing it from other defeasible estates by the automatic shift of property rights.
Key Differences Between Fee Simple Absolute and Fee Simple Defeasible
Fee Simple Absolute grants the owner complete ownership without conditions, allowing unrestricted transfer, sale, or inheritance of the property. Fee Simple Defeasible includes specific conditions or limitations that, if violated, can result in the loss of the estate and reversion to the original owner or their heirs. The primary difference lies in the unconditional ownership of Fee Simple Absolute versus the conditional ownership subject to termination in Fee Simple Defeasible.
Legal Implications of Ownership
Fee Simple Absolute grants the owner unlimited, perpetual ownership with complete control and no conditions, allowing unrestricted transfer, sale, or inheritance. Fee Simple Defeasible includes conditions or limitations that, if violated, can result in automatic reversion or forfeiture of the property to the original grantor or their heirs. Legal implications of Fee Simple Defeasible require owners to maintain specific conditions, creating potential risks of losing ownership rights, while Fee Simple Absolute ensures stability and clear title without risk of termination.
Common Examples in Real Estate Transactions
Fee Simple Absolute grants complete ownership of property with unlimited rights to use, sell, or transfer, commonly seen in residential home purchases. Fee Simple Defeasible includes conditions that may cause ownership to revert to the original grantor, often used in land gifts to nonprofits or properties with specific use restrictions. Common examples include a family estate transferred with the stipulation it remains a private residence (Fee Simple Determinable) or a property deeded for educational purposes only (Fee Simple Subject to Condition Subsequent).
Pros and Cons of Each Estate Type
Fee Simple Absolute provides the greatest ownership rights with no conditions, allowing owners to freely sell, lease, or bequeath the property, making it the most secure estate type; however, it offers no protection against undesirable uses by future owners. Fee Simple Defeasible grants ownership subject to specific conditions or limitations, allowing reversion to the grantor if conditions are violated, which can enforce intended land use but introduces uncertainty and potential legal disputes. Choosing between these estate types depends on balancing absolute control and marketability with conditional restrictions that safeguard property use.
Choosing the Right Estate: What to Consider
Choosing the right estate between Fee Simple Absolute and Fee Simple Defeasible hinges on the degree of ownership control and risk tolerance. Fee Simple Absolute offers the highest level of ownership with unlimited duration and no conditions, ideal for owners seeking permanent, unrestricted property rights. Fee Simple Defeasible imposes conditions that could terminate ownership if violated, making it suitable for those willing to accept potential forfeiture to maintain specific property use restrictions.
Fee Simple Absolute Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com