A writ of quo warranto challenges an individual's right to hold a public office or exercise authority. It serves as a legal tool to question the legitimacy of someone's claim to power. Explore the rest of the article to understand how this writ protects your rights and upholds lawful governance.
Table of Comparison
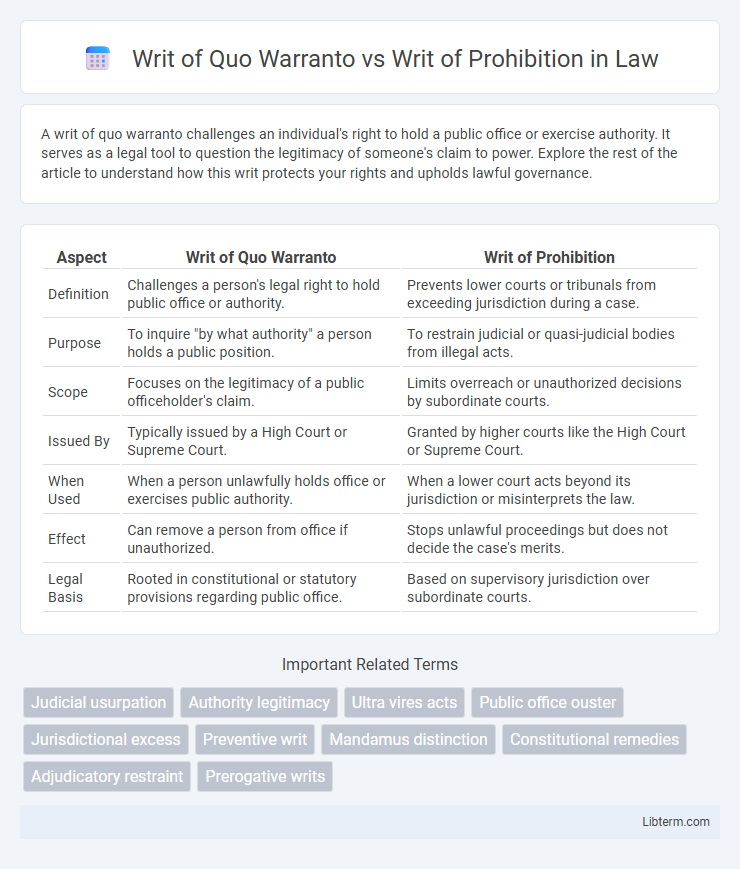
| Aspect | Writ of Quo Warranto | Writ of Prohibition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Challenges a person's legal right to hold public office or authority. | Prevents lower courts or tribunals from exceeding jurisdiction during a case. |
| Purpose | To inquire "by what authority" a person holds a public position. | To restrain judicial or quasi-judicial bodies from illegal acts. |
| Scope | Focuses on the legitimacy of a public officeholder's claim. | Limits overreach or unauthorized decisions by subordinate courts. |
| Issued By | Typically issued by a High Court or Supreme Court. | Granted by higher courts like the High Court or Supreme Court. |
| When Used | When a person unlawfully holds office or exercises public authority. | When a lower court acts beyond its jurisdiction or misinterprets the law. |
| Effect | Can remove a person from office if unauthorized. | Stops unlawful proceedings but does not decide the case's merits. |
| Legal Basis | Rooted in constitutional or statutory provisions regarding public office. | Based on supervisory jurisdiction over subordinate courts. |
Introduction to Extraordinary Writs
Extraordinary writs are judicial orders issued by superior courts to enforce rights or prevent abuses of power. The Writ of Quo Warranto challenges a person's legal right to hold a public office, questioning the authority under which they act. The Writ of Prohibition, on the other hand, directs a lower court or tribunal to stop proceedings that exceed their jurisdiction or violate legal standards.
Defining Writ of Quo Warranto
The Writ of Quo Warranto challenges an individual's legal authority to hold a public office or exercise certain powers, requiring proof of their rightful claim. It serves to prevent unauthorized or illegal claims to public positions and ensures adherence to legal eligibility criteria. This writ differs from the Writ of Prohibition, which stops lower courts or authorities from acting beyond their jurisdiction.
Defining Writ of Prohibition
The Writ of Prohibition is a judicial order directing a lower court or tribunal to stop proceedings in a case where it lacks jurisdiction or is exceeding its authority. It serves to prevent future illegal acts by restraining courts from acting beyond their legal bounds. Unlike the Writ of Quo Warranto, which challenges a person's right to hold public office, the Writ of Prohibition addresses the actions of judicial or quasi-judicial bodies.
Legal Basis and Historical Background
The writ of Quo Warranto originates from English common law, serving as a legal instrument to challenge a person's authority to hold a public office or corporate franchise, based on the principle of lawful entitlement under statutes such as the English Magna Carta of 1215. The writ of Prohibition also stems from common law, designed to prevent inferior courts or tribunals from exceeding their jurisdiction, ensuring compliance with legal boundaries established by English judicial precedents. Both writs reflect a centuries-old framework to uphold lawful governance and jurisdictional limits, solidified through legislative enactments and judicial interpretations.
Purpose and Scope of Quo Warranto
The Writ of Quo Warranto challenges a person's legal right to hold a public office or exercise a franchise, serving to prevent unauthorized usurpation of authority. Its scope focuses on the legitimacy of the individual's claim or right, ensuring conformity with law and preventing illegal occupation of public positions. In contrast, the Writ of Prohibition limits lower courts or tribunals from exceeding their jurisdiction, acting as a preventive mechanism to restrain judicial or quasi-judicial overreach.
Purpose and Scope of Prohibition
The Writ of Quo Warranto challenges a person's right to hold a public office or exercise a franchise, questioning the legality of their authority. The Writ of Prohibition serves to restrain a lower court or tribunal from acting beyond its jurisdiction, preventing unauthorized or unlawful proceedings. Its scope is limited to preventing excesses of jurisdiction without deciding the ultimate rights of the parties involved.
Grounds for Issuance
The writ of Quo Warranto is issued to question the authority of a person holding a public office or position, typically when there is a claim that the individual lacks legal right or certification to occupy that role. The writ of Prohibition is aimed at preventing a lower court, tribunal, or public authority from acting outside its jurisdiction or exceeding its lawful power to avoid miscarriage of justice. Both writs serve as safeguards in administrative and judicial oversight, with Quo Warranto focusing on legitimacy of office and Prohibition on jurisdictional boundaries.
Procedure and Jurisdiction
The Writ of Quo Warranto challenges a person's legal right to hold a public office, typically initiated by a petition filed before a competent court or tribunal with jurisdiction over the specific office in question. The procedure involves the court inquiring into the authority under which the individual claims office and requires proof of lawful entitlement. In contrast, the Writ of Prohibition is issued by a higher court to a lower court or tribunal, directing it to cease proceedings when there is a lack of jurisdiction or an excess of jurisdiction, effectively preventing unauthorized judicial action before it occurs.
Key Differences Between Quo Warranto and Prohibition
The key difference between a Writ of Quo Warranto and a Writ of Prohibition lies in their purposes and targets; Quo Warranto challenges a person's right to hold a public office or exercise a franchise, questioning the legality of their authority, whereas Prohibition restrains lower courts or tribunals from exceeding their jurisdiction or acting contrary to rules of natural justice. Quo Warranto focuses on the legality of authority already assumed, while Prohibition prevents unauthorized judicial or quasi-judicial action before it occurs. Both writs serve as essential remedies under constitutional law to maintain legal boundaries and uphold the rule of law.
Notable Cases and Judicial Interpretations
The writ of Quo Warranto has been pivotal in cases like *Bhagwati Prasad vs. Election Commission of India*, where courts examined the legality of a public officer's claim to office, emphasizing authority verification. In contrast, the writ of Prohibition played a critical role in *State of Maharashtra vs. Hindustan Petroleum*, where the judiciary restrained lower courts from exceeding jurisdiction, reinforcing limits on judicial overreach. Judicial interpretations distinguish Quo Warranto as a tool to challenge authority legitimacy, while Prohibition primarily serves to prevent lower courts or tribunals from acting beyond their prescribed powers.
Writ of Quo Warranto Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com