Integrate seamless solutions to enhance your business workflows and improve overall efficiency. By combining advanced technologies and tailored strategies, organizations can achieve smoother operations and stronger collaboration. Explore the full article to discover practical ways to integrate and elevate your processes.
Table of Comparison
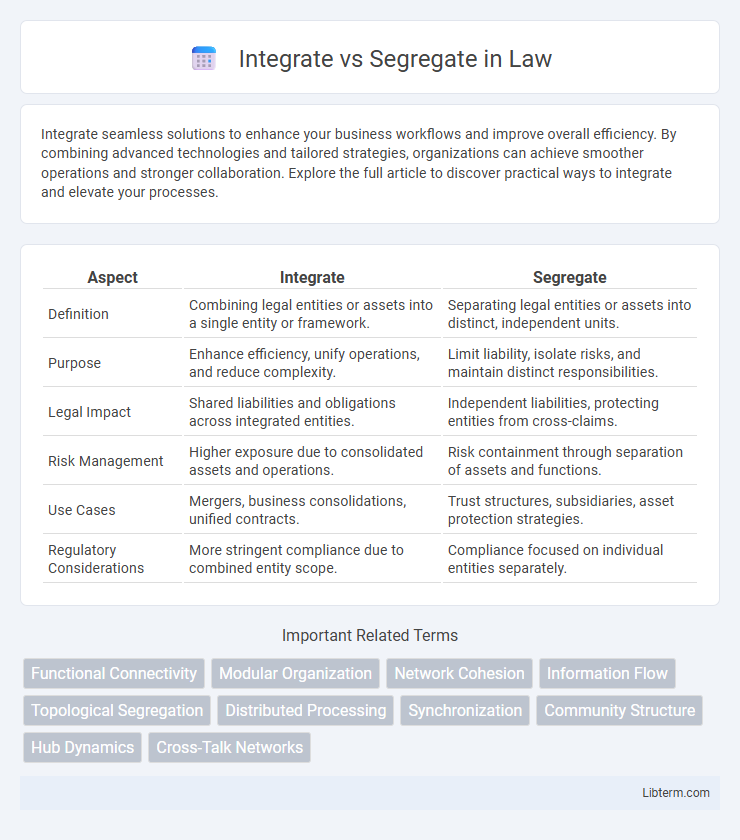
| Aspect | Integrate | Segregate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining legal entities or assets into a single entity or framework. | Separating legal entities or assets into distinct, independent units. |
| Purpose | Enhance efficiency, unify operations, and reduce complexity. | Limit liability, isolate risks, and maintain distinct responsibilities. |
| Legal Impact | Shared liabilities and obligations across integrated entities. | Independent liabilities, protecting entities from cross-claims. |
| Risk Management | Higher exposure due to consolidated assets and operations. | Risk containment through separation of assets and functions. |
| Use Cases | Mergers, business consolidations, unified contracts. | Trust structures, subsidiaries, asset protection strategies. |
| Regulatory Considerations | More stringent compliance due to combined entity scope. | Compliance focused on individual entities separately. |
Introduction to Integration vs Segregation
Integration involves combining diverse elements or groups into a unified whole, promoting collaboration, inclusion, and equal access to resources or opportunities. Segregation refers to the systematic separation of groups based on characteristics such as race, ethnicity, or socioeconomic status, leading to unequal access and social division. Understanding the dynamics of integration versus segregation is crucial for addressing social inequalities and fostering cohesive communities.
Historical Perspectives on Integration and Segregation
Historical perspectives on integration and segregation reveal deeply rooted social and political dynamics shaping racial and ethnic relations in societies worldwide. Integration efforts often emerged from civil rights movements advocating for equal access to education, housing, and employment, while segregation imposed systemic barriers maintaining racial hierarchies, exemplified by Jim Crow laws in the United States and apartheid in South Africa. These contrasting approaches highlight shifting power structures and ongoing struggles for social justice and equity.
Key Definitions: What Do Integrate and Segregate Mean?
Integrate refers to combining distinct elements or groups into a unified whole, promoting inclusion and cooperation within a system. Segregate means to separate or isolate components or groups based on specific criteria, often leading to division or exclusion. Understanding these key definitions is essential for analyzing social structures, organizational dynamics, and data systems.
Advantages of Integration
Integration enhances operational efficiency by enabling seamless communication and collaboration across departments, reducing redundancies and streamlining workflows. It fosters innovation through diverse perspectives and shared resources, facilitating faster problem-solving and adaptive strategies. Integrated systems improve data consistency and decision-making accuracy by consolidating information into a unified platform.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Segregation
Segregation fosters specialized environments that can enhance focus and reduce distractions, particularly in educational or workplace settings requiring distinct skill sets or roles. However, segregation often limits diversity, stifling creativity and innovation by restricting exposure to varied perspectives and experiences. This isolation can also entrench inequality and social divides, making collaboration across groups more challenging and reducing overall societal cohesion.
Real-World Examples of Integration
Real-world examples of integration include multicultural cities like New York, where diverse ethnic groups coexist, sharing cultural, economic, and social spaces to create inclusive communities. In business, companies like Amazon integrate various functions such as logistics, marketing, and customer service, streamlining operations and enhancing efficiency. Education systems embracing integrated classrooms promote social cohesion by mixing students of different backgrounds, improving mutual understanding and reducing segregation.
Case Studies: When Segregation Works
Segregation proves effective in case studies involving specialized education programs for students with specific learning disabilities, where tailored environments enhance academic outcomes. Industrial sectors utilizing segregated workflows, such as pharmaceutical manufacturing, benefit from increased safety and efficiency by isolating hazardous processes. Urban planning examples reveal that segregating residential areas from heavy industrial zones reduces pollution exposure and improves residents' quality of life.
Challenges in Balancing Integration and Segregation
Balancing integration and segregation presents challenges related to maintaining cultural identity while promoting social cohesion in diverse societies. Organizations face difficulties in merging distinct systems or teams without losing specialized expertise or creating inefficiencies. Effective strategies require nuanced understanding of context-specific needs to optimize collaboration without compromising autonomy or inclusiveness.
Integration vs Segregation in Modern Society
Integration in modern society promotes social cohesion by fostering diversity and equal opportunities in education, employment, and public spaces, enhancing cultural exchange and reducing systemic inequalities. Segregation, whether racial, economic, or social, perpetuates disparities by isolating groups, limiting access to resources, and reinforcing discrimination and social stratification. Policies that support integration contribute to inclusive communities, stronger democratic participation, and improved socioeconomic outcomes across diverse populations.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Choosing between integration and segregation depends on organizational goals, resource allocation, and desired outcomes. Integration fosters collaboration and unified systems, enhancing efficiency and innovation, while segregation allows for specialized focus and risk management in distinct areas. Evaluating specific business needs and operational contexts ensures the selection of the approach that maximizes productivity and aligns with strategic objectives.
Integrate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com