Ejectment is a legal action used to recover possession of real property wrongfully occupied by another party. It focuses on establishing your right to possession and removing unauthorized occupants through court proceedings. Discover how ejectment suits protect your property rights and the steps involved in this process by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
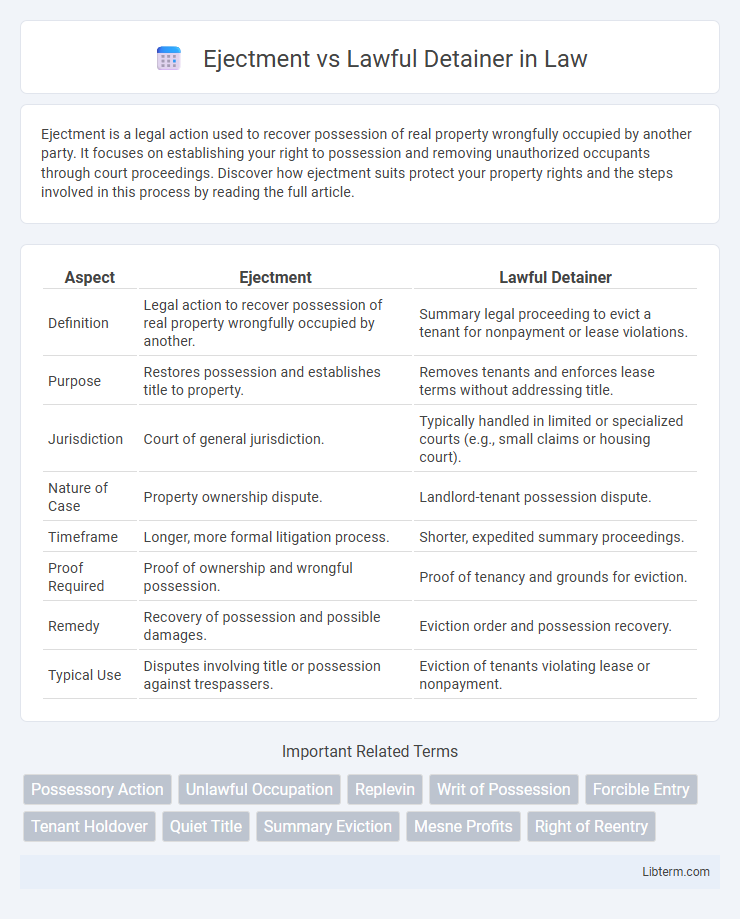
| Aspect | Ejectment | Lawful Detainer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal action to recover possession of real property wrongfully occupied by another. | Summary legal proceeding to evict a tenant for nonpayment or lease violations. |
| Purpose | Restores possession and establishes title to property. | Removes tenants and enforces lease terms without addressing title. |
| Jurisdiction | Court of general jurisdiction. | Typically handled in limited or specialized courts (e.g., small claims or housing court). |
| Nature of Case | Property ownership dispute. | Landlord-tenant possession dispute. |
| Timeframe | Longer, more formal litigation process. | Shorter, expedited summary proceedings. |
| Proof Required | Proof of ownership and wrongful possession. | Proof of tenancy and grounds for eviction. |
| Remedy | Recovery of possession and possible damages. | Eviction order and possession recovery. |
| Typical Use | Disputes involving title or possession against trespassers. | Eviction of tenants violating lease or nonpayment. |
Introduction to Ejectment and Lawful Detainer
Ejectment and lawful detainer are legal actions used to resolve disputes over property possession, with ejectment typically addressing the recovery of title and possession against wrongful claimants. Lawful detainer is a streamlined eviction process designed primarily for landlords to regain possession from tenants who violate lease terms or fail to pay rent. Understanding the distinct procedural requirements and remedies of ejectment and lawful detainer is crucial for effectively navigating property law disputes.
Legal Definitions and Distinctions
Ejectment is a legal action used to recover possession of real property when a person wrongfully occupies it without any legal right, focusing on the actual recovery of possession and any damages caused by the wrongful occupancy. Lawful detainer, also known as unlawful detainer, specifically addresses disputes where a tenant remains in possession of property after the expiration or termination of a lease, emphasizing eviction procedures based on lease violations or expiration. The key distinction lies in ejectment addressing ownership and wrongful possession while lawful detainer deals with tenant eviction and possession rights under lease agreements.
Grounds for Ejectment vs Lawful Detainer
Ejectment is grounded in the recovery of possession due to wrongful occupying or unlawful entry, often involving disputes over title or ownership rights to real property. Lawful detainer actions arise when a tenant remains on the property after a lease has expired or after violating lease terms, primarily focused on possession rather than title. Ejectment claims require proof of ownership or a superior title, while lawful detainer cases emphasize the tenant's failure to comply with rental agreements or timely vacate.
Parties Involved in Each Action
Ejectment involves a property owner suing a trespasser or unlawful possessor to regain possession of real estate, primarily between private parties contesting ownership rights. Lawful detainer actions are initiated by landlords against tenants who fail to comply with lease terms or refuse to vacate after lease expiration, focusing on landlord-tenant relationships. The key distinction lies in ejectment addressing ownership disputes, while lawful detainer resolves possession issues under a lease agreement.
Procedural Requirements and Timelines
Ejectment requires the plaintiff to prove rightful possession and typically involves filing a formal complaint, serving the defendant, and obtaining a court judgment to remove an unlawful occupant, with timelines varying by jurisdiction but often extending several months due to trial scheduling. Lawful detainer actions, focused on recovering possession following a tenant's breach or lease expiration, mandate expedited procedures including a shorter notice period (usually 3 to 30 days), swift court hearing dates, and rapid enforcement of eviction orders, often resolving within weeks. Procedural requirements for lawful detainer emphasize strict compliance with notice terms and prompt filing to avoid delays, whereas ejectment cases involve more complex property right disputes and lengthier judicial processes.
Burden of Proof in Ejectment and Lawful Detainer
The burden of proof in ejectment cases requires the plaintiff to demonstrate legal ownership or title to the property, establishing rightful possession against the defendant. In lawful detainer actions, the plaintiff must prove the tenant's unlawful possession, typically by showing the expiration or violation of the lease agreement. Courts generally hold ejectment plaintiffs to a higher evidentiary standard, as these cases resolve disputes over property titles, while lawful detainer focuses on possession and tenancy rights.
Remedies Available to Plaintiffs
Plaintiffs in ejectment actions seek possession and title to real property, often aiming for a court order to remove unlawful occupants and recover damages for trespass. Lawful detainer actions, primarily used for landlord-tenant disputes, provide plaintiffs remedies such as eviction and recovery of rent arrears without addressing ownership rights. Both remedies allow plaintiffs to regain property possession, but ejectment focuses on ownership claims, while lawful detainer prioritizes lease enforcement.
Defenses Against Ejectment and Lawful Detainer
Defenses against ejectment include proof of lawful ownership or tenancy, payment of rent, and challenging the validity of the landlord's title or lease termination. In lawful detainer actions, defenses often involve demonstrating proper notice was not given, unlawful eviction procedures, or the existence of a valid lease agreement that prevents eviction. Both actions require defendants to provide evidence negating the landlord's claims or procedural compliance to avoid losing possession of the property.
Effects and Consequences of Judgment
Judgment in ejectment actions typically results in the restoration of possession of real property to the rightful owner, emphasizing title disputes and clear ownership rights. Conversely, lawful detainer judgments primarily address possession issues, often leading to eviction without settling ownership claims, expediting recovery for landlords. Both judgments may result in eviction, but ejectment creates a definitive title outcome while lawful detainer enforces tenancy terms, impacting future property use and legal rights.
Choosing the Appropriate Legal Remedy
Choosing between ejectment and lawful detainer hinges on the nature of property possession disputes; ejectment suits address title and ownership rights, whereas lawful detainer focuses strictly on possession and eviction. Legal practitioners must evaluate if the issue involves recovery of possession without disputing ownership, which favors lawful detainer, or if there is a need to establish property title, warranting an ejectment action. Understanding jurisdictional nuances and procedural requirements ensures selecting the correct remedy expedites resolution and enforces landlord or owner rights effectively.
Ejectment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com