Judicial recusal ensures impartiality by requiring judges to abstain from cases where personal interests or biases might affect their decisions. This process protects the fairness and integrity of the judicial system by maintaining public trust. Explore this article to understand how judicial recusal safeguards your right to a fair trial.
Table of Comparison
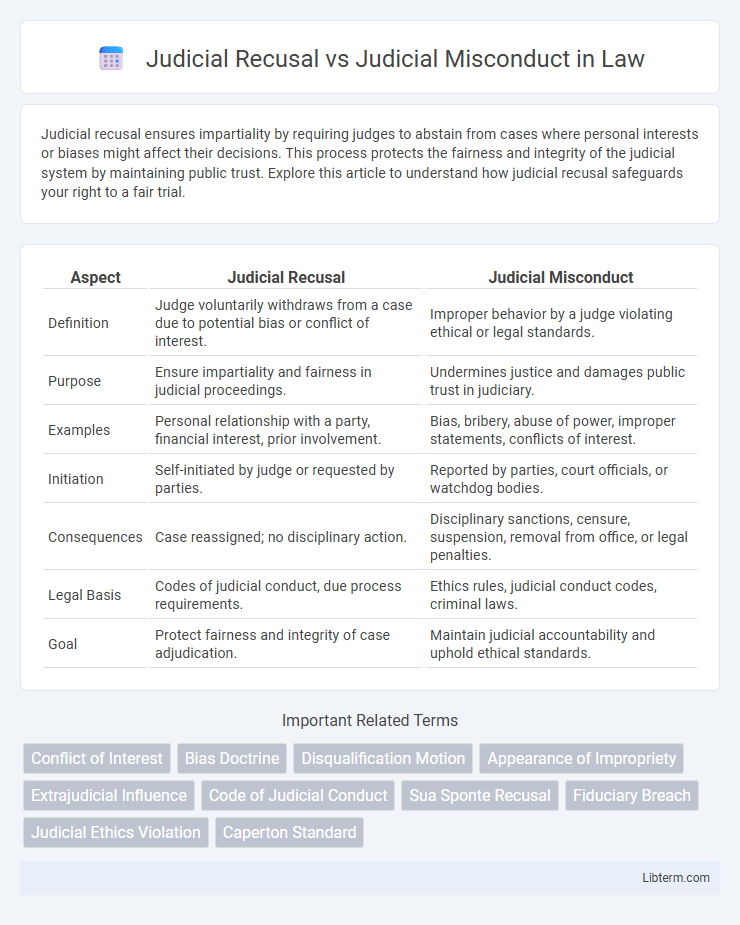
| Aspect | Judicial Recusal | Judicial Misconduct |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Judge voluntarily withdraws from a case due to potential bias or conflict of interest. | Improper behavior by a judge violating ethical or legal standards. |
| Purpose | Ensure impartiality and fairness in judicial proceedings. | Undermines justice and damages public trust in judiciary. |
| Examples | Personal relationship with a party, financial interest, prior involvement. | Bias, bribery, abuse of power, improper statements, conflicts of interest. |
| Initiation | Self-initiated by judge or requested by parties. | Reported by parties, court officials, or watchdog bodies. |
| Consequences | Case reassigned; no disciplinary action. | Disciplinary sanctions, censure, suspension, removal from office, or legal penalties. |
| Legal Basis | Codes of judicial conduct, due process requirements. | Ethics rules, judicial conduct codes, criminal laws. |
| Goal | Protect fairness and integrity of case adjudication. | Maintain judicial accountability and uphold ethical standards. |
Introduction to Judicial Recusal and Judicial Misconduct
Judicial recusal refers to a judge's voluntary withdrawal from a case due to potential conflicts of interest or bias that could affect impartiality, ensuring fair legal proceedings. Judicial misconduct involves actions by a judge that violate ethical standards or legal duties, such as corruption, bias, or abuse of authority, undermining public trust in the judiciary. Understanding the distinction is critical for maintaining judicial integrity and upholding the rule of law.
Defining Judicial Recusal
Judicial recusal refers to a judge's voluntary decision to withdraw from a case to avoid potential bias or conflict of interest, ensuring impartiality in legal proceedings. It is a procedural step designed to uphold judicial integrity and fairness, typically triggered by personal, financial, or relational connections to the case or parties involved. Clear standards for judicial recusal are outlined in codes of conduct and legal statutes to prevent questions of partiality or prejudice.
Understanding Judicial Misconduct
Judicial misconduct occurs when a judge violates ethical standards or engages in behavior that compromises impartiality, integrity, or independence. Examples include bias, conflicts of interest, or improper communication with parties involved in a case. Understanding judicial misconduct is crucial for maintaining public trust in the legal system and ensuring fair judicial proceedings.
Key Differences Between Recusal and Misconduct
Judicial recusal refers to a judge's voluntary withdrawal from a case due to potential conflicts of interest or bias, ensuring impartiality in legal proceedings. Judicial misconduct involves unethical or illegal behavior by a judge, such as corruption, bias, or abuse of authority, which undermines judicial integrity. The key difference lies in recusal being a preventive measure to maintain fairness, whereas misconduct constitutes a violation of ethical or legal standards requiring disciplinary action.
Legal Standards for Judicial Recusal
Legal standards for judicial recusal are grounded in ensuring impartiality and can be triggered by factors such as personal bias, financial interests, or prior involvement in a case. Courts often apply the "reasonable person" test to determine whether a judge's impartiality might reasonably be questioned under 28 U.S.C. SS 455 or similar state statutes. Judicial misconduct, by contrast, involves violations of ethical codes or improper behavior but does not automatically necessitate recusal unless it affects the judge's ability to remain impartial.
Common Examples of Judicial Misconduct
Common examples of judicial misconduct include bias or prejudice demonstrated by a judge, improper communication with one party without the other present, and financial conflicts of interest that may compromise impartiality. Judges may also engage in misconduct by exhibiting rude or abusive behavior toward attorneys or litigants, failing to disclose relationships that could affect their decisions, or manipulating court procedures to influence outcomes. Such actions undermine the integrity of the judicial system and differ significantly from judicial recusal, which is a formal process where a judge voluntarily withdraws from a case due to potential conflict of interest.
Procedures for Addressing Judicial Recusal
Procedures for addressing judicial recusal involve formal motions filed by parties requesting judges to withdraw from cases due to potential conflicts of interest, bias, or lack of impartiality. These motions are reviewed according to established court rules and ethical standards, often requiring judges to disclose any relevant information before deciding on recusal. Failure to comply with recusal procedures can lead to appeals or complaints for judicial misconduct, which are handled separately by judicial conduct commissions or disciplinary bodies.
Consequences of Judicial Misconduct
Judicial misconduct involves unethical or illegal actions by a judge, leading to severe consequences such as removal from office, suspension, or formal censure by judicial oversight bodies. Unlike judicial recusal, which is a voluntary withdrawal to avoid conflicts of interest and maintain impartiality, judicial misconduct undermines the integrity of the legal system and can result in criminal charges or disbarment. Consequences of judicial misconduct also include damage to public trust, potential civil liability, and impairments to a judge's professional reputation.
Safeguarding Judicial Impartiality
Judicial recusal is a critical mechanism for safeguarding judicial impartiality by ensuring judges step aside when conflicts of interest or biases may affect their decisions, thereby maintaining public confidence in the judicial process. Judicial misconduct involves unethical behavior by judges that compromises impartiality and undermines the integrity of the judiciary, often prompting investigations by judicial review boards. Emphasizing strict adherence to recusal standards and enforcing penalties for misconduct reinforces the foundational principle of unbiased justice within legal systems.
Conclusion: Upholding Judicial Integrity
Judicial recusal is a vital mechanism ensuring impartiality by allowing judges to withdraw from cases where conflicts of interest exist, thereby maintaining public trust. Judicial misconduct, involving actions that violate ethical standards, threatens the legitimacy of the judiciary and undermines confidence in legal outcomes. Upholding judicial integrity requires strict enforcement of recusal rules and accountability measures to preserve fairness and the rule of law.
Judicial Recusal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com