A void contract lacks legal enforceability from the outset due to missing essential elements such as mutual consent, lawful purpose, or competent parties. This invalidity means neither party can demand performance or damages under the agreement. Explore the rest of this article to fully understand how void contracts impact your agreements and legal rights.
Table of Comparison
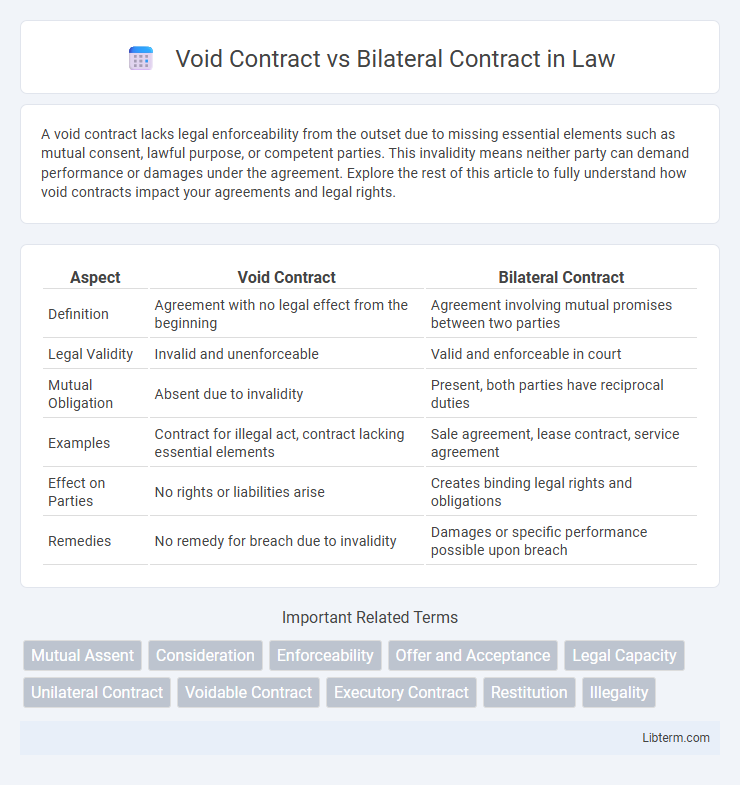
| Aspect | Void Contract | Bilateral Contract |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Agreement with no legal effect from the beginning | Agreement involving mutual promises between two parties |
| Legal Validity | Invalid and unenforceable | Valid and enforceable in court |
| Mutual Obligation | Absent due to invalidity | Present, both parties have reciprocal duties |
| Examples | Contract for illegal act, contract lacking essential elements | Sale agreement, lease contract, service agreement |
| Effect on Parties | No rights or liabilities arise | Creates binding legal rights and obligations |
| Remedies | No remedy for breach due to invalidity | Damages or specific performance possible upon breach |
Definition of Void Contract
A void contract is a legally invalid agreement that lacks enforceability from the outset due to the absence of essential elements such as mutual consent, lawful object, or consideration. Unlike bilateral contracts, which involve reciprocal promises and create binding obligations for both parties, a void contract cannot create any legal rights or duties. Courts typically disregard void contracts because they do not meet the requirements for a valid contract under contract law principles.
Definition of Bilateral Contract
A bilateral contract is a legally binding agreement where both parties exchange mutual promises to perform certain obligations, creating reciprocal rights and duties. Unlike a void contract, which lacks legal effect and cannot be enforced by law, a bilateral contract establishes clear terms and conditions that both parties agree to fulfill. The essence of a bilateral contract lies in its mutual consent and consideration, ensuring enforceability and valid transaction between the involved entities.
Key Legal Differences
A void contract is legally unenforceable from the outset due to factors such as illegality or lack of essential elements, whereas a bilateral contract involves mutual obligations where both parties promise performance. Void contracts lack valid consideration and lawful object, making them null and without legal effect, while bilateral contracts require valid consideration and lawful purposes to bind both parties legally. Courts do not recognize void contracts as valid agreements, but bilateral contracts create enforceable rights and duties enforceable by law.
Essential Elements for Validity
A void contract lacks one or more essential elements of validity, such as lawful object, competent parties, or mutual consent, rendering it unenforceable by law. In contrast, a bilateral contract requires an offer and acceptance between two parties with lawful consideration and the intention to create legal relations, ensuring its validity. The presence of lawful consideration, consent free from vitiating factors, and lawful object are fundamental for distinguishing a valid bilateral contract from a void one.
Common Examples of Void Contracts
Void contracts commonly include agreements for illegal activities, contracts made with minors, and agreements lacking essential elements like mutual consent or lawful purpose. These void contracts cannot be enforced by either party, distinguishing them from bilateral contracts where both parties have valid obligations to perform. In contrast, bilateral contracts involve mutual promises and legally binding commitments valid under contract law.
Examples of Bilateral Contracts
A bilateral contract involves mutual promises between two parties, such as a sales agreement where one party agrees to sell goods and the other agrees to pay for them. Employment contracts, where the employer promises to pay a salary and the employee agrees to perform work, serve as another common example. Unlike a void contract, which lacks legal enforceability, bilateral contracts create binding obligations for both parties.
Enforceability in Court
A void contract lacks legal enforceability from the outset due to fundamental defects such as illegality or lack of capacity, rendering it null and void in a court of law. In contrast, a bilateral contract involves mutual promises between parties and is generally enforceable if it meets essential elements like offer, acceptance, consideration, and lawful purpose. Courts typically uphold bilateral contracts by enforcing the agreed terms unless a valid defense, such as fraud or duress, invalidates the agreement.
Consequences of Breach
A breach of a void contract results in no legal obligations or remedies, as the contract is null from inception and cannot be enforced by either party. In contrast, a breach of a bilateral contract triggers legal consequences, including damages or specific performance, because both parties have mutually binding obligations. The injured party in a bilateral contract breach may seek compensation for losses incurred, emphasizing the enforceability and accountability inherent in bilateral agreements.
Factors Leading to a Void Contract
Factors leading to a void contract include illegality, lack of capacity, and absence of mutual consent, which invalidate the agreement from the outset. Void contracts often involve terms that are impossible to perform or agreements made under duress, fraud, or misrepresentation. Unlike bilateral contracts that are enforceable with mutual promises, void contracts hold no legal effect due to these fundamental defects.
Practical Implications for Parties
Void contracts hold no legal effect from inception, leaving parties without enforceable rights or obligations, which can result in wasted resources and uncertainty for those involved. Bilateral contracts create mutual obligations, ensuring both parties have clear duties and remedies in case of breach, facilitating smoother transactions and risk management. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for businesses to avoid disputes, allocate responsibilities effectively, and uphold contractual integrity in commercial dealings.
Void Contract Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com