Formalities play a crucial role in establishing clear communication and professionalism in both personal and business interactions. They help set expectations, maintain respect, and ensure that all parties understand the necessary procedures or protocols. Discover how mastering formalities can improve your interactions by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
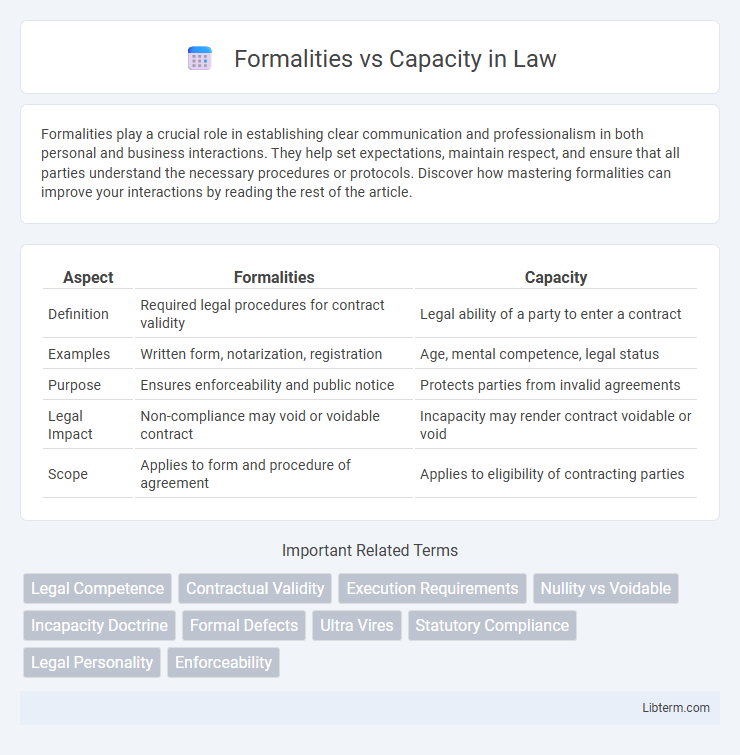
| Aspect | Formalities | Capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Required legal procedures for contract validity | Legal ability of a party to enter a contract |
| Examples | Written form, notarization, registration | Age, mental competence, legal status |
| Purpose | Ensures enforceability and public notice | Protects parties from invalid agreements |
| Legal Impact | Non-compliance may void or voidable contract | Incapacity may render contract voidable or void |
| Scope | Applies to form and procedure of agreement | Applies to eligibility of contracting parties |
Understanding Formalities in Legal Agreements
Understanding formalities in legal agreements involves recognizing specific procedural requirements such as notarization, witness signatures, and written documentation to ensure enforceability. These formalities serve as safeguards that validate the authenticity and intent of parties entering into contracts, differentiating from capacity, which addresses a party's legal ability to contract. Proper adherence to formalities reduces disputes by providing clear evidence that an agreement was consciously and willingly executed.
Defining Capacity in Contract Law
Capacity in contract law refers to a party's legal ability to enter into a binding agreement, generally requiring mental competence and legal age. Individuals lacking capacity, such as minors or those with mental incapacities, may have contracts voidable or unenforceable. Establishing capacity ensures that parties understand the contract's terms and consequences, protecting against exploitation and invalid agreements.
Key Differences: Formalities vs. Capacity
Formalities refer to the legal procedures and documents required to validate a contract, while capacity pertains to a party's legal ability to enter into a contract. Formalities include elements such as written agreements, notarization, or witnesses, which ensure the contract's enforceability. Capacity involves factors like age, mental competence, and authority, determining whether a party can legally bind themselves to a contract.
Importance of Formalities in Enforceability
Formalities play a critical role in the enforceability of contracts by providing clear evidence of the parties' intentions and the agreement's terms, thereby reducing disputes. Certain contracts, such as real estate transactions and wills, require specific formalities like written documentation and notarization to be legally valid. Ensuring adherence to these formalities helps protect parties from fraud and misunderstanding, making the contract legally binding and enforceable in courts.
Assessing Capacity: Who Can Enter Contracts?
Assessing capacity to enter contracts hinges on legal criteria, including age, mental competence, and statutory restrictions, ensuring parties understand contractual obligations. Minors, individuals with cognitive impairments, and those under the influence of substances often lack capacity, rendering agreements voidable or void. Courts evaluate capacity by examining the party's ability to comprehend contract terms and consequences at the time of agreement formation.
Common Pitfalls: Formality and Capacity Issues
Common pitfalls in formalities and capacity issues often arise from misunderstandings about legal requirements for contract validity. Failure to meet essential formalities such as writing, signatures, or notarization can render agreements unenforceable. Capacity problems frequently involve parties lacking legal ability due to age, mental competence, or intoxication, which can lead to contracts being void or voidable.
Formalities: Written vs. Oral Agreements
Written agreements provide clear evidence of terms, reducing disputes and enhancing enforceability in legal proceedings. Oral agreements, while legally binding in many jurisdictions, often face challenges due to lack of tangible proof and reliance on witness credibility. Understanding the formalities related to contract formation ensures parties are aware of the legal standards required for validity and enforceability.
Legal Consequences of Lack of Capacity
Lack of capacity in legal transactions renders agreements void or voidable, resulting in unenforceability and potential restitution claims. Minors, mentally incapacitated persons, and intoxicated individuals generally lack capacity, which protects them from contractual obligations. Courts may impose remedies such as contract rescission or damages to restore parties to their original position due to incapacity-related defects.
Validating Contracts: The Role of Formalities and Capacity
Validating contracts requires both formalities and capacity to ensure legal enforceability. Formalities, such as written agreements or notarization, authenticate the contract's legitimacy, while capacity confirms that parties have the legal ability to understand and enter into the contract. Failure to meet formalities or lack of capacity can render a contract void or voidable, impacting its validation in courts.
Practical Tips for Ensuring Compliance
To ensure compliance with formalities and capacity requirements, verify that all contracts are written according to relevant legal standards, including proper signatures, notarization, and witness presence if required. Confirm that parties involved have the legal capacity to enter agreements, considering age, mental competence, and absence of coercion. Regularly review jurisdiction-specific laws and conduct thorough due diligence to prevent disputes and enforceability issues.
Formalities Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com