Substantive law defines your legal rights and obligations in various areas such as contracts, property, torts, and criminal law. It establishes the framework that determines what conduct is lawful or unlawful, and the remedies available for breaches. Explore the rest of the article to understand how substantive law impacts your daily legal interactions.
Table of Comparison
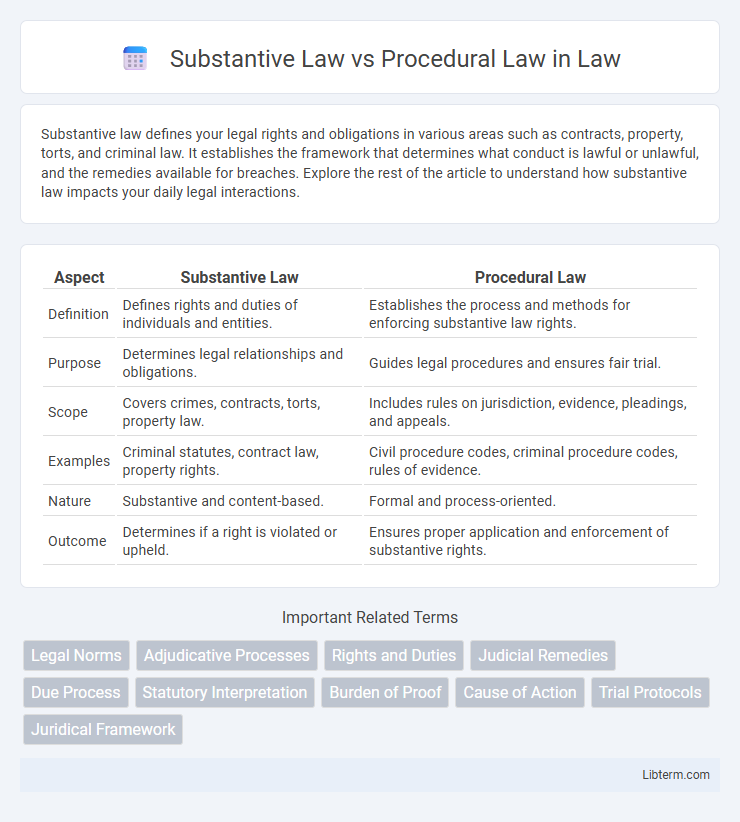
| Aspect | Substantive Law | Procedural Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Defines rights and duties of individuals and entities. | Establishes the process and methods for enforcing substantive law rights. |
| Purpose | Determines legal relationships and obligations. | Guides legal procedures and ensures fair trial. |
| Scope | Covers crimes, contracts, torts, property law. | Includes rules on jurisdiction, evidence, pleadings, and appeals. |
| Examples | Criminal statutes, contract law, property rights. | Civil procedure codes, criminal procedure codes, rules of evidence. |
| Nature | Substantive and content-based. | Formal and process-oriented. |
| Outcome | Determines if a right is violated or upheld. | Ensures proper application and enforcement of substantive rights. |
Introduction to Substantive Law and Procedural Law
Substantive law defines the rights and duties of individuals and collective entities, establishing the legal framework for issues such as contracts, property, and crimes. Procedural law, on the other hand, provides the rules and mechanisms through which courts enforce those substantive rights, including processes like jurisdiction, pleadings, and evidence handling. Understanding the distinction between substantive and procedural law is essential for navigating the legal system effectively.
Defining Substantive Law
Substantive law consists of the set of laws that define rights, duties, and liabilities, determining the legal relationship between individuals or between individuals and the state. It establishes the legal framework for what constitutes crimes, contracts, property rights, and torts, thereby shaping the substance of a case. Unlike procedural law, which governs the process of enforcing those rights, substantive law provides the basis for claims and defenses in civil and criminal matters.
Key Features of Substantive Law
Substantive law defines the rights and duties of individuals and collective bodies, establishing the legal relationship between parties. It encompasses laws related to contracts, torts, property, and criminal offenses, providing the foundation for legal claims and defenses. This branch of law determines the substance of a legal case by specifying what conduct is permissible and what consequences arise from actions.
Defining Procedural Law
Procedural law establishes the rules and methods courts follow for enforcing substantive rights, including how lawsuits are initiated, presented, and adjudicated. It governs processes like jurisdiction, pleadings, evidence, and appeals, ensuring fair and orderly administration of justice. Understanding procedural law is essential for navigating legal systems and effectively protecting substantive rights.
Key Features of Procedural Law
Procedural law governs the methods and means by which substantive laws are enforced, outlining the steps for legal processes such as filing lawsuits, conducting trials, and appealing decisions. Key features include rules on jurisdiction, evidence submission, pleadings, time limits, and court procedures to ensure fairness and consistency in the judicial system. This legal framework facilitates the practical application of substantive rights by defining how courts operate and how cases progress through the legal system.
Major Differences Between Substantive and Procedural Law
Substantive law defines the rights and duties of individuals and collective bodies, encompassing laws related to contracts, torts, property, and criminal offenses. Procedural law outlines the methods and means by which substantive laws are enforced, including rules of evidence, jurisdiction, and legal processes like filing lawsuits and appeals. Major differences lie in their purpose: substantive law governs the legal relationship and conduct, whereas procedural law governs the enforcement and administration of those rights and duties within the judicial system.
Real-World Examples of Substantive Law
Substantive law defines the rights and duties of individuals, such as laws against theft that establish penalties for stealing property. For instance, contract law, a key area of substantive law, outlines the obligations parties must fulfill under agreement terms. Criminal laws prohibiting murder or fraud demonstrate substantive law by setting forth offenses and corresponding punishments.
Real-World Examples of Procedural Law
Procedural law governs the methods and means by which substantive laws are enforced, such as rules of evidence, jurisdiction, and litigation processes. Real-world examples include the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure, which dictate how lawsuits are filed and conducted in U.S. federal courts, and the Miranda rights, requiring police to inform suspects of their legal rights during arrest. Understanding procedural law ensures that legal actions follow a structured process, guaranteeing fairness and due process in the judicial system.
Importance of Both in Legal Systems
Substantive law defines the rights and duties of individuals and collective entities, establishing the legal foundation for justice and social order. Procedural law provides the framework and rules for enforcing substantive rights through courts and judicial processes, ensuring fairness and consistency in legal proceedings. Both are crucial for a functional legal system, as substantive law addresses what the law is, while procedural law dictates how the law is applied and upheld.
Conclusion: Striking a Balance Between Substantive and Procedural Law
Striking a balance between substantive and procedural law ensures that legal rights are clearly defined while providing effective mechanisms for enforcement and dispute resolution. Substantive law establishes the legal standards and obligations, whereas procedural law outlines the methods and processes to uphold those standards in courts. A harmonious integration of both fosters fairness, justice, and efficiency within the legal system.
Substantive Law Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com