An agreement is a legally binding contract between two or more parties that outlines mutual obligations and rights. Clear agreements help prevent misunderstandings and provide a framework for resolving disputes. Explore this article to understand the key elements and benefits of creating effective agreements.
Table of Comparison
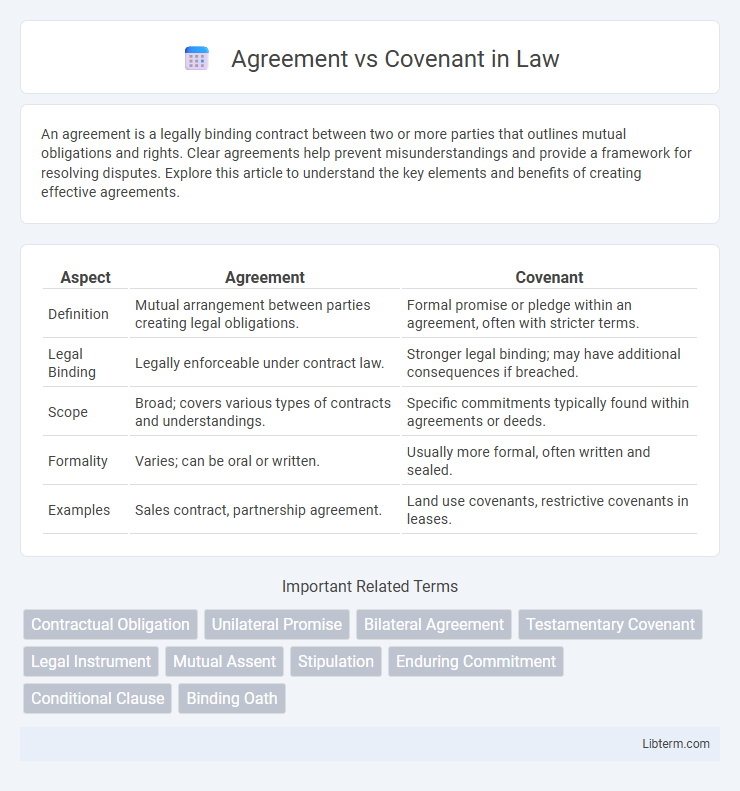
| Aspect | Agreement | Covenant |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mutual arrangement between parties creating legal obligations. | Formal promise or pledge within an agreement, often with stricter terms. |
| Legal Binding | Legally enforceable under contract law. | Stronger legal binding; may have additional consequences if breached. |
| Scope | Broad; covers various types of contracts and understandings. | Specific commitments typically found within agreements or deeds. |
| Formality | Varies; can be oral or written. | Usually more formal, often written and sealed. |
| Examples | Sales contract, partnership agreement. | Land use covenants, restrictive covenants in leases. |
Understanding Agreements: A Basic Overview
Agreements represent mutual arrangements between parties, often outlining specific terms and conditions to guide their relationship. Unlike covenants, which are typically binding promises with legal or religious significance, agreements can be either formal contracts or informal understandings. Key elements include offer, acceptance, and consideration, ensuring clarity and enforceability in various contexts.
Defining Covenant: More Than a Promise
A covenant represents a solemn, binding commitment that goes beyond a mere promise by establishing obligations with enduring moral and legal implications. Unlike typical agreements, covenants often involve mutual trust, sacred vows, and a deep sense of responsibility that reinforces long-term relational or contractual bonds. This distinct nature makes covenants foundational in legal, religious, and social contexts where trust and obligation are paramount.
Key Differences Between Agreement and Covenant
An agreement is a mutual understanding between two or more parties outlining rights and obligations, typically enforceable by law, while a covenant is a solemn promise or commitment often associated with formal or religious contexts. Agreements can be informal or formal contracts involving negotiable terms, whereas covenants usually involve more binding and morally or ethically significant commitments. Unlike agreements, covenants imply a deeper level of trust and often include conditions tied to ongoing relationships or future conduct.
Legal Implications: Agreement vs Covenant
Agreements typically outline mutually agreed-upon terms without creating legally binding obligations enforceable by courts, whereas covenants impose strict legal duties that parties must adhere to under contract law. Breaching a covenant can result in specific performance or damages as remedies, reflecting its stronger enforceability compared to general agreements. Understanding the distinction is crucial for drafting documents with clear intent and legal consequences in contracts, real estate, and business transactions.
Relational Aspects: What Sets Covenants Apart
Covenants emphasize deep relational bonds characterized by mutual commitment, trust, and often a sacred or spiritual dimension, unlike agreements which are primarily transactional and enforceable through legal terms. Covenants foster enduring relationships through shared values and ongoing obligations, creating a sense of community and loyalty beyond mere contractual duties. This relational depth differentiates covenants by prioritizing long-term connection and intentional partnership over simple compliance.
Enforceability: Which Holds More Weight?
A covenant generally holds more weight than an agreement in terms of enforceability, as covenants are formal promises often embedded within contracts, real estate, or religious contexts with explicit legal obligations. Agreements can be broader and may lack the detailed legal terms that make enforcement straightforward, especially if not written or lacking consideration. Courts typically prioritize covenants due to their clear intent and binding nature, making them more reliable for legal enforcement.
Historical Context of Covenants and Agreements
Covenants have roots in ancient legal and religious traditions, often involving solemn promises sealed by rituals or divine witness, which granted them binding authority in societies such as Ancient Israel and Mesopotamia. Agreements, by contrast, evolved as more flexible, secular contracts between parties, focusing on mutual benefit and enforceable terms without the necessity of spiritual or communal obligations. The historical context highlights covenants as foundational to communal identity and moral duty, whereas agreements reflect pragmatic arrangements tailored to changing social and economic conditions.
Examples of Agreements in Modern Life
Agreements in modern life include rental leases, employment contracts, and service agreements, all legally binding documents outlining the responsibilities of involved parties. These agreements facilitate clear communication and enforceability in personal and professional relationships, ensuring obligations such as payment terms, duration, and duties are clearly established. Examples like non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) protect sensitive information, while purchase agreements secure transactions between buyers and sellers, highlighting the practical use of agreements in everyday scenarios.
Covenants in Religion and Culture
Covenants in religion and culture represent solemn, binding promises often viewed as sacred, establishing deep relational obligations between individuals and the divine or within communities. Unlike standard agreements, covenants entail moral and spiritual commitments reinforced by rituals, symbols, or oaths found in traditions such as Judaism, Christianity, and indigenous practices. These covenants shape ethical frameworks and community identity, reflecting enduring values and divine laws that transcend legal contracts.
Choosing Between an Agreement and a Covenant
Choosing between an agreement and a covenant depends on the level of commitment and legal implications desired. Agreements are typically flexible, enforceable contracts outlining mutual promises, while covenants are solemn, often binding commitments with moral or spiritual significance. Selecting a covenant over an agreement signals a deeper, more enduring obligation that may extend beyond legal frameworks.
Agreement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com