A periodic tenancy provides flexibility by automatically renewing the lease at set intervals, such as weekly or monthly, until either party terminates it. This arrangement benefits tenants seeking short-term stability without long-term commitment and landlords who prefer adaptable leasing options. Explore the rest of the article to understand how a periodic tenancy could suit your rental needs.
Table of Comparison
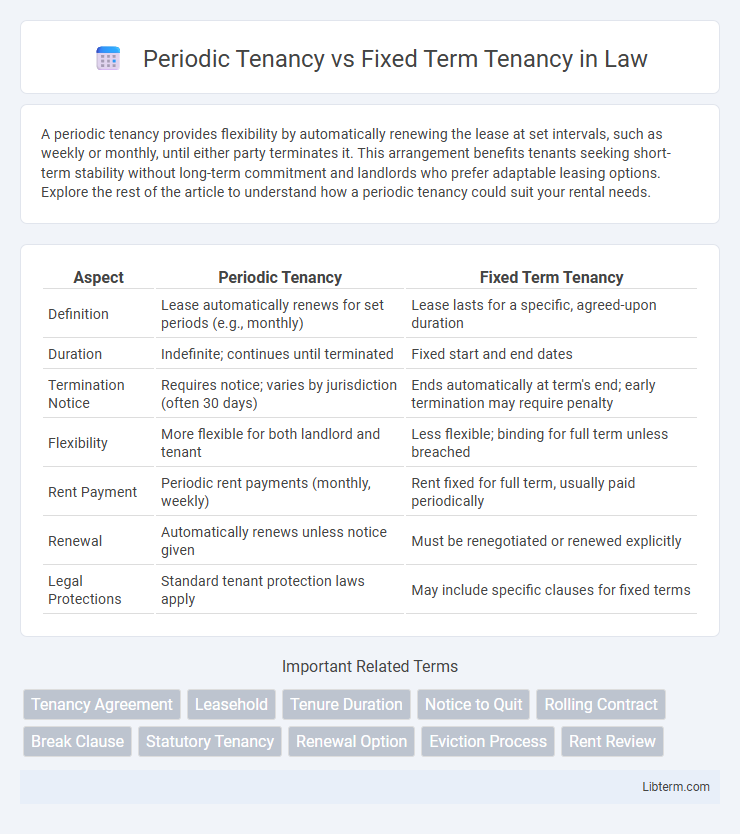
| Aspect | Periodic Tenancy | Fixed Term Tenancy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lease automatically renews for set periods (e.g., monthly) | Lease lasts for a specific, agreed-upon duration |
| Duration | Indefinite; continues until terminated | Fixed start and end dates |
| Termination Notice | Requires notice; varies by jurisdiction (often 30 days) | Ends automatically at term's end; early termination may require penalty |
| Flexibility | More flexible for both landlord and tenant | Less flexible; binding for full term unless breached |
| Rent Payment | Periodic rent payments (monthly, weekly) | Rent fixed for full term, usually paid periodically |
| Renewal | Automatically renews unless notice given | Must be renegotiated or renewed explicitly |
| Legal Protections | Standard tenant protection laws apply | May include specific clauses for fixed terms |
Understanding Periodic Tenancy
Periodic tenancy is a rental agreement that automatically renews at the end of each rental period, such as weekly or monthly, providing flexibility for both landlords and tenants. This type of tenancy requires notice from either party to terminate the lease, usually aligning with the length of the rental period, unlike fixed term tenancies which have a predetermined end date. Understanding periodic tenancy helps tenants avoid unexpected lease terminations and landlords manage ongoing tenancy arrangements effectively.
What Is a Fixed Term Tenancy?
A fixed term tenancy is a lease agreement set for a specific duration, such as six months or one year, with clearly defined start and end dates. This type of tenancy provides both landlord and tenant with certainty regarding the rental period and terms, often including rent amount, responsibilities, and renewal conditions. Unlike periodic tenancies, fixed term tenancies cannot be terminated early without mutual consent or breach of contract.
Key Differences Between Periodic and Fixed Term Tenancies
Periodic tenancies automatically renew after each rental period, such as monthly or weekly, providing flexibility for both landlord and tenant without a set end date. Fixed term tenancies have a defined lease duration, typically six months or one year, establishing clear start and end dates that offer stability and predictability in rent and occupancy. Termination of periodic tenancies requires proper notice aligned with the rental period, whereas fixed term tenancies usually end automatically at the lease's conclusion unless renewed or extended.
Advantages of Periodic Tenancy
Periodic tenancy offers flexibility by allowing tenants to continue their lease without a fixed end date, which facilitates easier adjustments to living arrangements. This type of tenancy also benefits landlords by providing steady rental income with the option to modify lease terms with proper notice. Furthermore, periodic tenancies generally reduce the risk of void periods between leases, ensuring continuous occupancy.
Benefits of Fixed Term Tenancy
Fixed term tenancy offers the benefit of consistent, predictable rental payments and defined lease duration, providing financial stability for both landlords and tenants. It ensures tenant security by locking in the rental rate and occupancy terms for a set period, reducing the risk of sudden rent increases or eviction during the lease term. Landlords benefit from reduced vacancy rates and administrative ease with fixed lease periods, simplifying property management and budgeting.
Drawbacks of Periodic Tenancy
Periodic tenancy often leads to uncertainty due to its indefinite duration, complicating long-term planning for both landlords and tenants. Rent increases and termination require advance notice, which may delay necessary adjustments or property turnover. This flexible arrangement can result in higher vacancy risks and less stable income streams compared to fixed term tenancy.
Disadvantages of Fixed Term Tenancy
Fixed Term Tenancy restricts flexibility by locking tenants into a lease for a set period, often resulting in penalties or difficulties when trying to end the agreement early. This rigidity can lead to financial strain if circumstances change, as tenants remain liable for rent until the lease expires or is legally terminated. Additionally, landlords may be less accommodating to lease modifications or early terminations compared to Periodic Tenancies.
Legal Implications and Notice Requirements
Periodic tenancy operates on a recurring basis, such as month-to-month or week-to-week, and typically requires a shorter notice period for termination, often 30 days, depending on jurisdiction. Fixed term tenancy involves a lease agreement set for a specific duration, commonly six months to one year, with termination generally only possible at the end of the lease term unless both parties agree or breach of contract occurs. Legal implications for periodic tenancies include automatic renewal and flexibility, while fixed term tenancies provide stability but may impose penalties or legal action if broken prematurely.
Choosing the Right Tenancy Agreement
Choosing the right tenancy agreement depends on the tenant's stability and landlord's flexibility needs. Periodic tenancy offers ongoing, typically month-to-month arrangements ideal for short-term occupancy or uncertain plans, while fixed term tenancy provides a set duration, offering security of tenure and predictable rent for both parties. Evaluating factors like duration, rent control, and termination terms ensures an agreement aligned with financial goals and lifestyle preferences.
Frequently Asked Questions about Tenancy Types
Periodic tenancy automatically renews after each rental period, offering flexibility for tenants and landlords without a fixed end date. Fixed term tenancy lasts for a specified duration, such as six months or one year, providing stability and defined lease terms. Common questions include how termination works: periodic tenancies require notice from either party, while fixed term tenancies end at the lease expiration unless renewed or extended.
Periodic Tenancy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com