A beneficiary is an individual or entity entitled to receive benefits or assets from a trust, will, insurance policy, or retirement account. Understanding the role and rights of a beneficiary is crucial for effective estate planning and financial management. Discover more about how beneficiaries impact your financial future as you continue reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
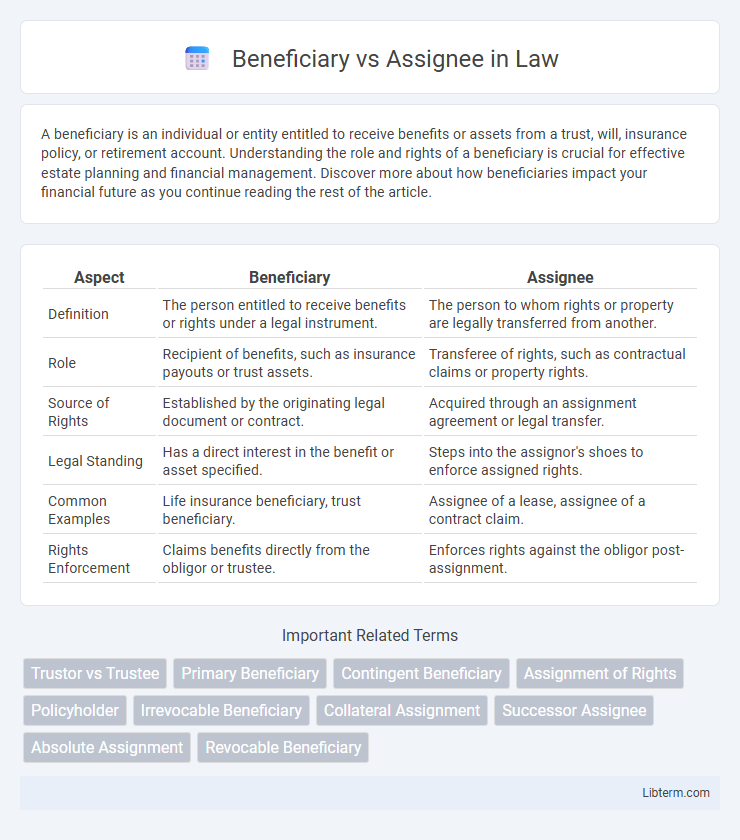
| Aspect | Beneficiary | Assignee |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The person entitled to receive benefits or rights under a legal instrument. | The person to whom rights or property are legally transferred from another. |
| Role | Recipient of benefits, such as insurance payouts or trust assets. | Transferee of rights, such as contractual claims or property rights. |
| Source of Rights | Established by the originating legal document or contract. | Acquired through an assignment agreement or legal transfer. |
| Legal Standing | Has a direct interest in the benefit or asset specified. | Steps into the assignor's shoes to enforce assigned rights. |
| Common Examples | Life insurance beneficiary, trust beneficiary. | Assignee of a lease, assignee of a contract claim. |
| Rights Enforcement | Claims benefits directly from the obligor or trustee. | Enforces rights against the obligor post-assignment. |
Understanding the Terms: Beneficiary vs Assignee
A beneficiary is the individual or entity entitled to receive benefits, assets, or proceeds from a contract, trust, or insurance policy, typically designated by the grantor or policyholder. An assignee, on the other hand, is a party who receives rights, interests, or property through a formal transfer or assignment from the assignor, often involving contractual obligations or legal claims. Understanding the key difference lies in the nature of entitlement: beneficiaries receive benefits by designation, while assignees acquire rights through assignment agreements.
Key Differences Between Beneficiary and Assignee
A beneficiary is an individual or entity designated to receive benefits, such as assets from a trust or insurance policy, whereas an assignee is a party to whom rights or interests are transferred through an assignment agreement. Key differences include that beneficiaries typically acquire rights through a will, trust, or contract without transferring those rights, while assignees obtain their rights by legal assignment, often involving contracts or debts. Beneficiaries usually have passive roles, receiving benefits upon occurrence of specified events, whereas assignees actively enforce or manage the assigned rights.
Legal Definitions: Beneficiary and Assignee Explained
A beneficiary is an individual or entity entitled to receive benefits or assets under a will, trust, insurance policy, or other legal arrangement, often without assuming duties or obligations. An assignee is a party to whom rights or interests are transferred by an assignor through a contract or legal instrument, gaining enforceable rights but sometimes also obligations. Understanding the distinction hinges on the beneficiary's passive receipt of benefits versus the assignee's active role in holding and exercising transferred legal rights.
Rights and Responsibilities of a Beneficiary
A beneficiary holds the right to receive benefits or assets from a trust, will, or insurance policy, but does not have control over the property or legal obligations to manage it. Responsibilities of a beneficiary are limited, primarily including the duty to notify the trustee or insurer of any change in status or contact information. Unlike an assignee who acquires contractual rights and obligations through assignment, the beneficiary's role is passive, centered on entitlement rather than administration.
Roles and Duties of an Assignee
An assignee receives the rights and duties of a contract or property from the assignor, stepping into their legal position to enforce or perform obligations. Unlike a beneficiary who passively benefits from a contract without responsibility, the assignee actively manages, collects, or fulfills contractual terms according to the assignment agreement. The assignee must ensure proper notification to involved parties and uphold the contractual rights transferred to them, bearing accountability for any obligations stipulated in the original contract.
Common Scenarios Involving Beneficiaries
Common scenarios involving beneficiaries include life insurance policies, retirement accounts, and wills where beneficiaries receive assets or benefits upon the owner's death. Beneficiaries have a right to inherit or claim specific property without the need to transfer ownership formally. Unlike assignees, beneficiaries typically have a predetermined entitlement under contractual or legal arrangements.
Typical Situations Involving Assignees
Typical situations involving assignees occur in contract law, where an assignor transfers rights or benefits under a contract to an assignee, such as in debt assignments, where lenders assign loan repayment rights. In insurance, assignees may receive policy benefits after the original policyholder assigns those rights, often in cases of collateral assignment for loans. Assignees also appear frequently in sales of receivables or other financial instruments, where businesses assign payment rights to third parties for cash flow management.
Impact on Contracts: Beneficiary vs Assignee
The difference between a beneficiary and an assignee significantly impacts contract rights and obligations, as a beneficiary typically gains benefits under a contract without assuming duties, while an assignee acquires both rights and responsibilities by transferring or receiving contractual interests. Beneficiaries often cannot enforce contract terms directly, whereas assignees may sue or be sued under the contract depending on jurisdictional rules and the nature of the assignment. Understanding this distinction is crucial for effective contract enforcement, risk management, and ensuring proper legal outcomes in transactions involving third parties.
How to Designate a Beneficiary or Assignee
Designating a beneficiary typically involves naming a specific individual or entity to receive assets, insurance proceeds, or benefits upon an event such as death, using clear, legally recognized documentation like beneficiary designation forms. Assigning rights or interests to an assignee requires a formal assignment agreement that explicitly transfers ownership or rights from the assignor to the assignee, often necessitating notarization or registration depending on the asset type. Proper designation ensures enforceability and clarity, minimizing disputes by specifying details like full legal names, relationship to the assignor, and the scope of rights or benefits transferred.
Frequently Asked Questions About Beneficiary and Assignee
Frequently asked questions about beneficiary and assignee often focus on their distinct roles in legal and financial contexts. A beneficiary is the individual or entity entitled to receive benefits from a contract or asset, such as life insurance or a trust, while an assignee is someone who receives rights or property through a transfer from the original holder. Clarification typically centers on how rights transfer, tax implications, and the ability of assignees to enforce contracts compared to beneficiaries.
Beneficiary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com