Res judicata prevents re-litigation of cases that have been conclusively resolved by a competent court, ensuring finality and judicial efficiency. This principle protects parties from the burden of multiple lawsuits over the same issue, saving time and resources. Discover how res judicata can impact your legal strategy and case resolution in the full article.
Table of Comparison
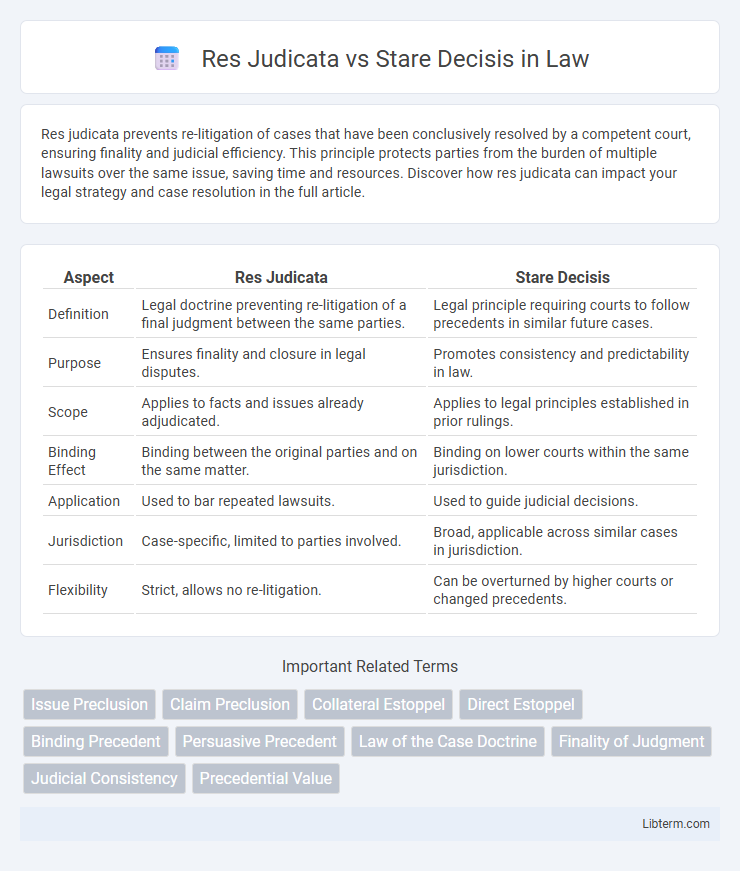
| Aspect | Res Judicata | Stare Decisis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal doctrine preventing re-litigation of a final judgment between the same parties. | Legal principle requiring courts to follow precedents in similar future cases. |
| Purpose | Ensures finality and closure in legal disputes. | Promotes consistency and predictability in law. |
| Scope | Applies to facts and issues already adjudicated. | Applies to legal principles established in prior rulings. |
| Binding Effect | Binding between the original parties and on the same matter. | Binding on lower courts within the same jurisdiction. |
| Application | Used to bar repeated lawsuits. | Used to guide judicial decisions. |
| Jurisdiction | Case-specific, limited to parties involved. | Broad, applicable across similar cases in jurisdiction. |
| Flexibility | Strict, allows no re-litigation. | Can be overturned by higher courts or changed precedents. |
Introduction to Res Judicata and Stare Decisis
Res Judicata is a legal doctrine that prevents the same dispute between parties from being litigated more than once after a final judgment has been rendered, ensuring finality and judicial efficiency. Stare Decisis, on the other hand, is the principle that courts should follow precedents set by higher courts or previous rulings, promoting consistency and stability in the law. Both doctrines serve to uphold the integrity of the legal system by balancing the need for finality with the need for predictability in judicial decisions.
Defining Res Judicata: Meaning and Scope
Res Judicata refers to the legal doctrine preventing the same dispute from being relitigated once a final judgment has been rendered by a competent court, ensuring judicial efficiency and consistency. Its scope extends to claims that were or could have been raised in the initial lawsuit, binding parties and courts to the final verdict. This principle differs from Stare Decisis, which mandates adherence to precedent in judicial decisions rather than barring repetitive litigation of identical cases.
Understanding Stare Decisis: Conceptual Framework
Stare Decisis is a legal doctrine that mandates courts to follow precedents established in previous rulings, ensuring consistency and predictability in judicial decisions. Unlike Res Judicata, which bars re-litigation of a final judgment between the same parties, Stare Decisis emphasizes adherence to established legal principles across different cases to maintain stability in the law. This conceptual framework fosters judicial efficiency by guiding courts to respect prior interpretations while allowing for legal evolution when precedents become outdated.
Core Differences Between Res Judicata and Stare Decisis
Res Judicata prevents parties from relitigating the same claim or cause of action after a final judgment, ensuring conclusiveness in individual disputes. Stare Decisis mandates courts to follow established judicial precedents, promoting consistency and predictability in legal decisions across cases. The core difference lies in Res Judicata's focus on finality of specific cases versus Stare Decisis' emphasis on adherence to prior legal principles in future cases.
Objectives and Rationale Behind Each Doctrine
Res Judicata aims to prevent legal disputes from being re-litigated by establishing finality and consistency in judicial decisions, thereby conserving judicial resources and protecting parties from multiple lawsuits. Stare Decisis focuses on maintaining legal stability and predictability by adhering to precedents set in prior court rulings, ensuring uniform application of the law over time. Both doctrines uphold the principle of legal certainty but differ in scope; Res Judicata applies to specific cases, while Stare Decisis governs the use of precedent across cases.
Practical Applications in Legal Proceedings
Res Judicata prevents parties from relitigating the same claim or cause of action once a final judgment is rendered, ensuring legal certainty and judicial efficiency. Stare Decisis binds courts to follow precedents set by higher courts within the same jurisdiction, promoting consistency and predictability in legal decisions. In practice, Res Judicata bars repetitive lawsuits, while Stare Decisis guides judges in ruling on novel or unsettled legal issues based on established case law.
Exceptions and Limitations of Res Judicata
Res Judicata, which prevents re-litigation of cases once a final judgment is rendered, has exceptions such as fraud, lack of jurisdiction, and newly discovered evidence that can invalidate the previous judgment. Limitations include the requirement that the issue must have been directly adjudicated and that parties or their privies must be the same in both cases. Unlike Stare Decisis, which emphasizes adherence to precedent in future cases, Res Judicata strictly applies to the finality of individual case decisions.
Exceptions and Limitations of Stare Decisis
Stare decisis mandates courts to follow precedents, ensuring legal consistency, but exceptions arise when past rulings are outdated, unjust, or detrimental to societal progress. Limitations include overruling precedents due to changes in statutory law, constitutional amendments, or evolving social values that render previous decisions inapplicable. The doctrine allows judicial flexibility to correct errors and adapt to new circumstances without undermining legal stability.
Impact on Judicial Consistency and Finality
Res judicata ensures judicial finality by preventing the re-litigation of cases that have already been conclusively decided, thereby promoting legal certainty and conserving judicial resources. Stare decisis contributes to judicial consistency by mandating courts to follow established precedents, fostering stability and predictability in legal decisions. Together, these doctrines balance the need for finality in individual cases with the uniform application of law across different cases.
Comparative Analysis: Res Judicata vs Stare Decisis
Res Judicata prevents re-litigation of the same case by ensuring finality and legal certainty after a court judgment is rendered, whereas Stare Decisis mandates adherence to precedent to maintain consistency in judicial decisions across cases. Res Judicata applies to identical parties and issues to bar subsequent lawsuits, while Stare Decisis influences judicial reasoning by obligating courts to follow established legal principles from previous rulings. Both doctrines promote stability in the legal system, but Res Judicata operates at the case level to conclude disputes, and Stare Decisis functions as a rule-based framework guiding interpretation and application of the law over time.
Res Judicata Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com