The appellee is the party who responds to an appeal in a court case, seeking to uphold the lower court's decision. Understanding the role of the appellee is crucial when navigating appellate procedures and legal arguments. Explore the rest of the article to learn how the appellee influences the outcome of appeals and protects your interests in the judicial process.
Table of Comparison
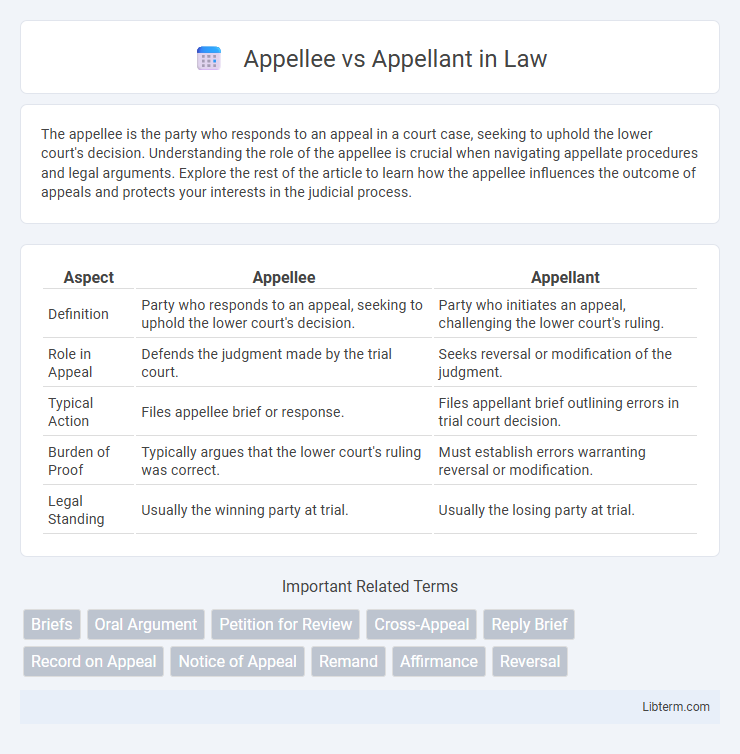
| Aspect | Appellee | Appellant |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Party who responds to an appeal, seeking to uphold the lower court's decision. | Party who initiates an appeal, challenging the lower court's ruling. |
| Role in Appeal | Defends the judgment made by the trial court. | Seeks reversal or modification of the judgment. |
| Typical Action | Files appellee brief or response. | Files appellant brief outlining errors in trial court decision. |
| Burden of Proof | Typically argues that the lower court's ruling was correct. | Must establish errors warranting reversal or modification. |
| Legal Standing | Usually the winning party at trial. | Usually the losing party at trial. |
Introduction to Appellee and Appellant
The appellant is the party who initiates an appeal by challenging a lower court's decision, seeking a reversal or modification. The appellee, also known as the respondent, is the party opposing the appeal, defending the original judgment. Understanding the roles of appellant and appellee is crucial in appellate law, as it defines each party's responsibilities and legal arguments during the appeals process.
Legal Definitions: Appellee vs Appellant
The appellant is the party who files an appeal to challenge a court's decision, seeking a review and reversal of the lower court's judgment. The appellee, also known as the respondent, is the party opposing the appeal, defending the original ruling and urging the appellate court to uphold it. These legal definitions clearly distinguish the roles and responsibilities each party holds during the appellate process.
Roles in the Appeals Process
The appellee is the party who responds to the appeal, usually the winner in the lower court, defending the original verdict. The appellant, as the party who initiates the appeal, seeks to overturn or modify the lower court's decision by challenging legal errors or procedural issues. Both roles are vital in the appeals process, with the appellant presenting grounds for reversal and the appellee advocating for affirming the initial judgment.
Key Differences Between Appellee and Appellant
The appellant is the party who initiates an appeal by challenging a court's decision, seeking to overturn or modify the judgment, while the appellee is the party responding to the appeal, aiming to uphold the original ruling. Key differences include their roles in the appellate process, with the appellant bearing the burden of proving errors in the trial court, whereas the appellee argues against such claims to maintain the verdict. The appellant files the initial appellate brief, and the appellee submits a responsive brief, highlighting contrasting perspectives on the case's legal issues.
Rights and Responsibilities of Each Party
The appellant holds the right to challenge a court's decision by filing an appeal and must provide a detailed record of errors claimed during the trial. The appellee has the responsibility to respond to the appellant's arguments and defend the lower court's ruling, often by submitting written briefs and oral arguments. Both parties bear the responsibility to comply with procedural rules and deadlines set by the appellate court to ensure their rights are preserved.
Common Legal Scenarios Involving Appellees and Appellants
In common legal scenarios, appellants initiate the appeal process by challenging a lower court's decision, seeking reversal or modification, while appellees respond to defend the original judgment. Appellants typically argue errors in the trial court's application of law or procedural issues, whereas appellees emphasize factual findings and uphold the trial court's verdict. Understanding the distinct roles of appellee and appellant is crucial in appellate practice, influencing legal strategy, briefing, and oral arguments.
Appellate Court Procedures Explained
Appellee refers to the party responding to an appeal, while appellant is the party that initiates the appeal in appellate court procedures. The appellate court reviews the appellant's claims for legal errors in the lower court's decision without re-examining factual evidence. Briefs, oral arguments, and the record of the original trial are essential components in the appellate review process to determine if the lower court's ruling should be upheld or reversed.
Implications of Being an Appellee or Appellant
The appellant initiates an appeal by challenging a lower court's decision, which can lead to a potential reversal or modification of the judgment, impacting the course of litigation and legal costs. The appellee defends the original ruling, aiming to uphold the decision and preserve legal status quo, often facing the burden of countering the appellant's arguments. Being an appellant involves seeking change and bears the risk of losing on appeal, whereas appellees focus on maintaining the favorable outcome and preventing further legal disputes.
Frequently Asked Questions: Appellee vs Appellant
The appellee is the party who responds to an appeal, typically the winner in the lower court, while the appellant is the party who initiates the appeal seeking a reversal of the decision. Frequently asked questions about appellee vs appellant include their roles in the appellate process, differences in filing briefs, and rights to oral arguments. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for navigating appellate procedures and ensuring proper legal representation.
Conclusion: Importance in the Legal System
The distinction between appellee and appellant is crucial for ensuring clarity and fairness in the legal process, as it defines the parties' roles during appeals. Appellants challenge the lower court's decision, while appellees defend it, maintaining the judicial system's balance and adherence to due process. This clear demarcation supports organized appellate review, promotes efficiency, and upholds the rule of law.
Appellee Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com