Expanding your business internationally opens opportunities for growth, increased revenue, and brand recognition across global markets. Navigating cultural differences, compliance regulations, and logistics is crucial for success in diverse regions. Explore the key strategies in this article to optimize your international expansion and achieve lasting results.
Table of Comparison
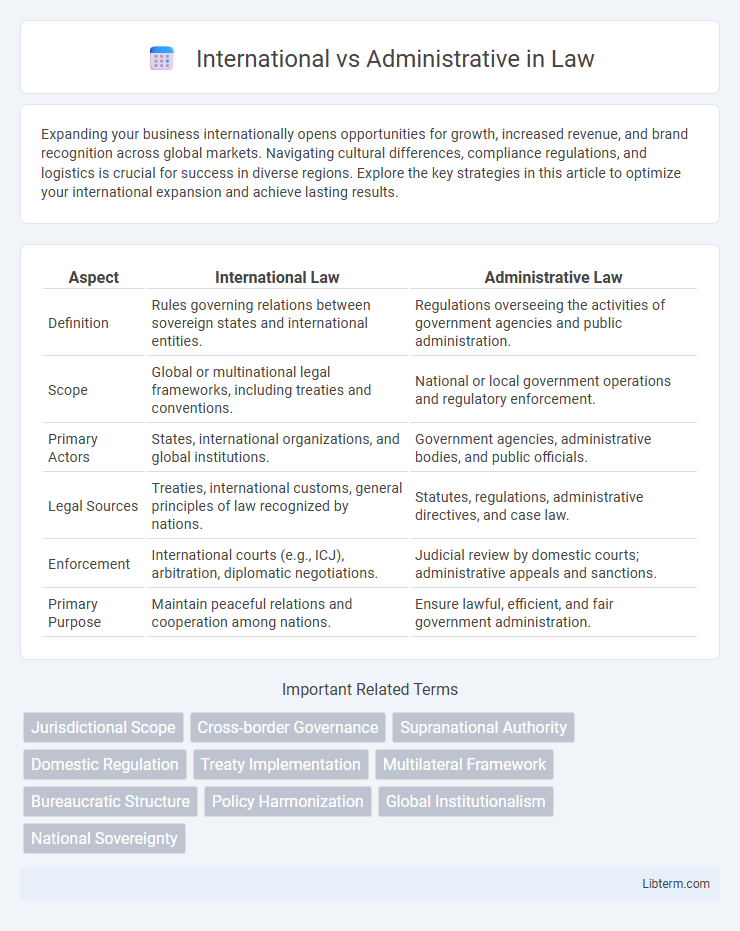
| Aspect | International Law | Administrative Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rules governing relations between sovereign states and international entities. | Regulations overseeing the activities of government agencies and public administration. |
| Scope | Global or multinational legal frameworks, including treaties and conventions. | National or local government operations and regulatory enforcement. |
| Primary Actors | States, international organizations, and global institutions. | Government agencies, administrative bodies, and public officials. |
| Legal Sources | Treaties, international customs, general principles of law recognized by nations. | Statutes, regulations, administrative directives, and case law. |
| Enforcement | International courts (e.g., ICJ), arbitration, diplomatic negotiations. | Judicial review by domestic courts; administrative appeals and sanctions. |
| Primary Purpose | Maintain peaceful relations and cooperation among nations. | Ensure lawful, efficient, and fair government administration. |
Introduction to International and Administrative Law
International law governs the relationships between sovereign states and international organizations, establishing norms on diplomacy, treaties, human rights, and conflict resolution. Administrative law regulates the actions and decisions of government agencies, ensuring legality, transparency, and accountability within public administration. Both fields are essential for maintaining order, but international law addresses global issues while administrative law focuses on domestic governance.
Key Differences Between International and Administrative Law
International law governs relations between sovereign states and international entities, focusing on treaties, human rights, and global regulations, while administrative law regulates the actions and operations of government agencies within a country. Key differences include jurisdiction--international law applies across borders, whereas administrative law is confined to national or local government. Enforcement mechanisms also vary, with international law relying on treaties and diplomatic consensus, whereas administrative law uses internal government procedures and judicial review.
Scope and Application of International Law
International law governs relations between sovereign states, international organizations, and sometimes individuals, covering areas such as treaties, human rights, and diplomatic relations, with its scope extending globally and transcending national borders. Administrative law, by contrast, regulates the activities of government agencies within a specific country, focusing on the implementation and enforcement of national legislation and ensuring public administration complies with statutory mandates. The application of international law affects multiple jurisdictions and requires cooperation among states, whereas administrative law applies domestically, directly influencing national governance and public administration.
Scope and Application of Administrative Law
Administrative law governs the activities of governmental agencies and ensures compliance with regulations within a domestic jurisdiction, focusing on rulemaking, adjudication, and enforcement of public policies at national and local levels. International law regulates relations between sovereign states and international entities, addressing treaties, human rights, and global agreements without direct enforcement over domestic administrative procedures. The scope of administrative law is confined to the internal governance and administrative actions within a country, while international law operates across borders, influencing states' behavior through cooperative frameworks and consensus.
Legal Sources: Treaties vs. Statutes and Regulations
International legal sources primarily consist of treaties, which are formal agreements between sovereign states that establish binding obligations under international law. Administrative law relies heavily on statutes and regulations, which are laws enacted by legislative bodies and rules created by governmental agencies to govern domestic governance. Treaties carry authority beyond national borders, while statutes and regulations operate within a state's legal framework, reflecting different scopes and enforcement mechanisms in international versus administrative law contexts.
Jurisdiction and Enforcement Mechanisms
International law governs relations between sovereign states with limited enforcement mechanisms relying on diplomatic negotiations, treaties, and international bodies like the International Court of Justice. Administrative law operates within a specific state's jurisdiction, focusing on regulating government agencies and their enforcement of national laws with more direct and effective mechanisms such as administrative orders, fines, and judicial review. Jurisdiction in international law often faces challenges due to state sovereignty and lack of centralized enforcement, whereas administrative law benefits from clear territorial authority and institutional frameworks to implement decisions.
Roles of International Organizations vs. National Agencies
International organizations such as the United Nations and the World Health Organization coordinate global initiatives, set international standards, and facilitate cooperation between countries on issues like security, health, and trade. National agencies implement these policies at the domestic level, enforcing laws, managing public services, and adapting international guidelines to local contexts. This division of roles ensures that global goals are aligned with national priorities, maintaining order in both international relations and internal governance.
Impact on Individuals and States
International law governs the relations between sovereign states and international entities, directly impacting state sovereignty by establishing legal agreements and obligations that influence national policies and diplomatic interactions. Administrative law, on the other hand, regulates the actions and decisions of domestic government agencies, affecting individuals by ensuring accountability, fairness, and protection of rights within national jurisdictions. The interplay between international and administrative law shapes how states implement global norms internally, balancing external commitments with individual rights protection.
Case Studies: Landmark International and Administrative Decisions
Landmark international case studies such as the International Court of Justice's rulings on territorial disputes demonstrate the binding nature of global legal frameworks and the complexities of state sovereignty. Administrative case studies, like the U.S. Supreme Court's Chevron Deference decisions, highlight the discretionary power of administrative agencies in interpreting statutes within domestic legal systems. These landmark decisions illustrate the intricate balance between international legal obligations and national administrative authority.
The Future of International and Administrative Law
The future of international and administrative law will increasingly intersect as global governance expands and national regulatory frameworks adapt to transnational challenges. Emerging issues such as climate change, cybersecurity, and global health require harmonized legal standards integrating international treaties with domestic administrative regulations. Advances in digital technologies and artificial intelligence will further reshape both fields, necessitating collaborative enforcement mechanisms and updated legal protocols to ensure effective compliance and accountability worldwide.
International Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com