Conviction is the firm belief in the truth or validity of an idea, guiding your decisions and actions with unwavering confidence. It shapes personal integrity and determines how effectively you pursue goals despite challenges. Discover how strengthening your conviction can transform your mindset and empower your journey in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
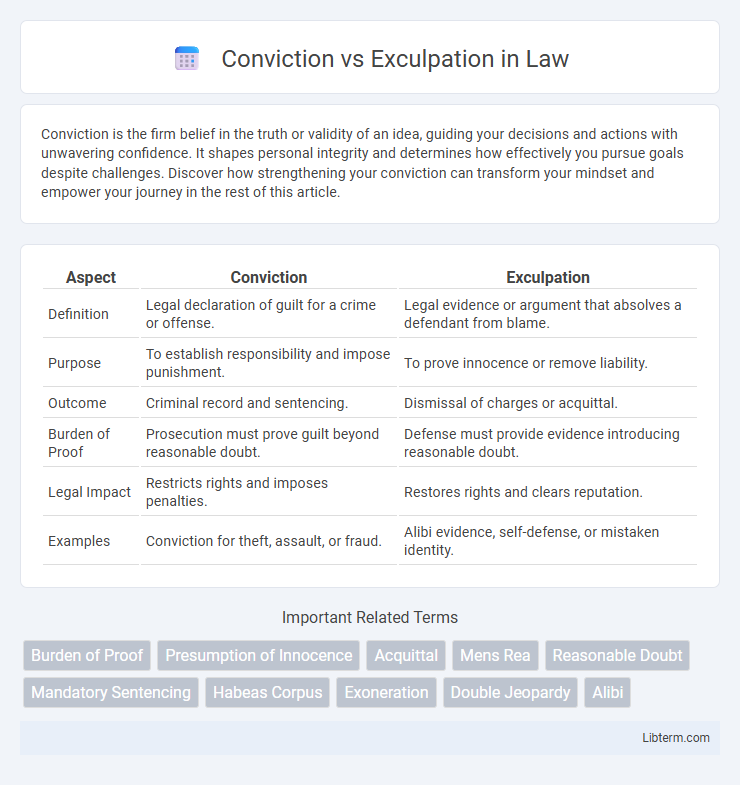
| Aspect | Conviction | Exculpation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal declaration of guilt for a crime or offense. | Legal evidence or argument that absolves a defendant from blame. |
| Purpose | To establish responsibility and impose punishment. | To prove innocence or remove liability. |
| Outcome | Criminal record and sentencing. | Dismissal of charges or acquittal. |
| Burden of Proof | Prosecution must prove guilt beyond reasonable doubt. | Defense must provide evidence introducing reasonable doubt. |
| Legal Impact | Restricts rights and imposes penalties. | Restores rights and clears reputation. |
| Examples | Conviction for theft, assault, or fraud. | Alibi evidence, self-defense, or mistaken identity. |
Understanding Conviction and Exculpation: Key Definitions
Conviction refers to the formal declaration that someone is guilty of a criminal offense, typically resulting from a court judgment based on evidence proving the defendant's culpability beyond a reasonable doubt. Exculpation involves the process or evidence that absolves a person from blame or proves their innocence, effectively negating guilt and preventing conviction. Understanding these key definitions is crucial for interpreting legal outcomes and the burden of proof required in criminal law.
Legal Foundations Behind Conviction
Conviction is legally grounded in the establishment of guilt beyond a reasonable doubt, requiring credible evidence, due process, and adherence to statutory laws and judicial precedents. The legal framework mandates rigorous investigation, prosecution, and fair trial procedures to ensure that convictions reflect the accurate application of criminal law. This foundation contrasts with exculpation, which involves proving innocence or introducing reasonable doubt to negate criminal liability.
What Constitutes Exculpation in Law?
Exculpation in law constitutes evidence or arguments demonstrating a defendant's innocence or negating criminal liability, such as alibis, lack of intent, or mistaken identity. It involves proving that the accused did not commit the alleged offense or that legal defenses, like insanity or self-defense, apply. Courts assess exculpatory evidence to determine whether charges should be dismissed or if the defendant should be acquitted during trial.
The Process from Accusation to Conviction
The process from accusation to conviction begins with an investigation that gathers evidence to establish probable cause. Following arrest, formal charges are filed, leading to arraignment and potential pretrial motions where the defense may seek exculpation by presenting evidence or alibis to negate guilt. If the case proceeds to trial, the prosecution must prove guilt beyond a reasonable doubt while the defense aims for exculpation to achieve acquittal or dismissal.
Pathways to Achieving Exculpation
Achieving exculpation involves obtaining evidence or legal arguments that clearly demonstrate a defendant's innocence or negate elements of the alleged crime, leading to dismissal or acquittal. Key pathways include presenting alibi evidence, uncovering procedural errors, proving mistaken identity, or submitting new DNA or forensic test results that contradict prosecution claims. Effective exculpation often requires strategic use of appeals, post-conviction relief motions, or habeas corpus petitions supported by robust factual or legal bases.
Impact of Evidence on Conviction and Exculpation
The impact of evidence on conviction and exculpation is pivotal in the legal process, as probative and credible evidence strengthens the likelihood of a conviction by establishing guilt beyond a reasonable doubt. Conversely, exculpatory evidence, such as alibis, DNA results, or witness recantations, plays a critical role in overturning wrongful convictions or preventing unjust punishment by proving innocence or raising reasonable doubt. The quality, relevance, and admissibility of forensic evidence often determine the balance between conviction and exculpation in criminal cases.
Rights of the Accused: Safeguards and Protections
Rights of the accused ensure safeguards such as the presumption of innocence, protection against self-incrimination, and the right to legal counsel, which collectively prevent wrongful convictions. Exculpation requires presenting clear, admissible evidence that negates guilt, reinforcing the principle that no one should be convicted without proof beyond a reasonable doubt. These protections uphold fairness within the criminal justice system by balancing prosecutorial power and the accused's right to a fair trial.
Common Misconceptions: Conviction vs Exculpation
Common misconceptions often conflate conviction with proof of guilt, ignoring that exculpation involves evidence or arguments that absolve a defendant of blame. Conviction is the formal judgment of guilt in a criminal case, while exculpation refers to actions or facts that demonstrate innocence or reduce culpability. Misunderstanding these terms can lead to false assumptions about legal outcomes and undermine the fairness of judicial processes.
High-Profile Cases Illustrating Conviction and Exculpation
High-profile cases such as the Central Park Five highlight wrongful convictions later overturned through DNA evidence and legal advocacy, demonstrating the critical role of exculpation in justice. The O.J. Simpson trial exemplifies a highly publicized conviction debate where exculpatory evidence influenced public opinion and the verdict. These cases underscore the importance of forensic science and rigorous legal scrutiny in distinguishing conviction from exculpation within complex criminal proceedings.
Future Trends in Criminal Justice: Balancing Conviction and Exculpation
Emerging technologies such as AI-driven forensic analysis and predictive analytics are reshaping the balance between conviction and exculpation by enhancing evidence accuracy and reducing wrongful convictions. Legal systems are increasingly adopting data-driven approaches to improve case outcomes and uphold justice, emphasizing the protection of innocent individuals while ensuring accountability. Future trends highlight the integration of real-time digital evidence and automated review processes to streamline judicial decisions and support equitable verdicts.
Conviction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com