The principle is a fundamental truth or proposition that serves as the foundation for a system of belief or behavior. It guides decision-making and actions across various contexts, ensuring consistency and integrity. Discover how understanding this core concept can enhance Your approach by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
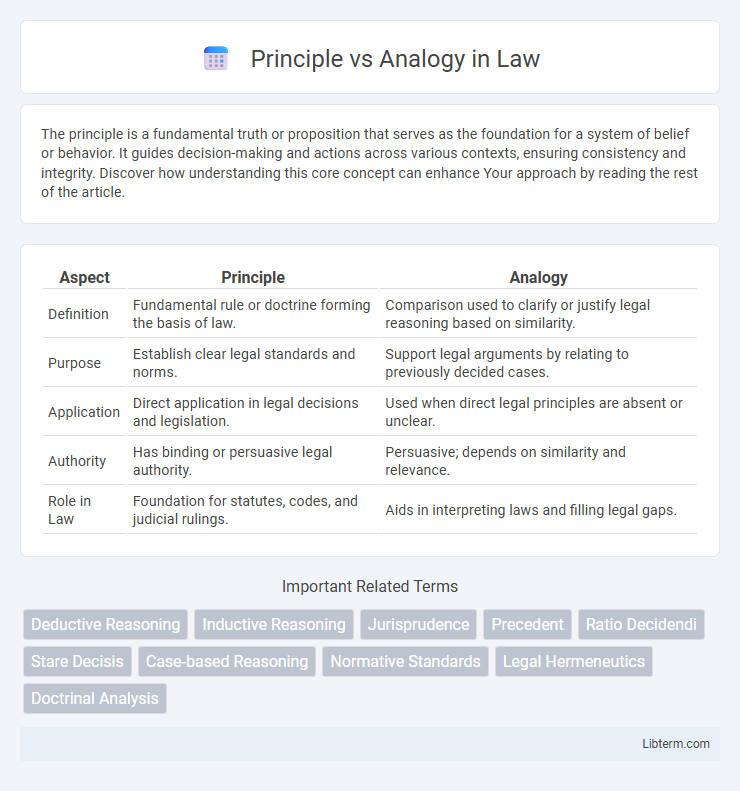
| Aspect | Principle | Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fundamental rule or doctrine forming the basis of law. | Comparison used to clarify or justify legal reasoning based on similarity. |
| Purpose | Establish clear legal standards and norms. | Support legal arguments by relating to previously decided cases. |
| Application | Direct application in legal decisions and legislation. | Used when direct legal principles are absent or unclear. |
| Authority | Has binding or persuasive legal authority. | Persuasive; depends on similarity and relevance. |
| Role in Law | Foundation for statutes, codes, and judicial rulings. | Aids in interpreting laws and filling legal gaps. |
Principle vs Analogy: Core Definitions
A principle is a fundamental truth or law that serves as the foundation for a system of belief or behavior, while an analogy is a comparison between two different things based on their similarity in some aspects. Principles provide universal guidelines or rules applicable across various contexts, whereas analogies are used to explain or clarify concepts by highlighting likenesses. Understanding the core definitions distinguishes principles as foundational truths from analogies as illustrative tools.
Key Differences Between Principles and Analogies
Principles represent fundamental truths or laws that serve as the foundation for reasoning and behavior, while analogies are comparisons between two different concepts used to explain or illustrate an idea. Principles provide universal guidelines applicable across various situations, whereas analogies are context-specific tools that enhance understanding by highlighting similarities. The key difference lies in principles being intrinsic and prescriptive, while analogies function as illustrative and descriptive devices.
Historical Contexts of Principles and Analogies
Principles have historically emerged from foundational philosophical and scientific inquiries, serving as universal truths guiding ethical, legal, and natural laws. Analogies, rooted in rhetorical and pedagogical traditions, have been used across cultures to simplify complex ideas by drawing parallels, aiding comprehension and persuasion. The historical use of principles reflects an emphasis on consistent, objective standards, while analogies demonstrate the evolving nature of human understanding through comparative reasoning.
Role of Principles in Logical Reasoning
Principles serve as foundational truths or established rules that underpin logical reasoning, providing consistent criteria for evaluating arguments and drawing valid conclusions. Unlike analogies, which rely on comparing similar cases to infer conclusions, principles offer universal standards that ensure objective and systematic analysis. The role of principles in logical reasoning is crucial for maintaining rigor, clarity, and reliability in problem-solving and decision-making processes.
How Analogies Enhance Understanding
Analogies enhance understanding by mapping complex or abstract principles onto familiar concepts, making new information more accessible and relatable. They create mental bridges that facilitate cognitive connections, improving memory retention and conceptual clarity. By aligning unfamiliar ideas with known experiences, analogies enable more effective learning and problem-solving.
Strengths and Weaknesses: Principle vs Analogy
Principles offer clear, foundational guidelines that provide consistency and predictability, making them strong tools for decision-making in complex scenarios but sometimes lack flexibility in novel situations. Analogies excel at simplifying complex concepts by drawing relatable comparisons, enhancing understanding and creativity, yet they can oversimplify or mislead if the compared entities differ significantly. Balancing the rigor of principles with the intuitive insight of analogies enables more robust problem-solving and communication strategies.
Applications in Science, Law, and Education
Principles serve as foundational truths guiding scientific research, legal reasoning, and educational frameworks by providing consistent, evidence-based standards. Analogies facilitate understanding and innovation by linking unfamiliar concepts to familiar ones, enhancing problem-solving in science, case interpretation in law, and curriculum design in education. Together, principles ensure rigor and reliability, while analogies foster creativity and accessibility across these disciplines.
Examples Illustrating Principles and Analogies
Principles like Newton's law of gravitation explain natural phenomena through fundamental truths, such as the force between two masses being proportional to their product and inversely proportional to the square of their distance. Analogies, for example comparing the flow of electricity in a circuit to water flowing through pipes, help simplify complex concepts by relating unfamiliar ideas to familiar experiences. While principles provide precise, scientific explanations, analogies serve as educational tools to enhance understanding and retention.
Avoiding Misinterpretation: Best Practices
Avoid misinterpretation between principle and analogy by clearly defining the foundational rule or law (principle) and distinguishing it from illustrative comparisons (analogy) used to explain complex ideas. Use precise language to emphasize the universal applicability of principles, while analogies should be framed as context-specific tools to aid understanding rather than concrete evidence. Incorporating explicit disclaimers and context references ensures clarity and prevents conflating fundamental truths with illustrative examples.
Choosing Between Principle and Analogy in Argumentation
Choosing between principle and analogy in argumentation depends on the context and strength of the evidence supporting each. Principles provide universal, abstract rules that apply broadly, offering clear guidance when consistency is essential. Analogies rely on comparing similar cases, proving effective when illustrating complex ideas but weaker if the cases lack sufficient similarity or relevance.
Principle Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com