Forcible entry is a critical technique used by emergency responders to gain access to locked or barricaded areas during rescue operations. Mastery of specialized tools and methods ensures rapid, safe entry while minimizing damage to property. Explore the article further to understand the essential skills and equipment that can enhance your effectiveness in emergency scenarios.
Table of Comparison
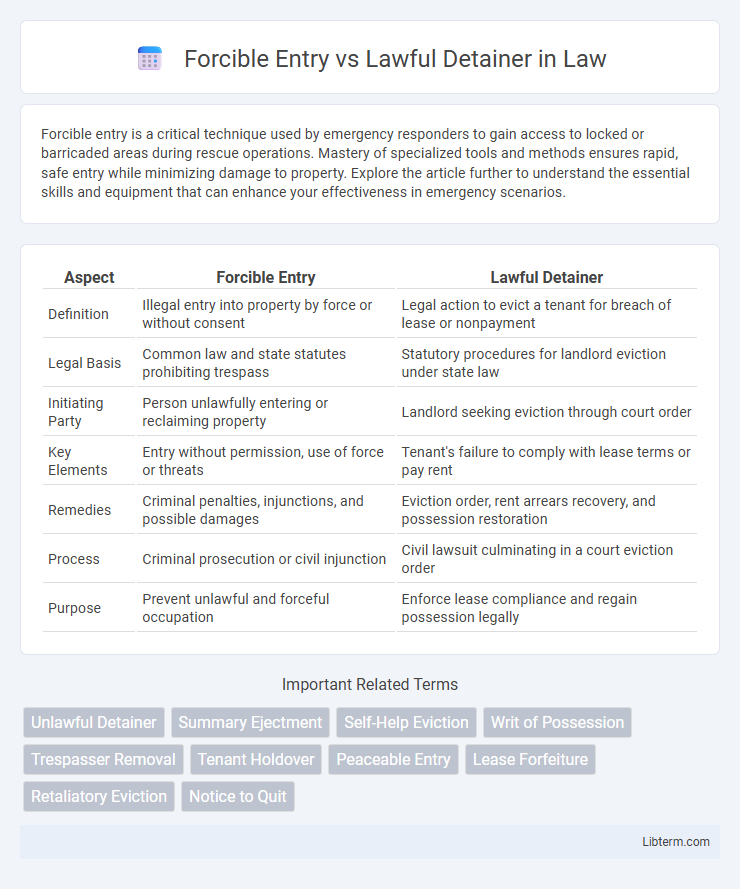
| Aspect | Forcible Entry | Lawful Detainer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Illegal entry into property by force or without consent | Legal action to evict a tenant for breach of lease or nonpayment |
| Legal Basis | Common law and state statutes prohibiting trespass | Statutory procedures for landlord eviction under state law |
| Initiating Party | Person unlawfully entering or reclaiming property | Landlord seeking eviction through court order |
| Key Elements | Entry without permission, use of force or threats | Tenant's failure to comply with lease terms or pay rent |
| Remedies | Criminal penalties, injunctions, and possible damages | Eviction order, rent arrears recovery, and possession restoration |
| Process | Criminal prosecution or civil injunction | Civil lawsuit culminating in a court eviction order |
| Purpose | Prevent unlawful and forceful occupation | Enforce lease compliance and regain possession legally |
Understanding Forcible Entry: Definition and Legal Implications
Forcible entry refers to the unlawful act of taking possession of property by using force, threats, or intimidation without legal authority or a court order. The legal implications of forcible entry include potential criminal charges, eviction invalidity, and possible civil liability for damages caused during the forced entry. Understanding the distinction between forcible entry and lawful detainer is crucial, as lawful detainer involves a landlord's legal eviction process following a court judgment, whereas forcible entry circumvents legal protocols, leading to serious legal consequences.
Lawful Detainer Explained: Rights of Landlords and Tenants
Lawful detainer is a legal process that allows landlords to regain possession of their property following a tenant's violation of lease terms or nonpayment of rent. Landlords must follow specific court procedures to evict tenants lawfully, protecting tenants' rights to due process and ensuring notices are properly served. Tenants have the right to contest evictions in court, present defenses such as improper notice or compliance with lease terms, and request additional time to vacate the premises under certain circumstances.
Key Differences Between Forcible Entry and Lawful Detainer
Forcible entry involves the illegal act of unlawfully taking possession of a property by force or without legal right, typically before the rightful owner has initiated eviction proceedings. Lawful detainer is a legal process used by landlords to regain possession of a property after a tenant has violated lease terms or failed to pay rent. Key differences include that forcible entry is an immediate, unauthorized act, while lawful detainer requires formal court authorization and due process.
Legal Procedures for Addressing Forcible Entry
Forcible entry involves unlawfully taking possession of property without the landlord's consent, often requiring immediate legal intervention. Legal procedures for addressing forcible entry typically include filing a complaint with the court, obtaining an injunction or restraining order, and pursuing eviction through formal judicial channels. Courts emphasize prompt action to prevent landlords or tenants from using force to resolve property disputes outside the legal framework.
Steps Involved in Lawful Detainer Proceedings
Lawful detainer proceedings begin with the landlord serving a written notice to the tenant, specifying the reason for eviction and the timeframe to remedy the issue or vacate the property. If the tenant fails to comply, the landlord files a complaint with the court, followed by a summons served to the tenant, compelling their appearance at a hearing. During the hearing, both parties present evidence and arguments before the judge issues a decision on possession and potential eviction enforcement.
Common Grounds for Filing Forcible Entry Cases
Forcible entry cases typically involve tenants who unlawfully occupy property by force or without legal right, such as breaking locks or refusing to vacate after lease termination. Common grounds for filing a forcible entry case include illegal possession, eviction without notice, or using violence or threats to maintain occupancy. These cases aim to restore possession to the rightful owner or landlord, distinguishing them from lawful detainer actions, which focus on rent arrears or lease violations under a valid tenancy.
When is a Lawful Detainer Suit Appropriate?
A Lawful Detainer suit is appropriate when a landlord seeks to regain possession of real property due to a tenant's failure to comply with the lease terms, such as nonpayment of rent or lease expiration. This legal action follows proper notice requirements, distinguishing it from forcible entry, which involves unlawful or violent attempts to reclaim property without court intervention. Lawful Detainer ensures eviction occurs through a court order, protecting tenants' rights and maintaining due process.
Evidentiary Requirements in Forcible Entry and Lawful Detainer
Forcible entry cases require the plaintiff to provide clear evidence of actual physical possession and an unlawful dispossession of the property, often supported by affidavits or witness testimonies showing force or intimidation. In lawful detainer actions, the primary evidentiary requirement is the presentation of a valid lease or rental agreement, proof of the tenant's failure to comply with lease terms, and proper notice of termination or eviction. Courts demand strict compliance with procedural rules in both cases to establish rightful possession and justify eviction.
Remedies and Penalties: Outcomes of Court Decisions
Forcible entry cases typically result in remedies such as immediate eviction and restoration of possession to the lawful occupant, with penalties including fines or criminal charges for unlawful entry. Lawful detainer actions focus on judicial orders for eviction after proper notice, emphasizing monetary damages or back rent owed, with penalties often limited to civil enforcement. Court decisions in forcible entry prioritize protecting property rights against illegal intrusions, whereas lawful detainer rulings balance tenant protections and landlord claims for recovery of possession and unpaid rent.
Preventive Measures Against Unlawful Dispossession
Forcible entry involves taking possession of property without legal right, often leading to immediate eviction, while a lawful detainer is a legal process used by landlords to remove tenants through court orders. Preventive measures against unlawful dispossession include securing written lease agreements, promptly addressing rental disputes, and maintaining thorough documentation of payments and communications. Implementing these strategies helps protect tenants' rights and reduces the risk of abrupt, illegal eviction actions.
Forcible Entry Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com