Lump sum alimony involves a one-time payment made by one spouse to the other instead of ongoing monthly support, offering financial closure after divorce. This arrangement can simplify budgeting and reduce future conflicts by clearly defining obligations upfront. Discover how lump sum alimony might fit Your situation and the key factors to consider in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
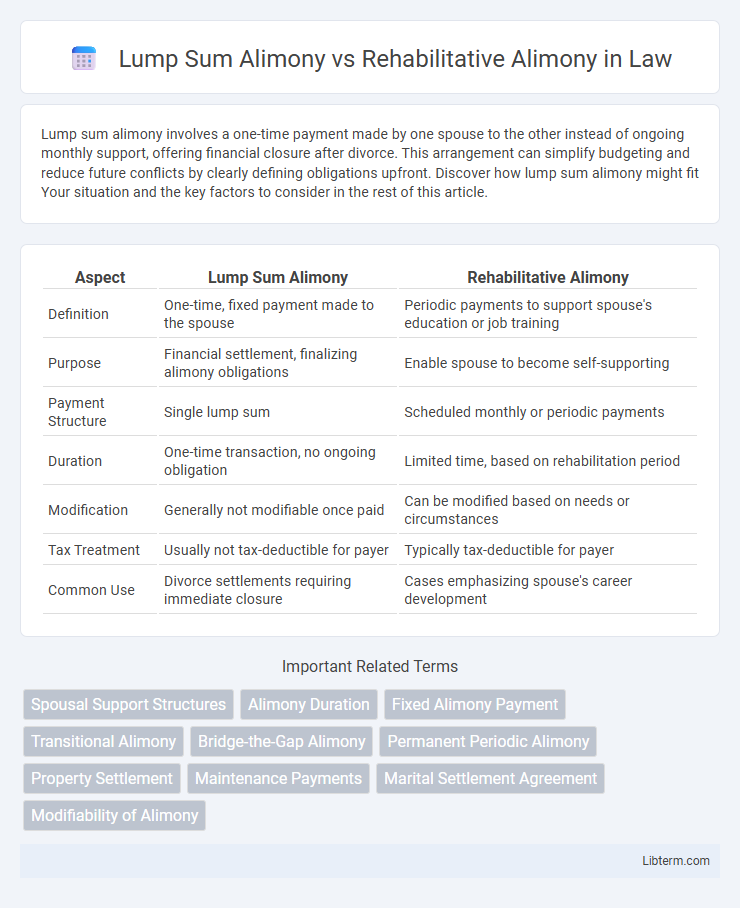
| Aspect | Lump Sum Alimony | Rehabilitative Alimony |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | One-time, fixed payment made to the spouse | Periodic payments to support spouse's education or job training |
| Purpose | Financial settlement, finalizing alimony obligations | Enable spouse to become self-supporting |
| Payment Structure | Single lump sum | Scheduled monthly or periodic payments |
| Duration | One-time transaction, no ongoing obligation | Limited time, based on rehabilitation period |
| Modification | Generally not modifiable once paid | Can be modified based on needs or circumstances |
| Tax Treatment | Usually not tax-deductible for payer | Typically tax-deductible for payer |
| Common Use | Divorce settlements requiring immediate closure | Cases emphasizing spouse's career development |
Introduction to Lump Sum and Rehabilitative Alimony
Lump sum alimony involves a one-time payment that settles spousal support obligations in full, often used to provide immediate financial security or to simplify divorce settlements. Rehabilitative alimony, on the other hand, provides temporary financial support aimed at helping the recipient spouse gain education, training, or skills to become self-supporting. Understanding the distinctions between these alimony types is essential for effectively negotiating financial arrangements during divorce proceedings.
Defining Lump Sum Alimony
Lump sum alimony is a one-time, fixed payment made from one spouse to the other, settling all future support obligations at once. This type of alimony is often used to provide financial security without ongoing payments, simplifying legal and financial arrangements. Unlike rehabilitative alimony, which supports the recipient's efforts to become self-sufficient, lump sum alimony is a final, non-modifiable settlement.
Understanding Rehabilitative Alimony
Rehabilitative alimony provides temporary financial support aimed at helping the recipient spouse gain education, training, or employment skills to become self-sufficient. This type of alimony typically has a set duration based on the time needed for rehabilitation and focuses on promoting long-term independence. Unlike lump sum alimony, which is a fixed, one-time payment, rehabilitative alimony is paid periodically and can be modified if circumstances change.
Key Differences Between Lump Sum and Rehabilitative Alimony
Lump sum alimony involves a fixed, one-time payment or set of payments that fully satisfies the obligation, providing immediate financial closure without ongoing court oversight. Rehabilitative alimony offers periodic payments designed to support the recipient while they gain education, training, or work skills to become self-sufficient, typically with a defined duration. Key differences include payment structure--lump sum is upfront and final, whereas rehabilitative is temporary and contingent on the recipient's progress toward financial independence.
Eligibility Criteria for Each Alimony Type
Eligibility for lump sum alimony typically requires one spouse to demonstrate significant financial need and the other spouse's ability to pay a fixed amount upfront or over a set period, often used when the paying spouse has substantial assets. Rehabilitative alimony eligibility depends on the recipient's need for financial support during a transition period to gain education, training, or employment, emphasizing temporary assistance until economic self-sufficiency is achieved. Courts evaluate factors such as income disparity, length of marriage, and the recipient's workforce readiness to determine the appropriate alimony type.
Financial Implications and Tax Considerations
Lump sum alimony provides a one-time, fixed payment, offering financial predictability but no ongoing income, while rehabilitative alimony supplies periodic payments aimed at supporting the recipient's return to financial independence. Lump sum alimony is typically non-taxable to the recipient and not deductible by the payer under IRS rules, whereas rehabilitative alimony payments are treated as taxable income for the recipient and deductible for the payer. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective financial planning and tax compliance in divorce settlements.
Benefits of Lump Sum Alimony
Lump sum alimony provides financial certainty by delivering a fixed, one-time payment that eliminates ongoing obligations and reduces future conflicts between parties. This form of alimony protects the recipient from potential changes in the payer's income or financial stability, ensuring immediate access to funds for essential needs such as housing, education, or healthcare. Courts often favor lump sum alimony when the payor has sufficient assets and the recipient requires a definitive financial arrangement for post-divorce independence.
Advantages of Rehabilitative Alimony
Rehabilitative alimony provides financial support for a limited period, allowing the recipient spouse to gain education, job training, or work experience necessary to become self-sufficient. It encourages personal development and long-term independence without imposing permanent financial obligations on the payer. This form of alimony is adaptable, aligning with changing circumstances and promoting fairness in spousal support arrangements.
Factors Courts Consider When Awarding Alimony
Courts consider factors such as the length of the marriage, the financial needs and earning capacities of both spouses, and the standard of living established during the marriage when awarding lump sum or rehabilitative alimony. Lump sum alimony is often awarded when a clean break is possible, while rehabilitative alimony focuses on supporting the recipient's education or job training to achieve financial independence. The court also evaluates the age, health, and contributions of each spouse to determine the appropriate type and amount of alimony.
Choosing the Right Alimony for Your Situation
Lump sum alimony provides a one-time, fixed payment that settles spousal support obligations, ideal for those seeking finality and no ongoing financial ties. Rehabilitative alimony offers temporary payments aimed at helping the recipient gain financial independence through education or job training, suited for individuals who are expected to become self-supporting. Choosing the right alimony depends on factors like the length of the marriage, recipient's employment prospects, and both parties' financial stability and goals.
Lump Sum Alimony Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com