Access to legal aid ensures that individuals facing financial difficulties can obtain crucial legal representation and advice, leveling the playing field in complex legal proceedings. Understanding your eligibility and the scope of services provided by legal aid organizations can help you secure the support needed during challenging legal situations. Explore the full article to learn how legal aid can protect your rights and guide you through the justice system effectively.
Table of Comparison
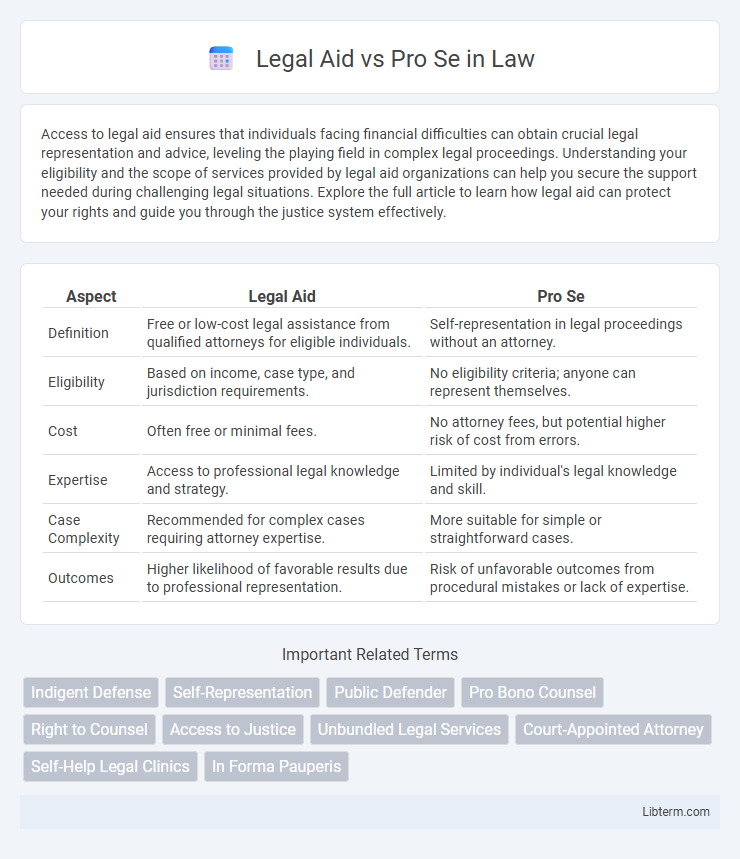
| Aspect | Legal Aid | Pro Se |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Free or low-cost legal assistance from qualified attorneys for eligible individuals. | Self-representation in legal proceedings without an attorney. |
| Eligibility | Based on income, case type, and jurisdiction requirements. | No eligibility criteria; anyone can represent themselves. |
| Cost | Often free or minimal fees. | No attorney fees, but potential higher risk of cost from errors. |
| Expertise | Access to professional legal knowledge and strategy. | Limited by individual's legal knowledge and skill. |
| Case Complexity | Recommended for complex cases requiring attorney expertise. | More suitable for simple or straightforward cases. |
| Outcomes | Higher likelihood of favorable results due to professional representation. | Risk of unfavorable outcomes from procedural mistakes or lack of expertise. |
Understanding Legal Aid: Definition and Purpose
Legal aid provides professional legal assistance to individuals unable to afford private representation, ensuring access to justice. It encompasses services such as legal advice, representation, and support in civil, criminal, and family law cases. The primary purpose of legal aid is to promote fairness by bridging the gap between disadvantaged populations and the legal system.
What Does Pro Se Representation Mean?
Pro se representation means a person represents themselves in court without hiring an attorney, managing all legal procedures independently. This approach requires understanding court rules, filing documents correctly, and advocating effectively during hearings. Legal aid provides professional assistance to those who cannot afford lawyers, whereas pro se relies solely on the individual's knowledge and skills.
Key Differences Between Legal Aid and Pro Se
Legal Aid involves professional legal assistance provided by qualified attorneys, often funded by government or nonprofit organizations, aimed at individuals who cannot afford private counsel. Pro Se representation means a litigant representing themselves in court without a lawyer, bearing full responsibility for understanding and applying legal procedures and rules. Key differences include the level of expertise, access to legal resources, and the potential impact on case outcomes, as Legal Aid offers skilled advocacy while Pro Se demands significant self-education and preparation.
Pros and Cons of Legal Aid Services
Legal aid services provide crucial access to professional legal representation for low-income individuals, enhancing their chances of a favorable outcome in complex legal matters. However, these services often face limitations such as strict eligibility requirements, limited funding, and high caseloads that can affect the quality and timeliness of assistance. While legal aid ensures expert guidance and reduces the risk of procedural errors, the scarcity of resources may lead to delays and restricted coverage compared to self-representation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Going Pro Se
Going pro se allows individuals to save on legal fees, gaining direct control over their case strategy and decisions. However, lack of legal expertise can lead to procedural errors, weaker arguments, and potentially unfavorable outcomes. Courts may show some leniency toward pro se litigants, but the complexity of legal rules often places them at a significant disadvantage compared to those with professional legal representation.
Eligibility Criteria for Legal Aid
Legal aid eligibility criteria typically require applicants to demonstrate low income, limited assets, and case merit related to civil, criminal, or family law matters. Applicants often must complete a financial assessment, providing proof of income such as pay stubs, tax returns, and bank statements to qualify for legal representation at reduced or no cost. Eligibility may also consider the complexity of the case and whether legal aid resources are available, differentiating from pro se representation, where individuals handle their own cases without legal assistance.
When Should You Consider Pro Se Representation?
Consider pro se representation when your case is straightforward, such as small claims or uncontested divorces, where legal procedures are simpler and easier to navigate without formal counsel. It is advisable if you have a strong understanding of the relevant laws and court rules, and if the potential costs of hiring a lawyer outweigh the benefits. Pro se is also suitable when financial constraints limit access to legal aid or private attorneys, but be aware of potential risks including procedural errors and lack of legal expertise.
Common Legal Issues Handled by Legal Aid
Legal Aid organizations primarily handle common legal issues such as family law matters, including divorce and child custody, housing disputes like eviction prevention, and public benefits cases involving welfare or disability claims. They provide essential support for civil cases where individuals lack financial resources to hire private attorneys. Access to Legal Aid improves outcomes in complex legal situations by offering expert guidance, unlike Pro Se representation where individuals represent themselves without professional legal assistance.
Success Rates: Legal Aid vs Pro Se
Legal Aid clients experience higher success rates compared to those representing themselves Pro Se, with studies showing up to a 40% increase in favorable outcomes. Legal Aid offers professional expertise in navigating complex legal procedures, which significantly enhances case preparation and argument effectiveness. Pro Se litigants often face challenges due to limited legal knowledge, resulting in lower success rates and increased likelihood of procedural errors.
Choosing the Right Path: Legal Aid or Pro Se?
Choosing between legal aid and proceeding pro se depends largely on the complexity of the case and the individual's financial situation. Legal aid offers access to professional attorneys for low-income individuals, ensuring expert representation and better chances of favorable outcomes, especially in complicated legal matters like family law or criminal defense. Pro se representation, where individuals navigate the legal system without a lawyer, suits simple cases or those with limited resources but carries risks of procedural errors and less effective advocacy.
Legal Aid Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com