Maintaining confidentiality protects sensitive information from unauthorized access and preserves trust in personal and professional relationships. Effective confidentiality measures include secure data handling, limited information sharing, and compliance with privacy regulations. Discover how to safeguard your data and uphold confidentiality by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
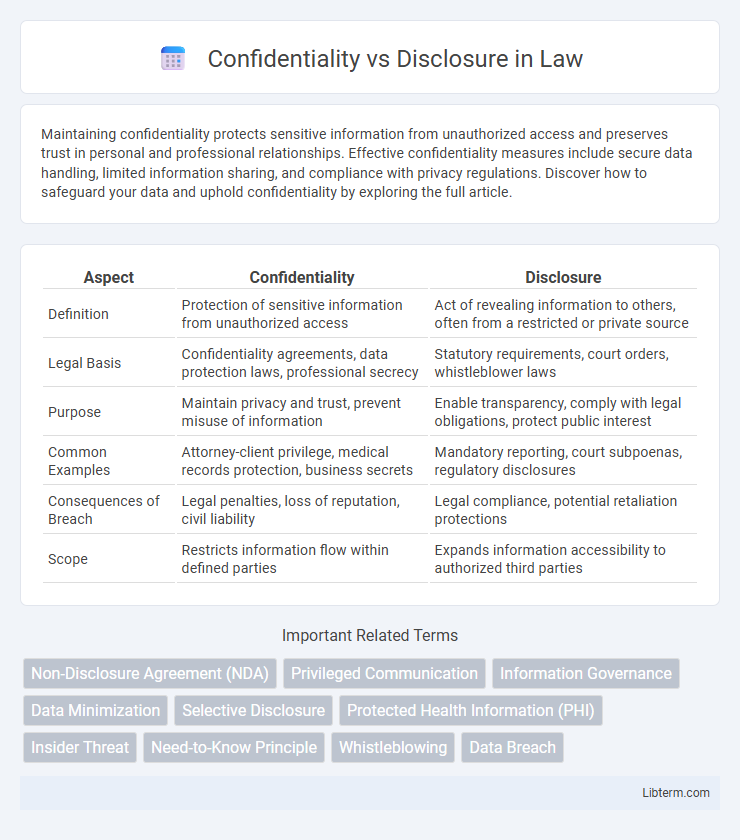
| Aspect | Confidentiality | Disclosure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Protection of sensitive information from unauthorized access | Act of revealing information to others, often from a restricted or private source |
| Legal Basis | Confidentiality agreements, data protection laws, professional secrecy | Statutory requirements, court orders, whistleblower laws |
| Purpose | Maintain privacy and trust, prevent misuse of information | Enable transparency, comply with legal obligations, protect public interest |
| Common Examples | Attorney-client privilege, medical records protection, business secrets | Mandatory reporting, court subpoenas, regulatory disclosures |
| Consequences of Breach | Legal penalties, loss of reputation, civil liability | Legal compliance, potential retaliation protections |
| Scope | Restricts information flow within defined parties | Expands information accessibility to authorized third parties |
Understanding Confidentiality: Core Principles
Confidentiality ensures sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access, maintaining trust and privacy in personal and professional contexts. Core principles include limiting information sharing to authorized individuals, safeguarding data through encryption and secure storage, and adhering to legal and ethical standards. Understanding these principles helps organizations and individuals prevent data breaches, comply with regulations like GDPR, and uphold ethical responsibilities.
What Constitutes Disclosure?
Disclosure constitutes the act of revealing or sharing confidential information to unauthorized parties, whether intentionally or accidentally. It includes verbal, written, or electronic communication that exposes sensitive data such as personal identities, trade secrets, or proprietary business information. Legal frameworks like GDPR and HIPAA strictly regulate disclosure to protect individual privacy and organizational security.
Legal Implications of Confidentiality
Confidentiality holds critical legal significance, mandating that sensitive information must be protected to prevent unauthorized disclosure, which can result in legal penalties, contractual liabilities, and reputational damage. Breaches of confidentiality laws, such as those outlined in GDPR or HIPAA, can lead to costly lawsuits, regulatory fines, and loss of client trust. Organizations must implement robust confidentiality agreements and data protection policies to ensure compliance and mitigate the risk of legal repercussions associated with improper disclosure.
Ethical Considerations in Disclosure
Ethical considerations in disclosure revolve around balancing the duty to maintain confidentiality with the need to protect others from harm. Professionals must assess the potential risks and benefits of revealing sensitive information, ensuring that disclosure is justified, minimal, and carried out with respect for the individual's privacy rights. Upholding ethical standards requires transparent decision-making, adherence to legal regulations, and prioritizing the well-being of all parties involved.
Comparing Confidentiality and Disclosure: Key Differences
Confidentiality involves protecting sensitive information by restricting access to authorized individuals, ensuring privacy and data security. Disclosure refers to the act of making information available to others, either voluntarily or legally mandated, which can lead to sharing confidential data under specific circumstances. The key difference lies in confidentiality's emphasis on safeguarding information, while disclosure emphasizes transparency and information sharing.
Situations Where Confidentiality is Compromised
Confidentiality is compromised in situations involving data breaches, unauthorized access, or insider threats where sensitive information is exposed without consent. Legal obligations such as court orders or mandatory reporting requirements may also force disclosure despite confidentiality agreements. Security vulnerabilities and human error often lead to inadvertent leaks, increasing risks to privacy and organizational trust.
When is Disclosure Necessary or Required?
Disclosure becomes necessary when legal obligations arise, such as in cases involving court orders, mandatory reporting laws, or regulatory compliance requirements. Confidential information must be disclosed to authorized parties when there is an imminent risk of harm, fraud, or criminal activity that requires intervention. Ethical guidelines also mandate disclosure when protecting public safety or preventing significant damage outweighs the duty of confidentiality.
Balancing the Rights: Protecting Information vs Public Interest
Balancing confidentiality and disclosure requires carefully protecting sensitive information while addressing the public interest in transparency and accountability. Legal frameworks like data protection laws and whistleblower statutes establish boundaries that safeguard personal or proprietary data yet permit disclosure when public safety or ethical concerns arise. Effective policies prioritize minimal necessary disclosure, ensuring both individual privacy rights and societal benefits are respected.
Best Practices for Maintaining Confidentiality
Implementing role-based access controls ensures that sensitive information is only accessible to authorized personnel, reducing the risk of unintended disclosure. Utilizing encryption for data both at rest and in transit safeguards confidentiality against cyber threats and unauthorized interception. Regular employee training on data privacy policies and secure communication protocols reinforces best practices for maintaining confidentiality in organizational environments.
Navigating Confidentiality and Disclosure in the Digital Age
Navigating confidentiality and disclosure in the digital age requires robust data protection strategies and compliance with privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. Organizations must implement encryption, access controls, and secure communication channels to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Balancing transparency and confidentiality involves clear policies on data sharing and informed consent to maintain trust and legal integrity in digital interactions.
Confidentiality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com