A waiver is a legal document that voluntarily relinquishes a known right or claim, often used to prevent liability in various agreements. Understanding the implications and proper use of waivers can protect you from potential legal disputes and ensure that your rights are clearly defined. Explore the full article to learn how waivers function and when you should consider using one.
Table of Comparison
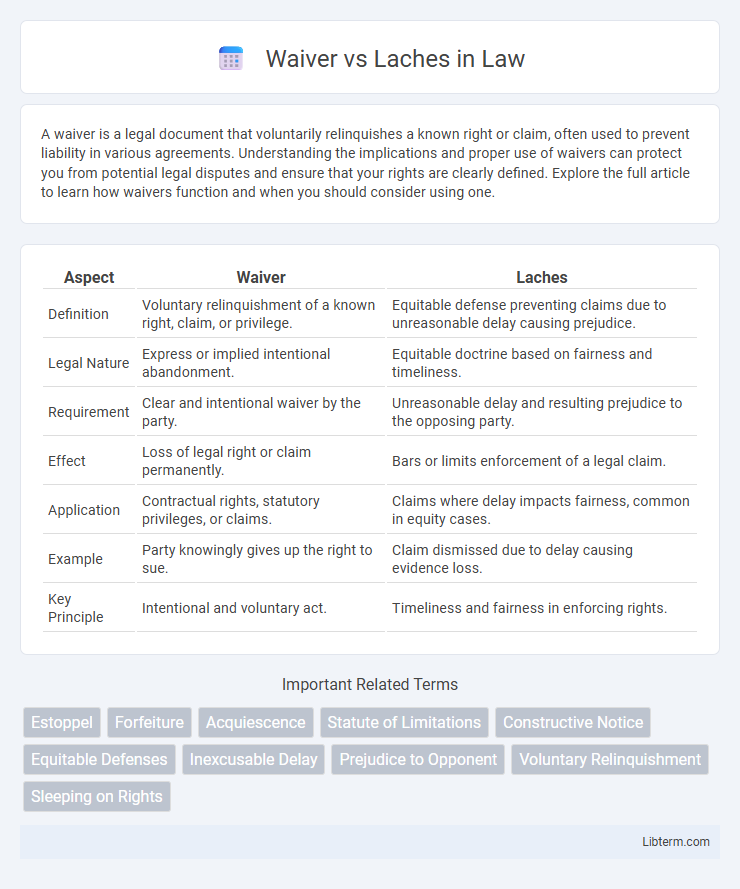
| Aspect | Waiver | Laches |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voluntary relinquishment of a known right, claim, or privilege. | Equitable defense preventing claims due to unreasonable delay causing prejudice. |
| Legal Nature | Express or implied intentional abandonment. | Equitable doctrine based on fairness and timeliness. |
| Requirement | Clear and intentional waiver by the party. | Unreasonable delay and resulting prejudice to the opposing party. |
| Effect | Loss of legal right or claim permanently. | Bars or limits enforcement of a legal claim. |
| Application | Contractual rights, statutory privileges, or claims. | Claims where delay impacts fairness, common in equity cases. |
| Example | Party knowingly gives up the right to sue. | Claim dismissed due to delay causing evidence loss. |
| Key Principle | Intentional and voluntary act. | Timeliness and fairness in enforcing rights. |
Introduction to Waiver and Laches
Waiver refers to the intentional relinquishment of a known right, often demonstrated through explicit actions or conduct indicating consent to forgo a claim or defense. Laches is an equitable doctrine preventing a party from asserting a claim due to an unreasonable delay in pursuing it, which causes prejudice to the opposing party. Both waiver and laches function as defenses in legal disputes, with waiver focusing on voluntary surrender of rights and laches emphasizing the detrimental effect of untimely enforcement.
Definition of Waiver
Waiver is the intentional relinquishment or abandonment of a known right, claim, or privilege, typically expressed through an explicit statement or conduct indicating the decision to forgo legal enforcement. It involves a voluntary and informed choice by the party holding the right, which results in the loss of the ability to assert that right in future disputes. Unlike laches, which is an equitable defense based on unreasonable delay in asserting a right, waiver centers on the deliberate consent to waive a legal entitlement.
Definition of Laches
Laches is an equitable defense in legal proceedings that bars a claim when a plaintiff unreasonably delays enforcing a right, causing prejudice to the defendant. Unlike waiver, which involves an intentional relinquishment of a known right, laches arises from neglect or inactivity over a period, making it unjust to grant relief. Courts apply laches to prevent unfairness resulting from stale claims where evidence may have been lost or memories faded.
Key Differences Between Waiver and Laches
Waiver involves the intentional relinquishment of a known right, often demonstrated through explicit or implicit actions, whereas laches is an equitable defense based on unreasonable delay in asserting a right, causing prejudice to the opposing party. The key difference lies in waiver being a voluntary and conscious act, while laches depends on the passage of time and the circumstances affecting fairness. Waiver generally requires clear evidence of intent, whereas laches requires proof of both delay and resulting harm.
Legal Elements of Waiver
Waiver involves the intentional relinquishment of a known right, requiring clear evidence of the party's voluntary and informed decision to forgo legal claims or defenses. The legal elements include the existence of a known right, the intentional and unequivocal act of relinquishment, and the knowledge of the right being waived. Unlike laches, which is an equitable defense based on unreasonable delay and prejudice, waiver focuses on the party's deliberate surrender of rights.
Legal Elements of Laches
Laches requires a plaintiff's unreasonable delay in asserting a right or claim, coupled with prejudice to the defendant due to that delay. The key legal elements include a detrimental delay that lacks a valid excuse and resulting harm to the opposing party's ability to defend or enforce their rights. This equitable doctrine prevents enforcement of rights when timing undermines fairness, distinguishing it from waiver, which involves intentional relinquishment of a known right.
Common Examples of Waiver in Law
Waiver commonly occurs when a party intentionally relinquishes a known right, such as a landlord accepting late rent without penalty or a tenant disregarding a lease violation without objection. In contract law, waiver is often seen when a party knowingly forgoes a contractual clause, like agreeing to partial performance without demanding full compliance. These examples highlight intentional forfeiture of legal rights, distinguishing waiver from laches, which involves unreasonable delay causing prejudice.
Common Examples of Laches in Law
Laches commonly arises in property disputes where a claimant delays asserting rights to a land claim, causing prejudice to the defendant. It also frequently appears in contract cases when a party waits excessively before enforcing contractual rights, leading to evidentiary challenges or changed circumstances. Trademark infringement suits often invoke laches when the trademark owner delays action, resulting in loss of enforceability due to harmful reliance by the alleged infringer.
Impact of Waiver vs Laches on Legal Proceedings
Waiver involves the intentional relinquishment of a known right, which can prevent a party from later asserting that right in legal proceedings, thereby directly impacting the enforceability of claims or defenses. Laches, on the other hand, is an equitable defense based on unreasonable delay in asserting a right, causing prejudice to the opposing party, and can lead to dismissal of claims even if the right exists. The impact of waiver is primarily procedural and based on consent, while laches affects the court's equitable discretion, influencing case outcomes through considerations of fairness and timeliness.
Choosing the Appropriate Defense: Waiver or Laches
Choosing the appropriate defense between waiver and laches requires understanding their distinct legal applications: waiver involves the intentional relinquishment of a known right, while laches is based on an unreasonable delay causing prejudice to the defendant. In cases where a party knowingly gives up a contractual right, waiver is the preferred defense due to its emphasis on explicit consent or conduct. When the issue centers on delayed enforcement leading to unfair disadvantage, courts often apply laches to deny relief, prioritizing equity and timeliness in litigation.
Waiver Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com