A defendant is an individual, company, or entity accused of wrongdoing in a legal case and required to respond to the plaintiff's claims in court. Understanding the rights and responsibilities of a defendant is crucial for navigating the legal process effectively. Explore the rest of the article to learn how being a defendant can impact your legal strategy and outcomes.
Table of Comparison
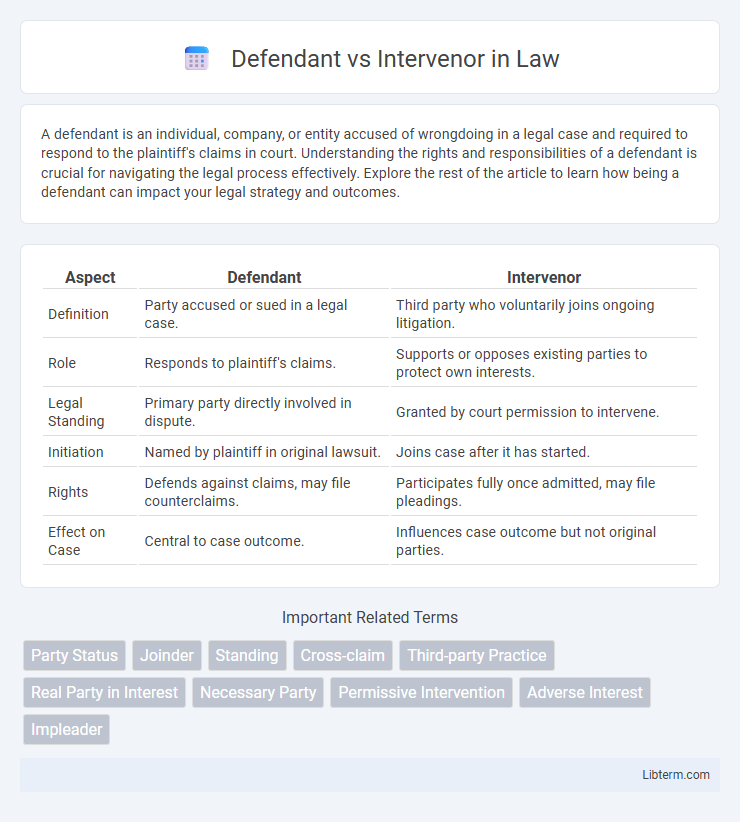
| Aspect | Defendant | Intervenor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Party accused or sued in a legal case. | Third party who voluntarily joins ongoing litigation. |
| Role | Responds to plaintiff's claims. | Supports or opposes existing parties to protect own interests. |
| Legal Standing | Primary party directly involved in dispute. | Granted by court permission to intervene. |
| Initiation | Named by plaintiff in original lawsuit. | Joins case after it has started. |
| Rights | Defends against claims, may file counterclaims. | Participates fully once admitted, may file pleadings. |
| Effect on Case | Central to case outcome. | Influences case outcome but not original parties. |
Understanding the Defendant in Legal Proceedings
The defendant is the party against whom a lawsuit is filed, responsible for responding to the plaintiff's claims in a court of law. Unlike an intervenor, who voluntarily joins an ongoing lawsuit to protect their interests, the defendant is directly named in the complaint and must defend against allegations. Understanding the defendant's role is essential for grasping the dynamics of legal liability and procedural rights in civil and criminal cases.
Who is an Intervenor in a Lawsuit?
An intervenor in a lawsuit is a third party who voluntarily enters an ongoing legal dispute to protect their own interests that may be affected by the court's decision. Unlike the defendant, who is originally named in the lawsuit and responds to the plaintiff's claims, the intervenor seeks permission from the court to join the case to assert rights or claims related to the subject matter. Courts typically require that the intervenor demonstrates a significant legal interest in the outcome, distinguishing their involvement from mere bystanders.
Key Differences: Defendant vs Intervenor
A defendant is a party accused or sued in a legal proceeding, required to respond to the plaintiff's claims, while an intervenor is a third party who voluntarily joins an ongoing lawsuit due to a significant interest in the outcome. Defendants have direct stakes and obligations in the case, including answering complaints and presenting defenses, whereas intervenors must seek court permission to participate and typically aim to protect their legal rights without initiating claims. Key differences lie in their procedural roles, with defendants as primary parties and intervenors as secondary participants influencing litigation from an ancillary position.
Legal Rights of Defendants
Defendants hold the fundamental legal right to receive notice of charges and a fair trial with due process protections, including the right to legal representation and the opportunity to present evidence and counterarguments. They have the right to challenge the plaintiff's claims, cross-examine witnesses, and appeal adverse decisions. Unlike intervenors, whose involvement is limited to supporting an existing party's position, defendants carry the primary burden of responding to allegations and defending their legal interests throughout the litigation.
Legal Rights of Intervenors
Intervenors possess specific legal rights allowing them to join ongoing litigation to protect their interests without initiating separate lawsuits. They can present evidence, file motions, and participate in hearings, ensuring their perspective is considered alongside the defendant and plaintiff. Courts grant intervenors these rights when their interests may be impaired by the case's outcome, safeguarding due process and equitable participation.
Procedures for Adding an Intervenor to a Case
Procedures for adding an intervenor to a case typically involve filing a motion to intervene, which must demonstrate the intervenor's interest in the subject matter and how it may be affected by the outcome. Courts consider factors such as timeliness, potential prejudice to the original parties, and the adequacy of the existing representation before allowing intervention. Unlike defendants who are originally named parties, intervenors join the litigation midstream to protect specific rights or interests related to the case.
Roles and Responsibilities: Defendant vs Intervenor
The defendant is the party against whom a legal action is brought, responsible for responding to the plaintiff's claims and defending their position in court. An intervenor voluntarily enters an ongoing lawsuit with the court's permission to protect their own interests, often providing additional information or perspectives relevant to the case. While defendants bear the primary responsibility for addressing the claims, intervenors support or oppose the parties' arguments without initiating a new lawsuit.
Impact on Case Outcomes: Defendants and Intervenors
Defendants directly influence case outcomes by responding to claims and presenting defenses, which shape the court's judgment and potential liability. Intervenors, while not original parties, impact outcomes by introducing additional perspectives or evidence, often supporting one side and potentially altering the case's scope or results. The presence of intervenors can complicate litigation dynamics, affecting legal strategies and judicial decisions.
Common Scenarios Involving Intervenors in Litigation
Common scenarios involving intervenors in litigation often arise when a third party claims a direct interest in the case's outcome, such as in environmental lawsuits where advocacy groups seek to protect natural resources. Intervenors frequently appear in government-related cases, like regulatory disputes, where they advocate for public policies or industry standards. Courts allow intervention to ensure all relevant perspectives and rights are considered, balancing interests beyond those of the original plaintiff and defendant.
Strategic Considerations for Defendants and Intervenors
Defendants strategically evaluate the risks and benefits of allowing or opposing intervention based on potential impacts on case outcomes, resource allocation, and control over legal arguments. Intervenors must assess their interest alignment with existing parties while ensuring their involvement strengthens their position without complicating litigation or introducing conflicting defenses. Both defendants and intervenors consider judicial efficiency, the likelihood of influencing verdicts, and preservation of legal rights when deciding intervention tactics.
Defendant Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com