A negotiated settlement resolves disputes by agreement between parties, avoiding lengthy litigation and reducing costs. This method promotes collaborative problem-solving and ensures both sides have input in the final terms. Explore the rest of the article to understand how a negotiated settlement can benefit your specific situation.
Table of Comparison
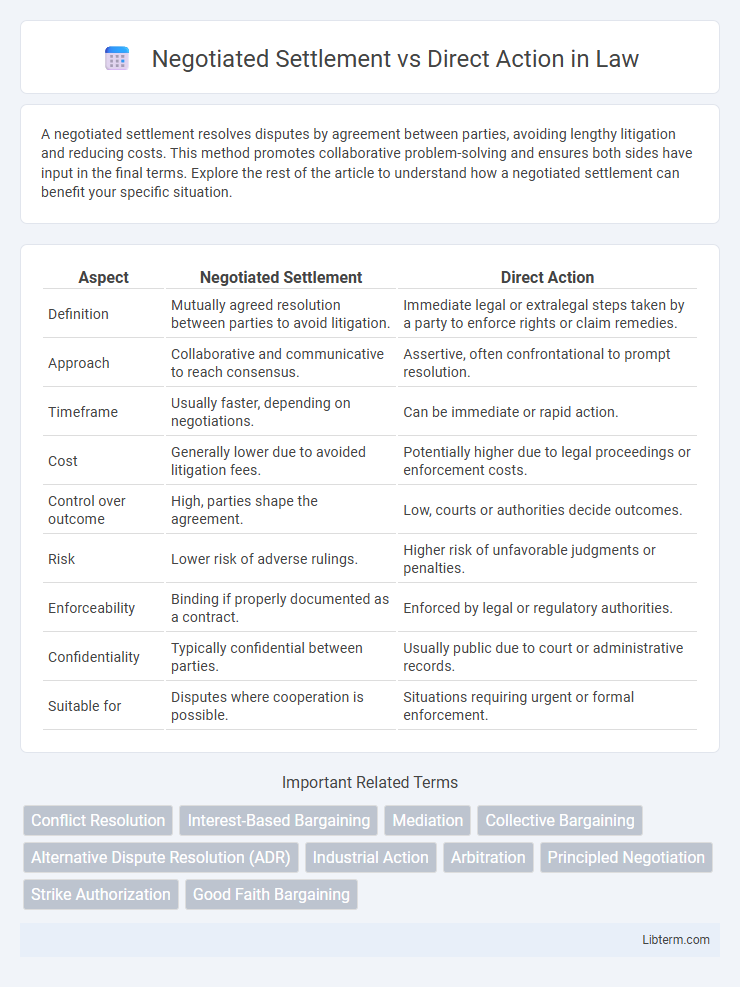
| Aspect | Negotiated Settlement | Direct Action |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mutually agreed resolution between parties to avoid litigation. | Immediate legal or extralegal steps taken by a party to enforce rights or claim remedies. |
| Approach | Collaborative and communicative to reach consensus. | Assertive, often confrontational to prompt resolution. |
| Timeframe | Usually faster, depending on negotiations. | Can be immediate or rapid action. |
| Cost | Generally lower due to avoided litigation fees. | Potentially higher due to legal proceedings or enforcement costs. |
| Control over outcome | High, parties shape the agreement. | Low, courts or authorities decide outcomes. |
| Risk | Lower risk of adverse rulings. | Higher risk of unfavorable judgments or penalties. |
| Enforceability | Binding if properly documented as a contract. | Enforced by legal or regulatory authorities. |
| Confidentiality | Typically confidential between parties. | Usually public due to court or administrative records. |
| Suitable for | Disputes where cooperation is possible. | Situations requiring urgent or formal enforcement. |
Understanding Negotiated Settlement
Understanding negotiated settlement involves recognizing it as a conflict resolution method where parties engage in dialogue to reach a mutually acceptable agreement without resorting to litigation. This approach emphasizes collaboration, communication, and compromise, often resulting in faster, cost-effective, and legally binding solutions. Key elements include voluntary participation, confidentiality, and the option to involve mediators or neutral third parties to facilitate the negotiation process.
Defining Direct Action
Direct Action involves individuals or groups taking immediate and confrontational measures, such as protests, strikes, or demonstrations, to achieve political or social goals without relying on intermediaries or formal negotiations. It bypasses traditional negotiation processes and seeks to directly influence decision-makers or public opinion through visible, often disruptive tactics. This approach contrasts with Negotiated Settlement, which relies on dialogue and compromise between conflicting parties to reach a mutually acceptable agreement.
Key Differences Between Negotiated Settlement and Direct Action
Negotiated settlement involves dialogue and compromise between disputing parties to reach a mutually agreeable solution, emphasizing collaboration and legal frameworks. Direct action, by contrast, includes protests, strikes, or other forms of assertive tactics aimed at exerting pressure without necessarily involving formal negotiation. Key differences lie in negotiation's reliance on communication and legal processes, whereas direct action employs immediate, often public measures to influence outcomes.
Pros and Cons of Negotiated Settlement
Negotiated settlements offer the advantage of preserving relationships by promoting cooperative dialogue and mutual agreement, often leading to faster and less costly resolutions compared to litigation or direct action. However, negotiated settlements may result in compromises that leave both parties partially dissatisfied and can sometimes lack enforceability if not properly structured. The process requires willingness from both parties to negotiate in good faith, which may not be feasible in highly adversarial or uncooperative disputes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Direct Action
Direct action offers the advantage of immediate impact and can compel swift responses from opposing parties without prolonged negotiations. However, it carries significant risks such as potential legal consequences, public backlash, and disruption to normal operations. The method may also lack the durability of negotiated settlements, which often result in more sustainable and mutually agreed-upon resolutions.
When to Choose Negotiated Settlement
Negotiated settlement is ideal when parties seek to preserve business relationships and avoid the costs and uncertainties of litigation. It is preferred in complex disputes where confidentiality is essential and when timely resolution is critical. This approach suits scenarios requiring customized solutions tailored to both parties' interests, fostering long-term collaboration.
Situations Favoring Direct Action
Situations favoring direct action include urgent conflicts where immediate resolution is necessary to prevent escalation or harm, such as labor strikes or public demonstrations demanding swift policy changes. Direct action tends to be effective when traditional negotiation methods have failed or when parties perceive negotiation as biased or insincere. It often applies in contexts where power imbalances exist, and stakeholders seek to leverage public visibility and pressure to achieve their goals.
Impact on Stakeholders: Settlement vs Action
Negotiated settlements often minimize disruption by involving stakeholders in collaborative problem-solving, preserving relationships and reducing uncertainty. Direct action can create immediate pressure on parties, potentially escalating conflicts and causing reputational or financial risks for stakeholders. The choice between settlement and direct action significantly affects stakeholder trust, operational continuity, and long-term cooperation.
Case Studies: Negotiated Settlement vs Direct Action
Case studies comparing negotiated settlements and direct action highlight distinct strategic outcomes in conflict resolution. Negotiated settlements often result in mutually acceptable agreements, preserving relationships and minimizing long-term costs, as seen in labor disputes like the 2008 Verizon contract negotiation. Direct action, exemplified by the 2019 General Motors strike, exerts immediate pressure to achieve rapid concessions but risks prolonged disruptions and strained relations.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider
Choosing between a negotiated settlement and direct action involves evaluating factors such as the complexity of the dispute, the willingness of parties to compromise, and time constraints. Negotiated settlements often save costs and preserve relationships by fostering cooperation, while direct action may be necessary in cases requiring immediate enforcement or where negotiations fail. Assessing the legal framework, potential outcomes, and long-term impacts ensures the right strategy is selected for effective dispute resolution.
Negotiated Settlement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com