A petition for prohibition is a legal request filed to seek the court's order to stop a particular action or proceeding, often used to prevent lower courts or authorities from exceeding their jurisdiction. It protects your rights by ensuring that unlawful acts or decisions are halted before causing irreversible harm. Explore the rest of this article to understand the process and significance of filing a petition for prohibition.
Table of Comparison
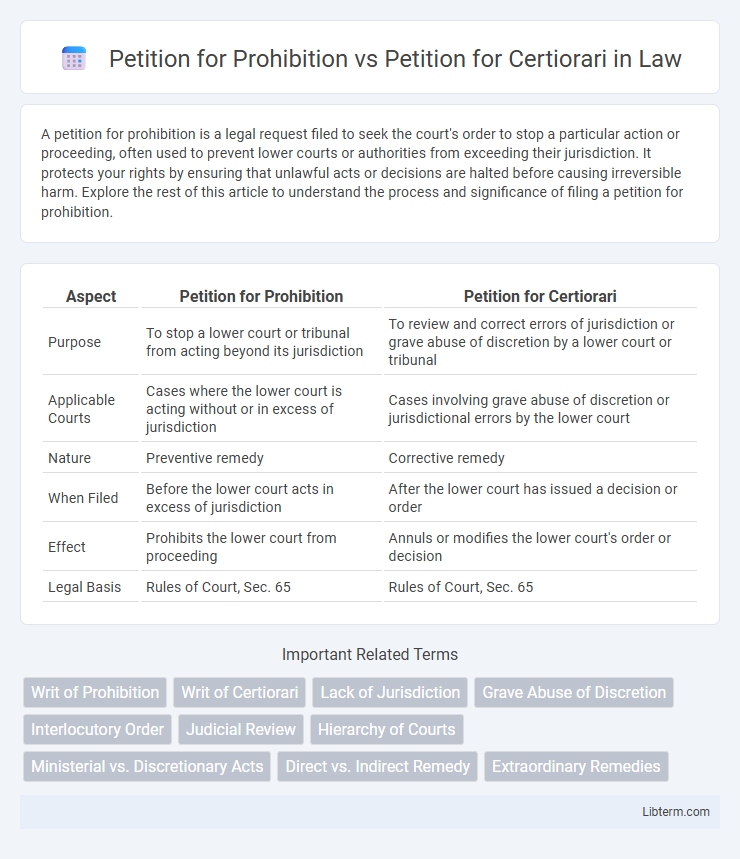
| Aspect | Petition for Prohibition | Petition for Certiorari |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To stop a lower court or tribunal from acting beyond its jurisdiction | To review and correct errors of jurisdiction or grave abuse of discretion by a lower court or tribunal |
| Applicable Courts | Cases where the lower court is acting without or in excess of jurisdiction | Cases involving grave abuse of discretion or jurisdictional errors by the lower court |
| Nature | Preventive remedy | Corrective remedy |
| When Filed | Before the lower court acts in excess of jurisdiction | After the lower court has issued a decision or order |
| Effect | Prohibits the lower court from proceeding | Annuls or modifies the lower court's order or decision |
| Legal Basis | Rules of Court, Sec. 65 | Rules of Court, Sec. 65 |
Definition of Petition for Prohibition
A Petition for Prohibition is a legal remedy filed to prevent an inferior court or tribunal from exceeding its jurisdiction or acting contrary to the rules of law. It serves as a preventive measure to stop unlawful proceedings or actions before they occur. This petition ensures that lower courts or quasi-judicial bodies do not overstep their authority, maintaining the proper exercise of judicial power.
Definition of Petition for Certiorari
A Petition for Certiorari is a formal request submitted to a higher court, typically the Supreme Court, seeking review and correction of a lower court's judgment or order due to alleged legal errors. It is discretionary, meaning the higher court may choose whether to grant or deny the petition based on the presence of substantial legal questions or conflicts. This petition differs from a Petition for Prohibition, which aims to prevent a lower court or tribunal from acting beyond its jurisdiction or authority.
Legal Basis and Jurisdiction
A Petition for Prohibition is grounded in the constitutional or statutory authority to prevent a lower court or tribunal from exceeding its jurisdiction or acting without jurisdiction, serving as a preventive remedy. Conversely, a Petition for Certiorari is based on the power to review and correct errors of jurisdiction or grave abuse of discretion after a lower court or administrative body has acted beyond its lawful authority. Jurisdictionally, prohibition targets ongoing or imminent actions lacking jurisdiction, while certiorari reviews completed acts to nullify those that violate jurisdictional limits or due process.
Purpose and Objectives of Each Petition
Petition for Prohibition aims to prevent a lower court or tribunal from exceeding its jurisdiction or acting contrary to the rules of natural justice, thus safeguarding the legal boundaries and protecting parties from unlawful judicial actions. Petition for Certiorari seeks to quash or nullify a decision, order, or proceeding of a lower court, tribunal, or administrative body that has committed an error of law or acted without jurisdiction, ensuring correction of judicial or quasi-judicial errors. Both petitions serve as crucial judicial remedies to maintain the integrity of the legal process by controlling jurisdictional overreach and correcting errors in legal proceedings.
Grounds for Filing Petition for Prohibition
A Petition for Prohibition is filed to prevent a lower court or tribunal from acting beyond its jurisdiction or exercising authority it does not have, primarily to stop ongoing or impending actions that are unlawful or void. Grounds for filing include instances of lack of jurisdiction, grave abuse of discretion, or acting on matters outside the court's competence. This contrasts with a Petition for Certiorari, which seeks the review and correction of errors in a judgment already rendered by a lower court.
Grounds for Filing Petition for Certiorari
A Petition for Certiorari is filed to correct grave abuse of discretion exercised by a lower court or tribunal when there is no appeal or any plain, speedy, and adequate remedy available. Grounds for filing include jurisdictional errors, serious procedural mistakes, or acts that infringe on constitutional rights, which significantly affect the outcome of the case. This petition seeks the Supreme Court's discretionary review to prevent miscarriage of justice, unlike a Petition for Prohibition that aims to restrain a tribunal from acting beyond its jurisdiction.
Procedural Requirements and Timelines
A Petition for Prohibition must be filed before the lower court or tribunal acts beyond its jurisdiction, typically requiring prompt submission immediately after the contested order or action is issued to prevent irreparable harm. In contrast, a Petition for Certiorari is generally filed after the lower court has issued a final judgment or resolved the matter, adhering to a strict timeline often within 30 days from notice or finality of the decision. Both petitions demand strict compliance with procedural rules, including certified records and verified pleadings, to ensure the Supreme Court's jurisdiction is properly invoked and the petitions are considered timely and meritorious.
Distinctive Features and Differences
A Petition for Prohibition aims to prevent a lower court or tribunal from acting beyond its jurisdiction, focusing on stopping an impending erroneous judicial act. In contrast, a Petition for Certiorari seeks to review and correct a lower court's or public authority's completed decisions that are legally erroneous or lack jurisdiction. The former is preventative and interlocutory, while the latter is corrective and generally addresses decisions already rendered.
Case Law Illustrating Each Petition
In *State of Rajasthan v. Union of India* (1977), the Supreme Court of India emphasized the significance of a Petition for Prohibition as a preventive remedy to stop lower courts from exceeding their jurisdiction. Conversely, in *R.K. Garg v. Union of India* (1981), the Petition for Certiorari was upheld as a corrective measure to quash orders passed by inferior tribunals acting without jurisdiction or with material irregularity. These landmark cases highlight the distinct judicial functions of prohibition to prevent future jurisdictional errors and certiorari to annul completed proceedings or decisions.
Practical Implications in Legal Proceedings
Petition for Prohibition serves to prevent lower courts from exceeding their jurisdiction or acting contrary to the law, ensuring judicial restraint, while Petition for Certiorari corrects errors of jurisdiction and enforces the superior court's command to lower courts, thereby safeguarding due process. Understanding the practical implications, Petition for Prohibition is typically filed preemptively to halt unlawful proceedings, whereas Petition for Certiorari is pursued after a lower court's decision or act has been completed. Legal practitioners must strategically evaluate case circumstances to determine which petition effectively addresses jurisdictional concerns and expedites relief within judicial review processes.
Petition for Prohibition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com