Constitutional law defines the structure, powers, and limits of government institutions while protecting fundamental rights and freedoms. It governs the relationship between individuals and the state, ensuring justice and equality under the law. Explore the rest of the article to understand how constitutional law impacts your rights and daily life.
Table of Comparison
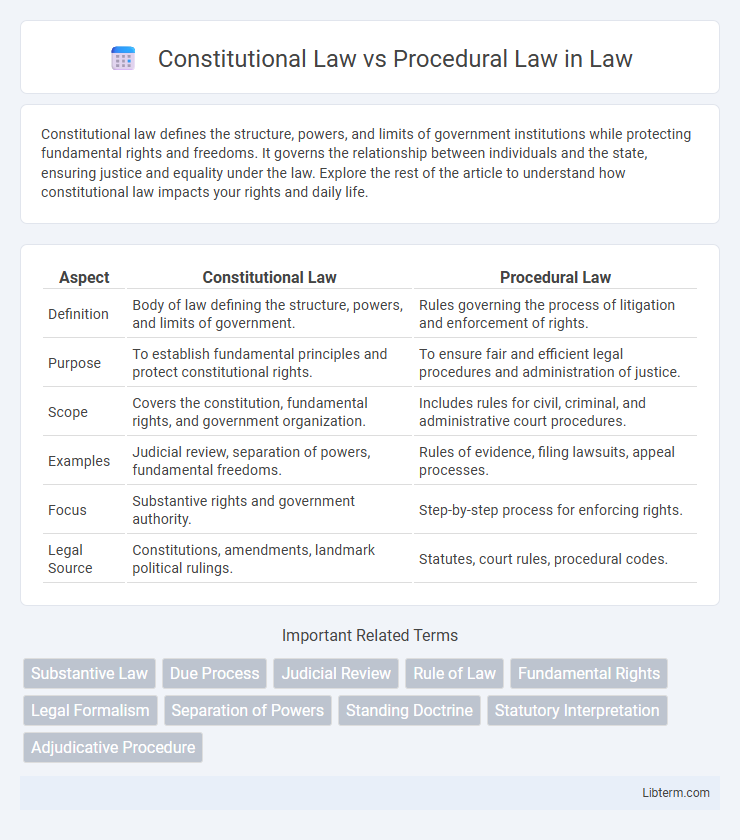
| Aspect | Constitutional Law | Procedural Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Body of law defining the structure, powers, and limits of government. | Rules governing the process of litigation and enforcement of rights. |
| Purpose | To establish fundamental principles and protect constitutional rights. | To ensure fair and efficient legal procedures and administration of justice. |
| Scope | Covers the constitution, fundamental rights, and government organization. | Includes rules for civil, criminal, and administrative court procedures. |
| Examples | Judicial review, separation of powers, fundamental freedoms. | Rules of evidence, filing lawsuits, appeal processes. |
| Focus | Substantive rights and government authority. | Step-by-step process for enforcing rights. |
| Legal Source | Constitutions, amendments, landmark political rulings. | Statutes, court rules, procedural codes. |
Introduction to Constitutional Law and Procedural Law
Constitutional Law establishes the fundamental principles and legal framework that govern a nation, defining the structure of government, the distribution of powers, and the protection of individual rights. Procedural Law outlines the rules and processes that courts follow to enforce constitutional rights and ensure justice, including litigation steps, jurisdiction, and evidence handling. Understanding these distinct yet interconnected areas is essential for comprehending how legal systems maintain order and protect civil liberties.
Defining Constitutional Law
Constitutional Law establishes the foundational principles and structures that govern a state's political and legal framework, including the distribution of power among government branches and the protection of individual rights. It defines the relationship between citizens and the state, ensuring laws comply with constitutional mandates. Unlike Procedural Law, which governs the methods and processes of legal enforcement, Constitutional Law sets the supreme legal standards for all legislation and government actions.
Defining Procedural Law
Procedural law establishes the rules and processes that govern how courts conduct litigation, ensuring fair and consistent application of justice. It defines the methods for enforcing rights and duties outlined in substantive law, including steps for filing lawsuits, trial procedures, and rules of evidence. Unlike constitutional law, which sets the framework for government powers and individual rights, procedural law focuses on the mechanisms and formalities necessary to implement those rights within the legal system.
Key Differences Between Constitutional and Procedural Law
Constitutional law defines the fundamental principles and framework of a government, establishing the powers and limitations of governmental bodies and the rights of individuals. Procedural law governs the processes and methods by which courts administer justice, including rules for conducting trials, filing lawsuits, and enforcing rights. Key differences lie in constitutional law's role in shaping legal authority and individual protections, whereas procedural law focuses on the mechanisms for applying and enforcing those legal principles within the judicial system.
Sources of Constitutional and Procedural Law
Constitutional law primarily derives from written constitutions, judicial interpretations, and foundational legal principles that establish the structure and powers of government. Procedural law sources include statutory enactments, court rules, and administrative regulations that govern the methods and processes by which courts handle cases. Both branches rely on judicial precedents, but constitutional law emphasizes fundamental rights and government organization, while procedural law focuses on the mechanisms for enforcing those rights.
Scope and Application in Legal Systems
Constitutional Law governs the fundamental principles and structures of government, defining the rights and duties of state institutions and citizens, thus shaping the legal framework of a nation. Procedural Law outlines the specific methods and processes through which courts enforce substantive laws, ensuring fair trials and due process within the judicial system. While Constitutional Law sets the broad legal context for governance and individual rights, Procedural Law applies these principles practically by regulating litigation, evidence, and court proceedings.
Importance in Protecting Individual Rights
Constitutional law establishes the fundamental principles and frameworks that safeguard individual rights by limiting governmental powers and ensuring equal protection under the law. Procedural law governs the methods and processes through which these rights are enforced and adjudicated within the legal system. Both are crucial for protecting civil liberties: constitutional law defines the rights, while procedural law ensures fair treatment and access to justice in upholding those rights.
Role in the Judicial Process
Constitutional law establishes the fundamental principles and framework governing the judicial system, defining the structure, powers, and limits of government entities while ensuring the protection of individual rights. Procedural law provides the detailed rules and processes that courts must follow to enforce constitutional rights and resolve disputes, including jurisdiction, pleadings, evidence, and appeals. Together, constitutional law shapes the foundational authority of courts, while procedural law directs the practical application and administration of justice within that framework.
Case Studies Illustrating Distinctions
Case studies such as Marbury v. Madison emphasize Constitutional Law by highlighting the judiciary's role in interpreting constitutional principles and ensuring governmental powers align with the Constitution. In contrast, cases like Gideon v. Wainwright demonstrate Procedural Law by focusing on the implementation of fair trial rights and procedural safeguards within the legal system. These cases illustrate how Constitutional Law sets foundational legal frameworks while Procedural Law governs the mechanisms of law enforcement and litigation processes.
Conclusion: Comparative Significance
Constitutional Law establishes the foundational framework and principles guiding the governance of a state, ensuring the protection of fundamental rights and the distribution of governmental powers. Procedural Law, by contrast, regulates the methods and processes through which legal rights and duties are enforced in courts, providing the mechanics for justice administration. Both are crucial; Constitutional Law safeguards the legal order's legitimacy, while Procedural Law guarantees fairness and efficiency in judicial proceedings, together maintaining the rule of law.
Constitutional Law Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com