Procedural justice refers to the fairness of the processes that lead to outcomes or decisions, emphasizing transparency, consistency, and impartiality. Ensuring procedural justice can enhance trust and cooperation within organizations and legal systems by giving individuals a sense of respect and voice. Explore the rest of the article to understand how procedural justice impacts your daily interactions and decision-making environments.
Table of Comparison
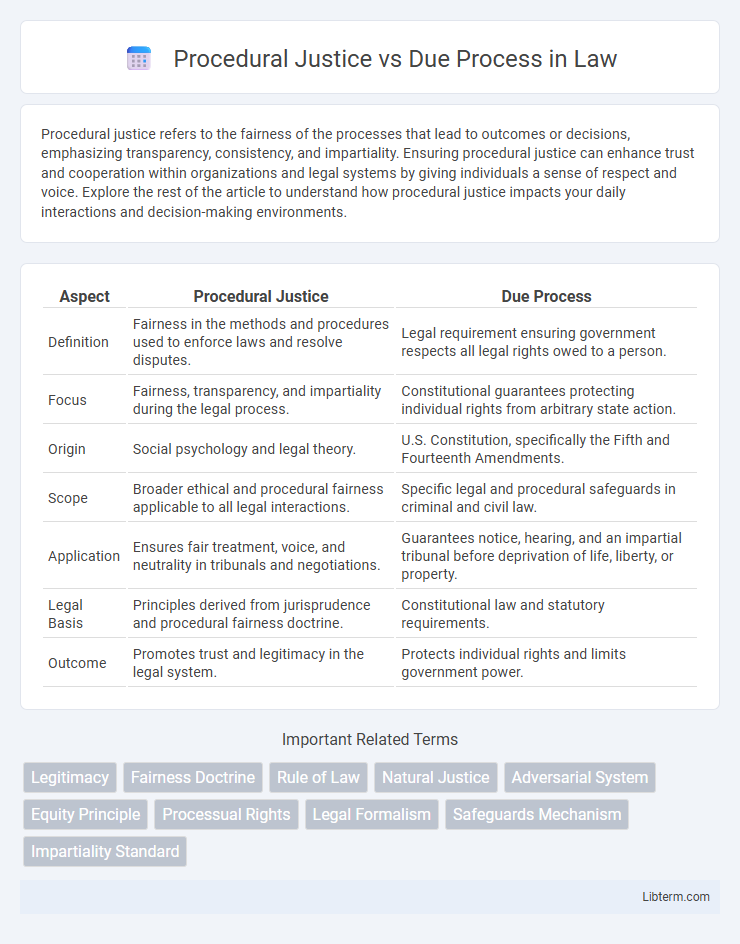
| Aspect | Procedural Justice | Due Process |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fairness in the methods and procedures used to enforce laws and resolve disputes. | Legal requirement ensuring government respects all legal rights owed to a person. |
| Focus | Fairness, transparency, and impartiality during the legal process. | Constitutional guarantees protecting individual rights from arbitrary state action. |
| Origin | Social psychology and legal theory. | U.S. Constitution, specifically the Fifth and Fourteenth Amendments. |
| Scope | Broader ethical and procedural fairness applicable to all legal interactions. | Specific legal and procedural safeguards in criminal and civil law. |
| Application | Ensures fair treatment, voice, and neutrality in tribunals and negotiations. | Guarantees notice, hearing, and an impartial tribunal before deprivation of life, liberty, or property. |
| Legal Basis | Principles derived from jurisprudence and procedural fairness doctrine. | Constitutional law and statutory requirements. |
| Outcome | Promotes trust and legitimacy in the legal system. | Protects individual rights and limits government power. |
Introduction to Procedural Justice and Due Process
Procedural Justice emphasizes fairness in the processes that resolve disputes and allocate resources, focusing on transparency, consistency, and impartiality to ensure individuals feel respected and heard. Due Process is a constitutional guarantee that legal proceedings will be conducted fairly, protecting individuals from arbitrary denial of life, liberty, or property by requiring notice, a fair hearing, and an unbiased tribunal. Both concepts are foundational in legal and organizational settings to ensure legitimacy, trust, and equitable treatment.
Defining Procedural Justice
Procedural justice refers to the fairness of the processes that resolve disputes and allocate resources, emphasizing transparency, consistency, and neutrality in decision-making. It prioritizes individuals' perceptions of fairness in how decisions are made rather than the outcomes themselves, fostering trust and legitimacy in authorities and institutions. This concept contrasts with due process, which is a legal guarantee ensuring all individuals receive fair treatment under the law through established legal procedures and safeguards.
Understanding Due Process
Due process refers to the legal requirement that the government must respect all legal rights owed to a person, ensuring fair treatment through the normal judicial system, especially as a citizen's entitlement. Procedural justice emphasizes the fairness of the procedures used to make decisions, focusing on transparency, consistency, and the opportunity for individuals to voice their concerns. Understanding due process involves recognizing its role in safeguarding individual rights by mandating proper notice, impartial hearings, and the right to appeal in administrative and judicial proceedings.
Historical Origins and Legal Foundations
Procedural justice traces its roots to ancient philosophical discussions on fairness and equitable treatment in decision-making, emphasizing the moral legitimacy of processes. Due process, enshrined in the Magna Carta (1215) and later the Fifth and Fourteenth Amendments of the U.S. Constitution, provides concrete legal protections ensuring fair treatment through established legal procedures. Both concepts underpin modern justice systems by balancing ethical procedural fairness with codified legal guarantees.
Key Principles of Procedural Justice
Procedural justice centers on key principles such as fairness, transparency, and voice, ensuring individuals feel respected and heard during decision-making processes. It emphasizes unbiased procedures and consistent application of rules to build trust and legitimacy in institutions. These elements differ from due process, which primarily guarantees legal rights and formal protections under the law.
Essential Elements of Due Process
The essential elements of due process include the right to a fair hearing, notice of the charges or proceedings, and an opportunity to present evidence and defend oneself. Procedural justice emphasizes fairness in the processes and treatment individuals receive during legal or administrative procedures, aligning closely with the principles embodied in due process. Ensuring impartiality, transparency, and consistency in decision-making safeguards fundamental rights and upholds the legitimacy of judicial and administrative outcomes.
Procedural Justice in Criminal vs Civil Law
Procedural justice emphasizes fairness in the processes that resolve disputes and allocate resources, ensuring impartiality, consistency, and transparency in both criminal and civil law contexts. In criminal law, procedural justice centers on safeguarding defendants' rights through unbiased investigations, fair trials, and protection from arbitrary punishment. In civil law, procedural justice ensures equitable access to dispute resolution mechanisms, timely hearings, and adherence to rules that promote fair outcomes for all parties involved.
Comparative Analysis: Procedural Justice vs Due Process
Procedural justice emphasizes fairness in the methods and processes used during decision-making, focusing on transparency, voice, and neutrality to ensure perceived legitimacy. Due process is a legal principle protecting individuals' rights through formal procedures, such as timely hearings, right to counsel, and impartial adjudication, primarily within the judicial system. While procedural justice enhances trust and cooperation in various settings, due process legally guarantees protection against arbitrary state actions and ensures compliance with constitutional standards.
Impact on Legal Outcomes and Public Perception
Procedural justice emphasizes fairness in the methods and processes used to make decisions, significantly enhancing public trust and perceived legitimacy of legal institutions. Due process, rooted in constitutional law, ensures legal rights and formal protections, directly influencing the consistency and validity of court rulings. Studies show that when individuals perceive procedural justice, compliance with the law increases, whereas strict adherence to due process safeguards minimizes wrongful convictions and appeals.
Future Trends in Justice System Reform
Future trends in justice system reform emphasize integrating procedural justice principles to enhance fairness, transparency, and community trust, moving beyond traditional due process frameworks that primarily focus on legal formalities. Innovations such as restorative justice programs, technology-driven case management, and increased public participation aim to create more equitable outcomes and reduce systemic biases. Data-driven policymaking and AI-assisted decision tools are expected to support these reforms by improving consistency and accountability in judicial procedures.
Procedural Justice Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com