Advisory verdicts provide non-binding opinions from juries or judges to guide decision-making in complex legal cases. These verdicts can influence the final judgment by offering insights into the evidence and merits without legally determining the outcome. Explore the rest of the article to understand how advisory verdicts impact your legal strategy and court proceedings.
Table of Comparison
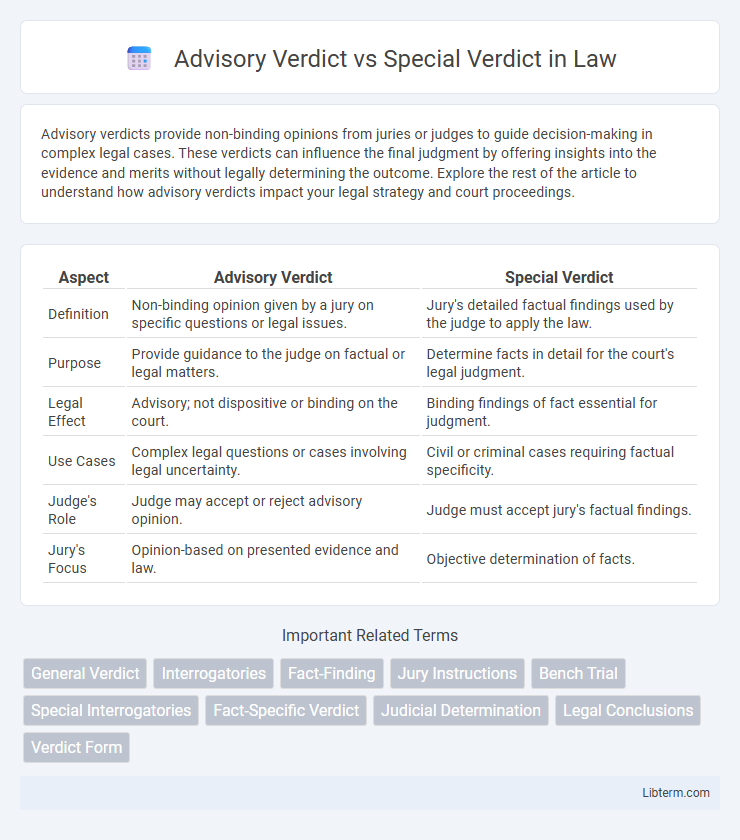
| Aspect | Advisory Verdict | Special Verdict |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-binding opinion given by a jury on specific questions or legal issues. | Jury's detailed factual findings used by the judge to apply the law. |
| Purpose | Provide guidance to the judge on factual or legal matters. | Determine facts in detail for the court's legal judgment. |
| Legal Effect | Advisory; not dispositive or binding on the court. | Binding findings of fact essential for judgment. |
| Use Cases | Complex legal questions or cases involving legal uncertainty. | Civil or criminal cases requiring factual specificity. |
| Judge's Role | Judge may accept or reject advisory opinion. | Judge must accept jury's factual findings. |
| Jury's Focus | Opinion-based on presented evidence and law. | Objective determination of facts. |
Introduction to Advisory Verdict and Special Verdict
An advisory verdict is a non-binding opinion given by a jury to assist the judge in making a decision, commonly used in complex or civil cases where the jury's input aids judicial discretion. A special verdict requires the jury to find facts from specific questions posed by the judge, focusing on factual determinations without delivering a general conclusion of guilt or liability. Both verdict types provide detailed insight into the jury's reasoning, enhancing judicial accuracy and case clarity.
Definition of Advisory Verdict
An advisory verdict is a non-binding opinion given by a jury to guide the court on issues of fact or law, typically requested at the judge's discretion. Unlike a special verdict, which requires the jury to make specific findings on factual questions that the court uses to determine the final judgment, an advisory verdict serves as a recommendation without legal obligation. Courts often seek advisory verdicts in complex cases where the judge needs jurors' perspectives but retains ultimate decision-making authority.
Definition of Special Verdict
A Special Verdict requires the jury to find facts only, leaving the application of the law to the judge, unlike an Advisory Verdict where the jury's opinion guides the court without binding effect. In a Special Verdict, the jury lists factual findings in response to specific questions posed by the court, enabling the judge to render the final legal decision based on those facts. This type of verdict is particularly useful in complex cases requiring judicial interpretation of legal standards after a factual determination.
Key Differences Between Advisory and Special Verdicts
Advisory verdicts are non-binding recommendations provided by a jury to assist the judge in reaching a final decision, whereas special verdicts require the jury to answer specific factual questions that directly determine the case outcome. The advisory verdict allows the judge discretion in applying the jury's opinion, while the special verdict mandates a verdict based strictly on the jury's findings on factual issues. This key difference impacts how judicial authority and jury input are balanced during the trial process.
Legal Contexts for Advisory Verdicts
Advisory verdicts are non-binding opinions provided by a jury in complex legal cases where the judge seeks guidance but retains ultimate decision-making authority. These verdicts occur primarily in civil trials or cases involving special questions that require expert judgment beyond typical jury determinations. Unlike special verdicts, which are binding and consist of specific factual findings, advisory verdicts serve as consultative tools to assist judges in interpreting evidence or legal issues.
Legal Contexts for Special Verdicts
Special verdicts in legal contexts require the jury to find facts based on evidence, leaving the application of law to the judge, which ensures precise legal interpretations. Advisory verdicts serve as non-binding opinions that assist judges in making informed decisions without determining final verdicts. Special verdicts enhance judicial control over legal outcomes by separating fact-finding from legal conclusions in trials.
Role of the Jury in Advisory Verdicts
In Advisory Verdicts, the jury provides a non-binding opinion on issues of fact, guiding the judge without conclusively determining the case outcome. This role allows the jury to assess evidence and offer recommendations, while the judge retains ultimate authority in decision-making. Unlike Special Verdicts, where the jury answers specific factual questions resulting in a binding determination, Advisory Verdicts emphasize the jury's consultative input rather than final judgment.
Role of the Jury in Special Verdicts
In special verdicts, the jury's role is to determine specific factual issues rather than delivering a general judgment, providing detailed findings for the judge to apply the law. This contrasts with advisory verdicts where the jury offers a non-binding opinion to guide the judge's decision-making process. The specificity of jury findings in special verdicts enhances judicial accuracy in complex cases by clarifying the factual basis for legal conclusions.
Impact on Court Decisions
An advisory verdict provides the court with non-binding recommendations that influence judicial discretion without determining the final legal outcome, allowing judges to consider but not be compelled by the jury's opinion. In contrast, a special verdict requires the jury to make specific factual findings that legally bind the court's decision, directly shaping the application of law to the case. This distinction impacts court decisions by balancing judicial authority with jury input, where advisory verdicts offer guidance and special verdicts mandate factual determinations critical to legal rulings.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Advisory and Special Verdicts
Selecting between advisory and special verdicts hinges on the court's need for guidance versus definitive factual findings; advisory verdicts offer non-binding recommendations that assist judges in shaping legal conclusions, while special verdicts provide explicit answers to factual questions, empowering judges to apply the law based on detailed factual determinations. Advisory verdicts enhance judicial flexibility by incorporating jury insights without constraining judicial authority, whereas special verdicts ensure precise factual resolutions, minimizing ambiguity in complex cases. Courts favor advisory verdicts in matters requiring legal interpretation influenced by jury experience, and special verdicts when clear-cut factual findings are essential for a legally sound judgment.
Advisory Verdict Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com