Annulment legally declares a marriage null and void, as if it never existed, differing from a divorce which ends a valid marriage. Common grounds include fraud, coercion, or incapacity at the time of marriage. Explore the rest of the article to understand how annulment might apply to your situation and the processes involved.
Table of Comparison
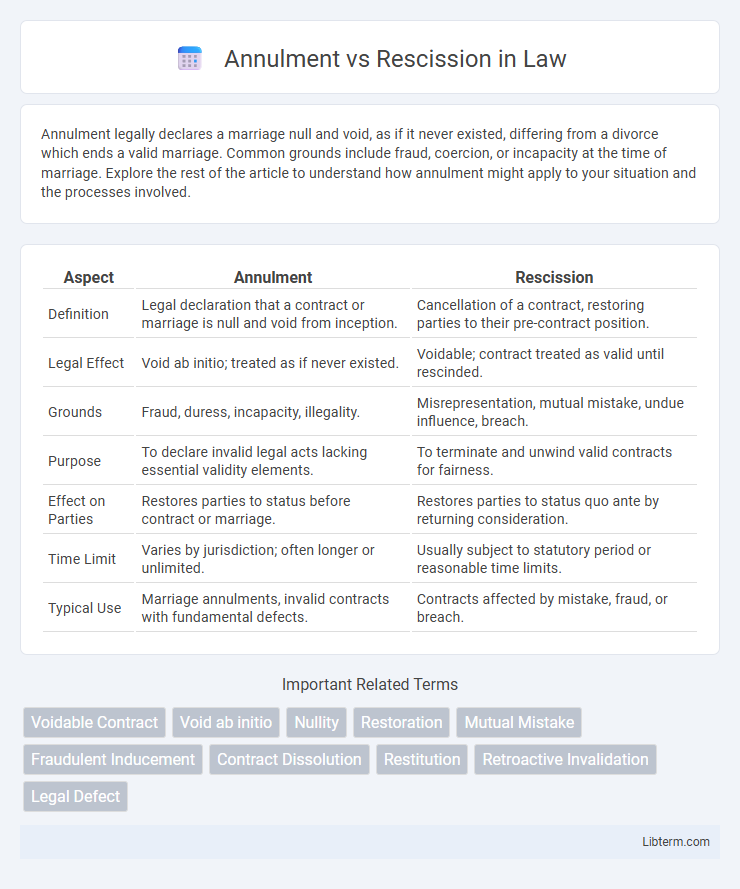
| Aspect | Annulment | Rescission |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal declaration that a contract or marriage is null and void from inception. | Cancellation of a contract, restoring parties to their pre-contract position. |
| Legal Effect | Void ab initio; treated as if never existed. | Voidable; contract treated as valid until rescinded. |
| Grounds | Fraud, duress, incapacity, illegality. | Misrepresentation, mutual mistake, undue influence, breach. |
| Purpose | To declare invalid legal acts lacking essential validity elements. | To terminate and unwind valid contracts for fairness. |
| Effect on Parties | Restores parties to status before contract or marriage. | Restores parties to status quo ante by returning consideration. |
| Time Limit | Varies by jurisdiction; often longer or unlimited. | Usually subject to statutory period or reasonable time limits. |
| Typical Use | Marriage annulments, invalid contracts with fundamental defects. | Contracts affected by mistake, fraud, or breach. |
Understanding Annulment and Rescission
Annulment legally declares a marriage null and void as if it never existed by proving factors like fraud, duress, or incapacity at the time of marriage. Rescission cancels a contract or agreement due to reasons such as misrepresentation, mistake, or mutual consent, restoring parties to their pre-contractual positions. Both annulment and rescission serve to negate legal obligations but apply in distinct contexts--annulment primarily in marital law and rescission in contract law.
Key Legal Definitions
Annulment refers to a legal declaration that a marriage is null and void, as if it never existed, based on grounds such as fraud, coercion, or incapacity at the time of marriage. Rescission involves canceling a contract or agreement due to misrepresentation, mistake, or undue influence, rendering the contract voidable and restoring parties to their original positions. Understanding the key legal distinctions highlights that annulment applies specifically to marital status, while rescission pertains broadly to contractual obligations.
Grounds for Annulment
Grounds for annulment typically include factors such as fraud, duress, lack of capacity, or bigamy, which render a marriage void or voidable from the outset. Courts examine whether one party was incapacitated due to age, mental state, or coercion, invalidating genuine consent. Unlike rescission, annulment addresses the fundamental legality of the marriage itself rather than contractual obligations.
Grounds for Rescission
Grounds for rescission include mutual mistake, fraud, duress, undue influence, and misrepresentation, which render the contract voidable rather than inherently void. Rescission aims to restore parties to their original positions by canceling the contract due to these defects. Courts require proof that the aggrieved party was induced into the contract by these factors, justifying the contract's annulment.
Differences in Legal Effects
Annulment declares a marriage null and void as if it never legally existed, whereas rescission terminates a contract and restores parties to their original positions before the agreement. Annulment affects marital status, often impacting legitimacy of offspring and property rights, while rescission addresses contractual obligations without altering personal status. Legal consequences of annulment typically involve family law courts, whereas rescission is resolved in contract law jurisdictions.
Procedures for Annulment
Procedures for annulment typically require filing a petition in a court that has jurisdiction over the marriage, accompanied by evidence proving that the marriage is void or voidable under specific legal grounds such as fraud, coercion, or incapacity. The court then schedules a hearing to evaluate the validity of the claims before issuing a judgment to declare the marriage null and void, as if it never legally existed. Annulment procedures vary by jurisdiction but generally involve strict adherence to statutory timelines and mandatory documentation of the cause for annulment to prevent abuse of the process.
Procedures for Rescission
Procedures for rescission involve filing a petition in court to prove the existence of valid grounds such as fraud, mistake, duress, or undue influence that justify nullifying the contract. The petitioner must present clear and convincing evidence demonstrating that the rescission is necessary to restore the parties to their original positions before the contract was formed. The court examines the merits, and if the grounds are deemed sufficient, it issues an order rescinding the contract and terminating all obligations arising from it.
Real-World Examples
Annulment legally voids a marriage from its inception due to factors like fraud or bigamy, as seen in cases where one spouse conceals a prior marriage, rendering the union invalid. Rescission cancels contracts, such as real estate agreements, when parties prove misrepresentation or mutual mistake, exemplified by a buyer rescinding a home purchase after discovering undisclosed property defects. Courts differentiate these remedies based on whether the issue affects the existence of the marriage (annulment) or the enforceability of a contract (rescission), impacting legal rights and obligations accordingly.
Implications for Contracting Parties
Annulment declares a contract null from the outset, erasing all legal effects and restoring parties to their original positions, impacting rights and obligations as if the contract never existed. Rescission, on the other hand, cancels a contract prospectively due to factors like fraud or mutual mistake, requiring restitution to return parties to the status quo ante while recognizing the contract's prior validity. Both remedies significantly affect contractual relationships, but annulment removes the contract's foundation entirely, whereas rescission treats the contract as operative until invalidated.
Choosing Between Annulment and Rescission
Choosing between annulment and rescission depends on the nature of the contract defect and desired legal outcome. Annulment declares a contract void from the beginning due to factors like fraud, duress, or incapacity, effectively erasing its validity. Rescission terminates a valid contract by mutual agreement or court order, restoring parties to their pre-contract positions, often used in cases of misrepresentation or mutual mistake.
Annulment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com