Authorization is the process of granting or denying specific permissions to users, devices, or systems based on their identity and access rights. It ensures secure access control by verifying that Your credentials match the required privileges for a particular resource or action. Explore the rest of this article to deepen your understanding of how authorization strengthens security frameworks.
Table of Comparison
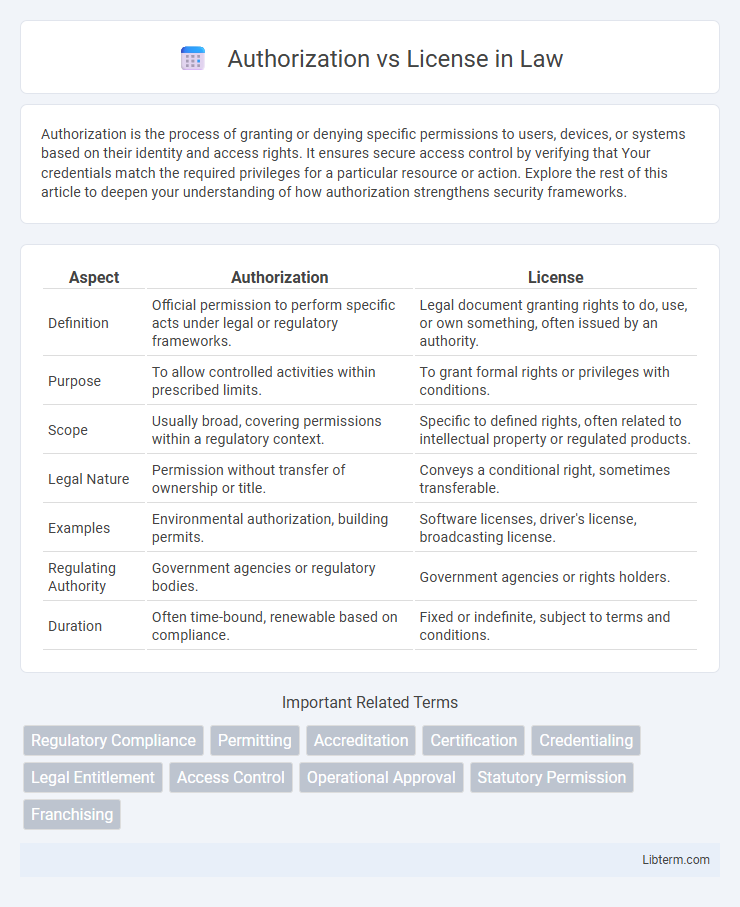
| Aspect | Authorization | License |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official permission to perform specific acts under legal or regulatory frameworks. | Legal document granting rights to do, use, or own something, often issued by an authority. |
| Purpose | To allow controlled activities within prescribed limits. | To grant formal rights or privileges with conditions. |
| Scope | Usually broad, covering permissions within a regulatory context. | Specific to defined rights, often related to intellectual property or regulated products. |
| Legal Nature | Permission without transfer of ownership or title. | Conveys a conditional right, sometimes transferable. |
| Examples | Environmental authorization, building permits. | Software licenses, driver's license, broadcasting license. |
| Regulating Authority | Government agencies or regulatory bodies. | Government agencies or rights holders. |
| Duration | Often time-bound, renewable based on compliance. | Fixed or indefinite, subject to terms and conditions. |
Understanding Authorization and License
Authorization refers to the process of granting permission to access resources or perform actions within a system, typically controlled by an entity such as an administrator or policy. A license is a formal legal agreement that specifies the terms under which a user or organization may use intellectual property, software, or services. Understanding the distinction helps organizations enforce security through authorization while ensuring compliance and legal usage via licensing agreements.
Definition of Authorization
Authorization is the formal permission granted by an authority that allows an individual or entity to perform specific actions or access certain resources within a system or organization. It defines the scope and limits of what is permitted, ensuring compliance with policies or regulations. Unlike a license, which is often a legal document granting rights over intellectual property or business operations, authorization primarily controls access and actions within a defined framework.
Definition of License
A license is a formal permission granted by a competent authority allowing an individual or entity to perform specific activities or use particular rights within legal boundaries. Unlike general authorization, which may be broader or informal, a license often requires compliance with regulatory standards and may involve fees or periodic renewals. Licenses provide verifiable proof of eligibility and are essential in fields such as driving, broadcasting, software use, and business operations.
Key Differences Between Authorization and License
Authorization grants permission to perform specific actions or access resources within a system, while a license is a formal legal agreement granting rights to use intellectual property or products. Authorization is typically managed by an organization to control user privileges, whereas licenses are issued by regulatory bodies or intellectual property owners to regulate usage and compliance. The key difference lies in authorization being a system-level access control mechanism, whereas a license represents a legal entitlement to utilize certain rights or materials.
Legal Implications of Authorization
Authorization grants specific legal permissions to individuals or entities to perform certain actions under regulated frameworks, often tied to compliance with statutory requirements. It creates a legal obligation ensuring that the authorized party operates within the scope of granted powers, with potential liabilities for unauthorized activities. Violations of authorization terms can result in administrative penalties, fines, or criminal charges, depending on jurisdictional laws.
Legal Implications of License
A license grants permission to use intellectual property under specific terms, creating legally binding obligations between the licensor and licensee. Unlike authorization, which may be informal or temporary, a license establishes enforceable rights and duties regulated by contract law and relevant statutes. Legal implications include potential liability for breach, scope limitations, and termination conditions that protect proprietary interests and ensure compliance.
Practical Examples of Authorization
Authorization grants individuals or entities specific permissions to access resources or perform actions within a system, such as an employee being authorized to access confidential company files. For instance, a software application may authorize a user to edit documents while restricting others to view-only access. In comparison, a license generally refers to a formal legal agreement granting rights to use copyrighted materials or products under defined conditions.
Practical Examples of License
A license grants legal permission to use, create, or distribute intellectual property, such as software licenses allowing users to install applications on multiple devices under specified terms. For example, a commercial software license permits businesses to operate proprietary programs, while an open-source license authorizes developers to modify and share code freely. Licensing agreements define usage scope, duration, and restrictions, ensuring compliance and protection for both licensors and licensees in various industries.
When to Use Authorization vs License
Authorization is used when granting permission to access, operate, or perform specific actions within a system, process, or environment, typically controlling user roles and privileges. A license is appropriate when legally permitting the use, distribution, or production of intellectual property, software, or products under defined terms and conditions. Choose authorization for internal security and access control, and license for formal legal rights and compliance management.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Choosing between authorization and license depends on the specific legal framework and intended use of intellectual property or regulated activities. Authorization typically grants permission within a defined scope without transferring ownership, whereas a license provides a formal agreement outlining rights, obligations, and often includes royalties or fees. Understanding the nuances of each ensures compliance and optimizes control over the use of protected assets.
Authorization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com