Joint liability holds multiple parties equally responsible for a debt or obligation, ensuring that creditors can pursue any one party for the full amount owed. This legal concept protects creditors by distributing risk among debtors, potentially impacting your financial commitments in partnerships or business ventures. Explore the rest of the article to understand how joint liability influences your agreements and legal responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
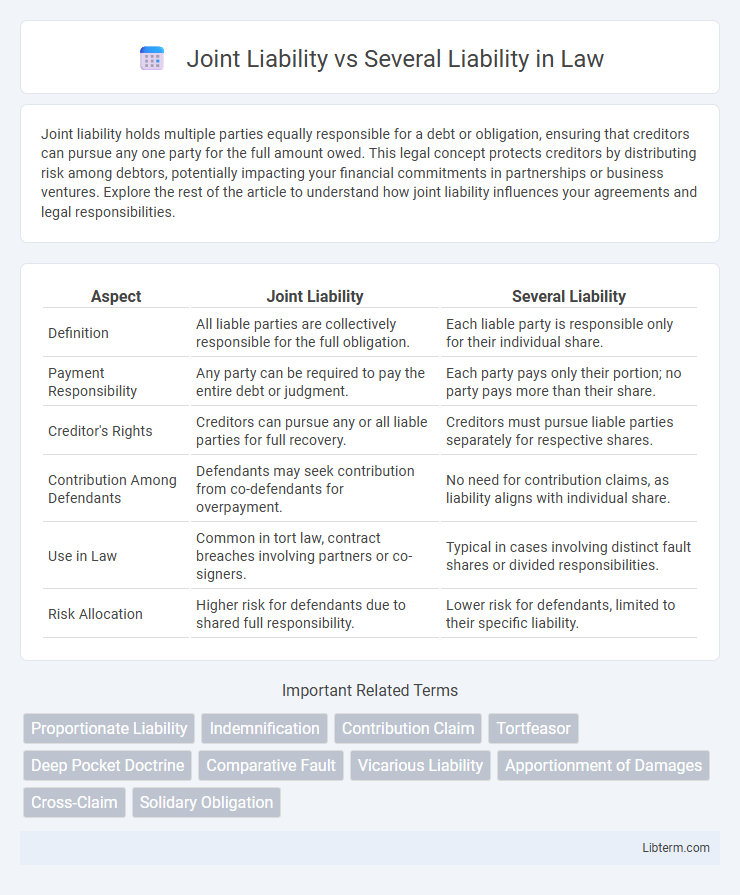
| Aspect | Joint Liability | Several Liability |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | All liable parties are collectively responsible for the full obligation. | Each liable party is responsible only for their individual share. |
| Payment Responsibility | Any party can be required to pay the entire debt or judgment. | Each party pays only their portion; no party pays more than their share. |
| Creditor's Rights | Creditors can pursue any or all liable parties for full recovery. | Creditors must pursue liable parties separately for respective shares. |
| Contribution Among Defendants | Defendants may seek contribution from co-defendants for overpayment. | No need for contribution claims, as liability aligns with individual share. |
| Use in Law | Common in tort law, contract breaches involving partners or co-signers. | Typical in cases involving distinct fault shares or divided responsibilities. |
| Risk Allocation | Higher risk for defendants due to shared full responsibility. | Lower risk for defendants, limited to their specific liability. |
Introduction to Joint Liability and Several Liability
Joint liability occurs when two or more parties are collectively responsible for an obligation, making each party liable for the full amount of the debt or damages. Several liability, on the other hand, means each party is only responsible for their specific share or proportion of the obligation. Understanding the distinction clarifies how financial or legal responsibilities are assigned in contracts, torts, or partnerships.
Definition of Joint Liability
Joint liability refers to a legal obligation where two or more parties are collectively responsible for fulfilling a debt or duty, meaning each party can be held accountable for the entire obligation. This contrasts with several liability, where parties are independently responsible only for their respective shares. In cases involving joint liability, creditors can pursue any or all obligors for full repayment, enhancing creditor protection but increasing risk among co-debtors.
Definition of Several Liability
Several liability refers to a legal responsibility where each party is liable only for their specific portion of the obligation or debt, without bearing the burden for others' shares. Unlike joint liability, where all parties can be held collectively responsible for the entire amount, several liability limits financial exposure to an individual's direct involvement or contribution. This distinction is crucial in contracts and tort cases, ensuring liability is allocated according to each party's actual fault or participation.
Key Differences Between Joint and Several Liability
Joint liability requires all parties to be collectively responsible for the full obligation, meaning each defendant can be held liable for the entire debt. Several liability, on the other hand, holds each party responsible only for their specific share of the obligation, limiting financial exposure. The key difference lies in enforcement: joint liability permits creditors to pursue any liable party for total recovery, whereas several liability restricts recovery to individual parties based on their proportional responsibility.
Legal Implications of Joint Liability
Joint liability imposes collective responsibility on co-obligors, meaning each party can be held accountable for the entire debt or obligation, ensuring creditors have multiple sources for recovery. This legal structure increases the risk exposure for each liable party, as one obligor's default may require others to cover the full extent of the obligation. Courts often enforce joint liability to protect creditors' interests, promoting prompt and complete performance by obligors.
Legal Implications of Several Liability
Several liability imposes legal responsibility on each defendant individually for the entire obligation, allowing plaintiffs to recover full damages from any one party without pursuing others. This legal framework ensures that the burden of compensation does not fall on multiple defendants simultaneously, but may lead to unequal financial impact depending on each party's ability to pay. Courts often enforce several liability to promote fairness and prevent disproportionate hardship among defendants in tort and contract cases.
Real-World Examples of Joint Liability
Joint liability occurs when multiple parties are collectively responsible for a debt or obligation, as seen in real estate co-ownership where each owner is liable for the entire mortgage balance if others default. In construction contracts, subcontractors and contractors share joint liability for project defects, requiring any party to cover full damages if others cannot. This legal framework ensures creditors can pursue total recovery from any liable party, emphasizing shared financial responsibility.
Real-World Examples of Several Liability
Several liability allows each defendant to be responsible only for their specific share of damages, as seen in tort cases like the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill where multiple companies were held liable for their individual contributions. In construction defects litigation, subcontractors are often held severally liable for the portion of damage linked to their work, preventing disproportionate financial burden. This approach is essential in complex multi-defendant cases to ensure equitable distribution of liability based on fault percentages.
Pros and Cons: Joint vs Several Liability
Joint liability requires all parties to be collectively responsible for the entire obligation, ensuring easier recovery for the claimant but potentially burdening individual defendants unfairly. Several liability limits each party's responsibility to their specific share of the obligation, providing protection against disproportionate financial harm but complicating the claimant's ability to collect full damages. Understanding these pros and cons is crucial for parties negotiating contracts or facing litigation involving multiple defendants.
Choosing the Right Liability Structure
Choosing the right liability structure between joint liability and several liability depends on the nature of the obligations and risk distribution among parties. Joint liability requires all parties to be collectively responsible for the full obligation, ensuring creditors can recover the entire debt from any party, while several liability limits each party's responsibility to their individual share, reducing individual exposure. Assessing factors such as the potential for contribution disputes, enforcement ease, and the parties' financial stability helps determine the optimal liability framework for contractual agreements or partnerships.
Joint Liability Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com