Ratio decidendi refers to the legal principle or rationale underlying a court's decision, forming the binding precedent for future cases. Understanding this core element is crucial for interpreting case law and applying legal precedents effectively in your practice. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how ratio decidendi shapes judicial reasoning and impacts legal outcomes.
Table of Comparison
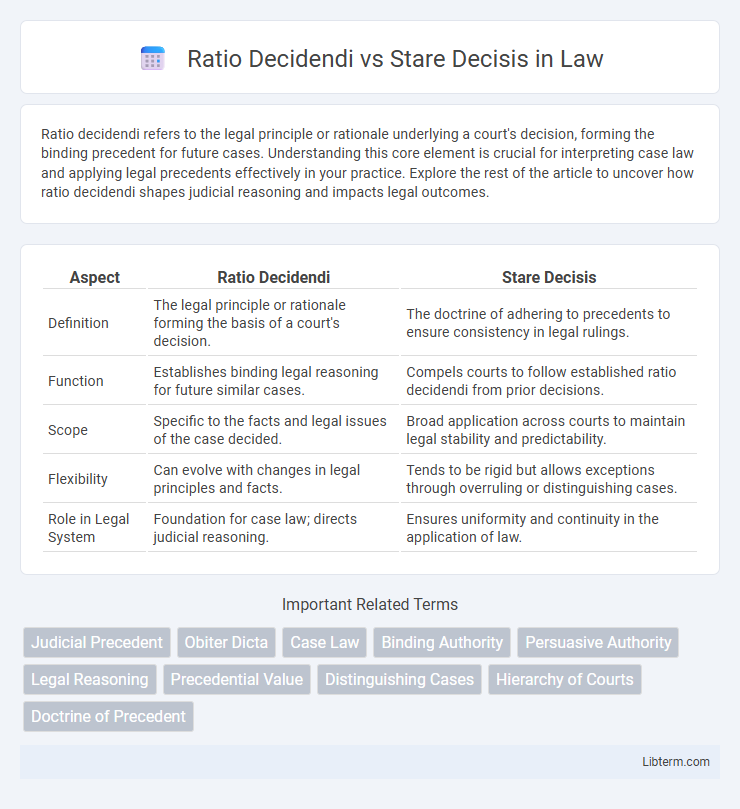
| Aspect | Ratio Decidendi | Stare Decisis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The legal principle or rationale forming the basis of a court's decision. | The doctrine of adhering to precedents to ensure consistency in legal rulings. |
| Function | Establishes binding legal reasoning for future similar cases. | Compels courts to follow established ratio decidendi from prior decisions. |
| Scope | Specific to the facts and legal issues of the case decided. | Broad application across courts to maintain legal stability and predictability. |
| Flexibility | Can evolve with changes in legal principles and facts. | Tends to be rigid but allows exceptions through overruling or distinguishing cases. |
| Role in Legal System | Foundation for case law; directs judicial reasoning. | Ensures uniformity and continuity in the application of law. |
Introduction to Ratio Decidendi and Stare Decisis
Ratio decidendi refers to the legal principle or rationale underlying a court's decision that serves as binding precedent for future cases. Stare decisis is the doctrine obligating courts to follow established precedents to ensure consistency and predictability in the law. Understanding the distinction between ratio decidendi and stare decisis is essential for analyzing how judicial decisions influence subsequent case law.
Defining Ratio Decidendi: The Legal Principle
Ratio decidendi refers to the legal principle or rationale that forms the binding foundation of a judicial decision. It represents the essential rule or reasoning that courts rely on to determine the outcome of a case and sets a precedent for future cases under the doctrine of stare decisis. Understanding ratio decidendi requires analyzing the core legal issue and the court's explanation that directly influences subsequent judicial interpretations.
Understanding Stare Decisis: The Doctrine of Precedent
Stare decisis is the legal principle that mandates courts to follow precedents set by previous decisions to ensure consistency and predictability in the law. It relies heavily on the ratio decidendi, the binding legal reasoning within a case judgment, which courts must adhere to in subsequent cases with similar facts. This doctrine limits judicial discretion by promoting legal stability and uniform application of laws over time.
Key Differences Between Ratio Decidendi and Stare Decisis
Ratio decidendi refers to the legal principle or rationale underlying a judicial decision, forming the binding precedent for future cases, while stare decisis is the doctrine that obligates courts to follow these established precedents. Ratio decidendi constitutes the specific reason that governs the judgment in a case, whereas stare decisis ensures consistency and predictability in the law by requiring lower courts to adhere to higher court rulings. The key difference lies in ratio decidendi being the actual legal reasoning, and stare decisis functioning as the principle of adhering to such reasoning in subsequent cases.
Importance of Ratio Decidendi in Judicial Decisions
Ratio decidendi constitutes the fundamental legal principle or rationale underpinning a judicial decision, serving as the binding precedent in subsequent cases within the common law system. Its importance lies in providing consistency and predictability in judicial rulings by guiding courts in applying legal principles to similar fact patterns. Unlike stare decisis, which refers broadly to the practice of adhering to precedent, ratio decidendi specifically identifies the core legal reasoning that shapes binding authority.
Role of Stare Decisis in Legal Stability
Stare decisis plays a critical role in legal stability by ensuring that courts follow established precedents, maintaining consistency and predictability in judicial decisions. This doctrine binds lower courts to the rulings of higher courts in similar cases, reducing arbitrary interpretations and fostering respect for the rule of law. While ratio decidendi refers to the legal reasoning behind a decision, stare decisis applies that reasoning to future cases, enabling a coherent and stable legal system.
Illustrative Case Examples: Ratio Decidendi vs Stare Decisis
In the landmark case Donoghue v Stevenson [1932] AC 562, the ratio decidendi established the principle of duty of care in negligence, which has since guided countless tort law decisions. Stare decisis was applied in Brown v Board of Education, where the U.S. Supreme Court overturned Plessy v Ferguson's "separate but equal" doctrine, demonstrating how precedent can be re-evaluated to reflect evolving legal and social standards. The contrast between these cases illustrates how ratio decidendi forms the legal reasoning binding in future cases, while stare decisis enforces adherence to established precedents unless overturned by higher courts.
Challenges in Identifying Ratio Decidendi
Identifying the ratio decidendi poses significant challenges due to the complexity and variability of judicial opinions, where distinguishing the binding legal principle from obiter dicta requires careful analysis of case facts and reasoning. Courts often provide multiple reasons for their decisions, complicating the extraction of the essential legal rule that establishes precedent under stare decisis. Ambiguities in judgments and divergent interpretations undermine consistency in applying ratio decidendi, impacting the predictability and stability inherent to the doctrine of stare decisis.
The Impact of Stare Decisis on Legal Evolution
Stare decisis, the principle of adhering to precedent, ensures legal consistency and predictability, stabilizing judicial decisions over time. Its impact on legal evolution involves balancing respect for established rulings with the necessity for adapting laws in response to societal changes and emerging issues. By anchoring new decisions to authoritative ratio decidendi, courts maintain continuity while allowing gradual and reasoned development within the legal system.
Conclusion: Balancing Precedent and Principle in Law
Ratio decidendi establishes the legal principle essential to a case's outcome, while stare decisis mandates adherence to these principles in future rulings to ensure consistency. Balancing precedent and principle requires courts to apply ratio decidendi flexibly, preserving legal stability without perpetuating outdated or unjust decisions. This equilibrium promotes a dynamic legal system that respects precedent but adapts to evolving societal values and contexts.
Ratio Decidendi Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com