The rule of law ensures that all individuals and institutions are accountable under clear, consistent legal principles, safeguarding fairness and preventing abuse of power. Its foundation supports democratic governance, protects human rights, and promotes social stability by maintaining an impartial legal system. Discover how this essential concept shapes societies and why your understanding of its principles matters by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
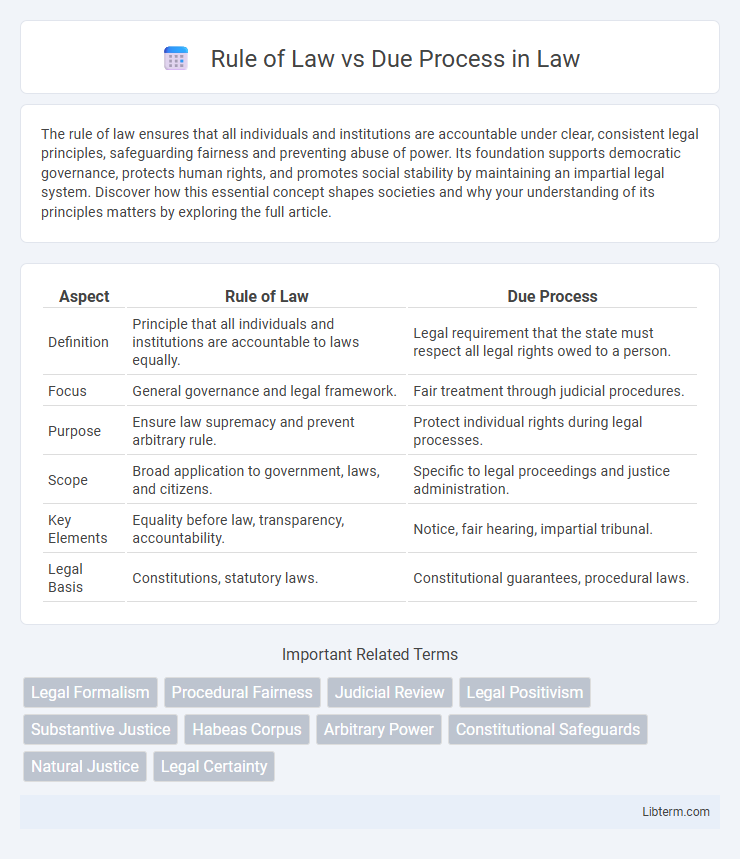
| Aspect | Rule of Law | Due Process |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Principle that all individuals and institutions are accountable to laws equally. | Legal requirement that the state must respect all legal rights owed to a person. |
| Focus | General governance and legal framework. | Fair treatment through judicial procedures. |
| Purpose | Ensure law supremacy and prevent arbitrary rule. | Protect individual rights during legal processes. |
| Scope | Broad application to government, laws, and citizens. | Specific to legal proceedings and justice administration. |
| Key Elements | Equality before law, transparency, accountability. | Notice, fair hearing, impartial tribunal. |
| Legal Basis | Constitutions, statutory laws. | Constitutional guarantees, procedural laws. |
Understanding the Rule of Law
The Rule of Law establishes a framework where all individuals and institutions are accountable to laws that are publicly promulgated, equally enforced, and independently adjudicated, ensuring fairness and preventing arbitrary power. It serves as the foundation for legal certainty, protecting fundamental rights by requiring laws to be clear, stable, and applied consistently. Understanding the Rule of Law is critical to recognizing its role in upholding justice and limiting the influence of subjective discretion within legal systems.
Defining Due Process
Due Process refers to the legal requirement that the state must respect all legal rights owed to a person, ensuring fair treatment through the normal judicial system. It includes procedural safeguards such as the right to a fair trial, the right to be heard, and protection against arbitrary denial of life, liberty, or property. Unlike the broader concept of the Rule of Law, Due Process specifically emphasizes individual protections within the legal framework to prevent unjust governmental actions.
Historical Origins of Rule of Law
The Rule of Law traces its roots to ancient civilizations, notably the Code of Hammurabi and Roman legal principles, emphasizing that law governs society rather than arbitrary decisions by rulers. Its development advanced through English common law and the Magna Carta of 1215, which established that even the monarchy must abide by the law. This historical foundation contrasts with Due Process, which evolved primarily from constitutional guarantees ensuring fair legal procedures and protections for individuals in judicial settings.
The Evolution of Due Process
The evolution of due process reflects a critical development within the broader framework of the rule of law, emphasizing fair treatment through established legal procedures. Rooted in Magna Carta and expanded through landmark cases like *Murray's Lessee v. Hoboken Land & Improvement Co.* (1856), due process now encompasses both procedural and substantive protections. This evolution ensures that laws are not only transparently enforced but also justly applied to protect individual rights against arbitrary state actions.
Key Principles of the Rule of Law
The Rule of Law is founded on key principles such as legality, equality before the law, and the accountability of government authorities, ensuring that no one is above the law. It emphasizes transparency, stability, and the protection of fundamental human rights, creating a predictable legal environment. Due Process, by contrast, specifically guarantees fair procedures and safeguards individual rights during legal proceedings, but it operates within the broader framework established by the Rule of Law.
Fundamental Elements of Due Process
Due process is centered on fundamental elements such as the right to a fair trial, impartial tribunal, notice of charges, and the opportunity to be heard, ensuring procedural fairness in legal proceedings. The rule of law emphasizes that laws must be clear, publicized, and equally enforced, providing a framework within which due process operates. Due process guarantees that individual rights are protected from arbitrary government actions, reinforcing the enforcement of laws consistent with the rule of law principle.
Rule of Law vs Due Process: Core Differences
The Rule of Law establishes a foundation where all individuals and institutions are accountable to transparent, consistent, and fair laws, preventing arbitrary governance. Due Process specifically ensures fair treatment through judicial procedures when legal rights are at stake, emphasizing the right to a fair trial and protection against wrongful deprivation of liberty or property. The core difference lies in Rule of Law being the overarching principle of law's supremacy, while Due Process functions as a procedural safeguard within that framework to uphold justice.
Significance in Modern Legal Systems
The rule of law ensures that all individuals and institutions are subject to and accountable under laws that are publicly promulgated, equally enforced, and independently adjudicated, forming the foundation of legal order and governance. Due process guarantees fair treatment through the normal judicial system, protecting individuals against arbitrary denial of life, liberty, or property by requiring legal procedures and safeguards. Together, they uphold justice and protect individual rights, maintaining legitimacy and public trust in modern legal systems worldwide.
Case Studies Illustrating the Concepts
The Rule of Law ensures that all individuals and institutions are accountable to laws that are publicly promulgated, equally enforced, and independently adjudicated, as demonstrated in the landmark case Brown v. Board of Education which highlighted equal protection under the law. Due Process guarantees fair treatment through the judicial system, exemplified by Miranda v. Arizona where the Supreme Court established procedural safeguards to protect individual rights during police interrogations. These cases illustrate the practical application of Rule of Law and Due Process in safeguarding justice and preventing arbitrary governance.
Impact on Justice and Governance
The Rule of Law ensures that all individuals and institutions are subject to and accountable under clear, consistent legal principles, fostering fairness and predictability in justice systems. Due Process guarantees procedural protections during legal proceedings, preventing arbitrary decisions and safeguarding individual rights. Together, they enhance governance by promoting transparency, accountability, and equitable treatment within legal frameworks.
Rule of Law Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com