Enforcement action refers to the process by which authorities implement legal measures to ensure compliance with laws, regulations, or court orders. These actions can include fines, penalties, or other corrective steps aimed at addressing violations and maintaining order. Explore the full article to understand the different types of enforcement actions and how they may impact your situation.
Table of Comparison
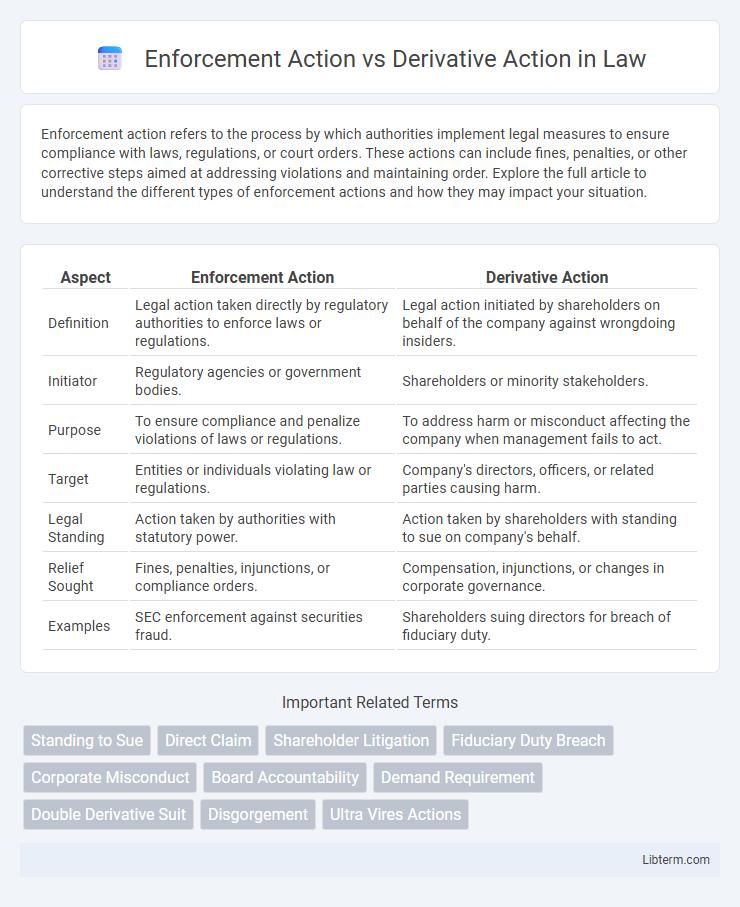
| Aspect | Enforcement Action | Derivative Action |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal action taken directly by regulatory authorities to enforce laws or regulations. | Legal action initiated by shareholders on behalf of the company against wrongdoing insiders. |
| Initiator | Regulatory agencies or government bodies. | Shareholders or minority stakeholders. |
| Purpose | To ensure compliance and penalize violations of laws or regulations. | To address harm or misconduct affecting the company when management fails to act. |
| Target | Entities or individuals violating law or regulations. | Company's directors, officers, or related parties causing harm. |
| Legal Standing | Action taken by authorities with statutory power. | Action taken by shareholders with standing to sue on company's behalf. |
| Relief Sought | Fines, penalties, injunctions, or compliance orders. | Compensation, injunctions, or changes in corporate governance. |
| Examples | SEC enforcement against securities fraud. | Shareholders suing directors for breach of fiduciary duty. |
Understanding Enforcement Action: Definition and Scope
Enforcement action refers to legal measures initiated by regulatory authorities or government agencies to ensure compliance with laws and regulations, targeting violations such as fraud, corporate misconduct, or breaches of statutory duties. Its scope includes investigations, administrative penalties, sanctions, and court proceedings aimed at protecting public interest and maintaining market integrity. Enforcement actions differ from derivative actions, which are shareholder-initiated lawsuits addressing wrongs against the corporation itself rather than regulatory breaches.
What is a Derivative Action? Key Features
A derivative action is a lawsuit initiated by a shareholder on behalf of the corporation, typically against insiders such as directors or officers for breaches of fiduciary duty. Key features include the requirement that the shareholder demonstrates a demand on the board to address the issue or justifies demand futility, and any recovery from the lawsuit benefits the corporation rather than the individual shareholder. This legal mechanism serves as a tool to enforce corporate governance and hold management accountable when the corporation fails to act on wrongdoing.
Legal Basis of Enforcement Actions in Corporate Law
Enforcement actions in corporate law are primarily grounded in statutory provisions such as the Securities Exchange Act and the Companies Act, which empower regulatory bodies to impose penalties for violations like fraud or insider trading. These legal frameworks enable authorities to act directly against corporations or their officers to uphold compliance and protect shareholders' interests. Derivative actions, in contrast, are initiated by shareholders based on common law principles, allowing them to sue on behalf of the corporation for breaches of fiduciary duty or corporate misconduct.
The Purpose and Importance of Derivative Actions
Derivative actions serve to protect shareholders' interests by enabling them to initiate lawsuits on behalf of the corporation against directors or officers who have breached fiduciary duties or acted against the company's best interests. This legal mechanism ensures accountability and corporate governance by allowing minority shareholders to seek remedies when those in control fail to act. The importance of derivative actions lies in their role as a crucial tool for upholding corporate integrity and preventing abuses of power within the company.
Differences Between Enforcement Action and Derivative Action
Enforcement action involves regulatory bodies or authorities initiating legal proceedings to ensure compliance with laws and regulations, often targeting violations impacting the public or market integrity. Derivative action is a lawsuit brought by shareholders on behalf of a corporation against insiders such as directors or executives for breaches of fiduciary duties or mismanagement harming the company. The key difference lies in enforcement action being regulatory-driven to protect public interest, whereas derivative action is shareholder-driven to address internal corporate governance issues.
Initiating an Enforcement Action: Step-by-Step Process
Initiating an enforcement action involves filing a formal complaint with the relevant regulatory authority, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) or the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA), depending on the jurisdiction and nature of the violation. The complainant must provide detailed evidence and legal grounds demonstrating the alleged misconduct, which triggers an investigation phase where regulators gather further information and assess the validity of the claims. If sufficient evidence is found, the authority proceeds with formal charges, leading to potential penalties, fines, or other enforcement remedies against the entity or individual involved.
Filing a Derivative Action: Legal Requirements and Procedures
Filing a derivative action requires shareholders to demonstrate that the corporation's management has failed to protect the company's interests, specifying the alleged wrongdoing and showing the demand to the board was made or why such demand was excused. Legal prerequisites include holding shares at the time of the alleged misconduct, proper notification to the corporation, and adhering to jurisdiction-specific statutes of limitations and procedural rules. Courts closely scrutinize derivative suits to balance shareholders' rights with preventing frivolous litigation, often requiring detailed factual pleadings and compliance with stringent procedural steps such as motion to dismiss and mandatory mediation.
Key Parties Involved: Who Can Bring Each Action?
Enforcement actions are typically initiated by regulatory authorities or government agencies to address violations of laws or regulations, while derivative actions are brought by shareholders on behalf of a corporation to remedy wrongs committed against the company. In enforcement actions, the key parties involved are the regulator as the plaintiff and the offending entity as the defendant. In derivative actions, the shareholders act as plaintiffs, the corporation is nominally the defendant, and the actual wrongdoers often include corporate officers or directors.
Remedies and Outcomes: Enforcement vs. Derivative Actions
Enforcement actions pursue remedies such as cease and desist orders, monetary penalties, and injunctions aimed at correcting regulatory violations directly by authorities. Derivative actions allow shareholders to seek remedies like damages, restitution, or corporate governance reforms on behalf of the corporation when directors fail to act. Enforcement actions typically result in penalties against violators, while derivative actions lead to compensation for the company and improvements in management accountability.
Choosing the Right Course: Factors to Consider
Choosing between enforcement action and derivative action hinges on factors like the nature of the alleged wrongdoing, the plaintiff's standing, and whether the corporation's internal decision-making aligns with shareholder interests. Enforcement actions are typically suited for directly addressing regulatory violations by authorities, while derivative actions empower shareholders to seek redress for harm done to the corporation, requiring proof of demand futility or refusal. Evaluating corporate governance structures, potential remedies, and litigation costs is crucial in determining the appropriate legal strategy.
Enforcement Action Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com