Guardianship establishes a legal relationship where a guardian is appointed to care for an individual incapable of managing their own affairs due to age, disability, or incapacity. This arrangement ensures the protection of the ward's personal, financial, and medical interests under the supervision of the court. Explore the full article to understand how guardianship may affect your rights and responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
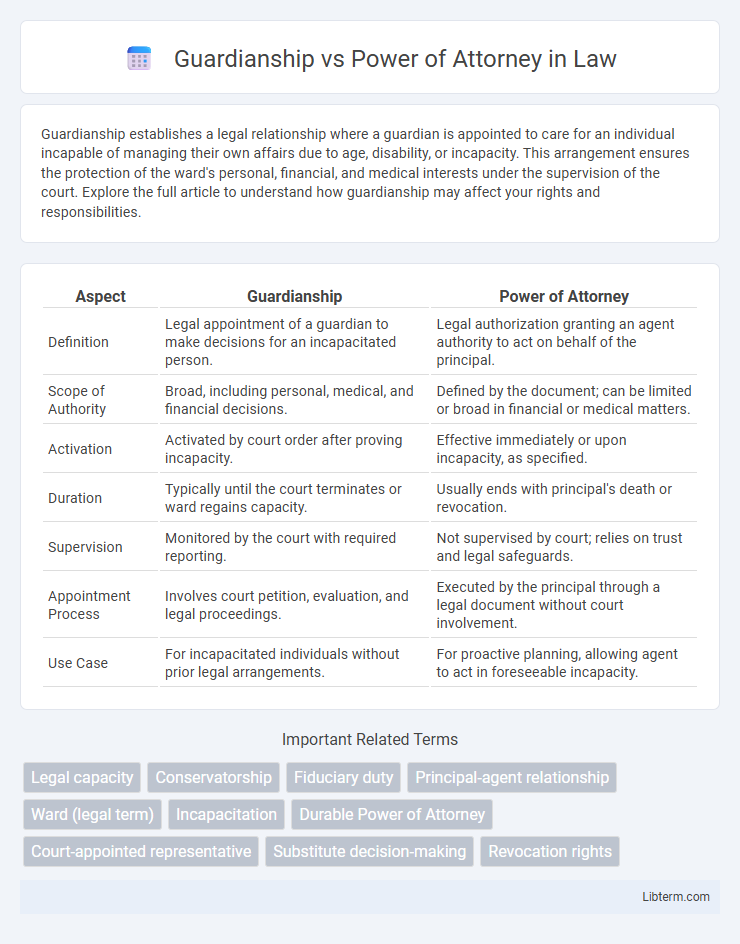
| Aspect | Guardianship | Power of Attorney |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal appointment of a guardian to make decisions for an incapacitated person. | Legal authorization granting an agent authority to act on behalf of the principal. |
| Scope of Authority | Broad, including personal, medical, and financial decisions. | Defined by the document; can be limited or broad in financial or medical matters. |
| Activation | Activated by court order after proving incapacity. | Effective immediately or upon incapacity, as specified. |
| Duration | Typically until the court terminates or ward regains capacity. | Usually ends with principal's death or revocation. |
| Supervision | Monitored by the court with required reporting. | Not supervised by court; relies on trust and legal safeguards. |
| Appointment Process | Involves court petition, evaluation, and legal proceedings. | Executed by the principal through a legal document without court involvement. |
| Use Case | For incapacitated individuals without prior legal arrangements. | For proactive planning, allowing agent to act in foreseeable incapacity. |
Understanding Guardianship: Definition and Scope
Guardianship is a legal relationship where a court appoints an individual, known as a guardian, to make decisions on behalf of a person deemed incapacitated or unable to manage their own affairs. The scope of guardianship can include personal, medical, and financial decisions, often requiring court supervision and adherence to fiduciary duties. Unlike power of attorney, which is granted voluntarily by the individual, guardianship is imposed by the court to protect the interests of those lacking decision-making capacity.
What is Power of Attorney? Key Concepts
Power of attorney (POA) is a legal document granting an individual, known as the agent or attorney-in-fact, the authority to act on behalf of another person, called the principal, in financial, legal, or healthcare matters. Key concepts include the scope of authority, which can be general or specific, and the duration, which may be limited or durable, remaining effective even if the principal becomes incapacitated. Unlike guardianship, power of attorney is typically established voluntarily by the principal without court intervention.
Legal Differences Between Guardianship and Power of Attorney
Guardianship grants a court-appointed individual the authority to make personal, financial, and medical decisions for someone deemed incapacitated, typically after a legal proceeding. Power of Attorney is a legal document allowing a designated person to act on behalf of another in specified matters, effective only while the principal is mentally competent or as outlined in the document. Guardianship involves ongoing court supervision, whereas Power of Attorney operates without court intervention unless challenged.
Situations Requiring Guardianship
Situations requiring guardianship typically involve individuals who are incapacitated due to age, disability, or mental illness and cannot manage their personal or financial affairs independently. Guardianship is often necessary when a court determines that the person is unable to make safe and informed decisions, such as in cases of severe cognitive impairment or permanent disability. Unlike power of attorney, which can be revoked and only applies when the individual willingly grants authority, guardianship is a legal status appointed by a court to protect those lacking decision-making capacity.
When to Consider a Power of Attorney
Consider a Power of Attorney when you want to grant someone legal authority to manage your financial, medical, or legal affairs without court intervention. This option is ideal if you anticipate temporary or specific decision-making needs due to travel, illness, or aging but still retain mental capacity. Powers of Attorney are typically faster to establish and can provide flexibility and control compared to guardianship, which is often reserved for individuals who are incapacitated and require comprehensive oversight.
Decision-Making Authority: Guardianship vs Power of Attorney
Guardianship grants a court-appointed individual comprehensive decision-making authority over an incapacitated person's personal, medical, and financial matters, often overriding prior wishes. Power of Attorney (POA) allows a designated agent to make specific or general decisions on behalf of the principal while they are competent or become incapacitated, with authority limited to the scope defined in the POA document. Unlike guardianship, POA is typically revocable and based on the principal's consent, preserving autonomy until incapacity occurs.
How to Establish Guardianship: Legal Process
Establishing guardianship requires filing a petition with the appropriate probate or family court, detailing the need for a guardian and the proposed ward's condition. A court-appointed evaluation, including medical and psychological assessments, is conducted to determine the individual's capacity and best interests. After a hearing where evidence is presented, the judge decides whether to grant guardianship, appointing a guardian who assumes legal responsibility for the ward's personal and financial decisions.
Creating a Power of Attorney: Steps and Requirements
Creating a power of attorney involves selecting a trusted agent, clearly defining the scope of authority, and drafting a legally binding document according to state laws. The principal must be mentally competent at the time of signing, and the document often requires notarization and witnesses to be valid. Filing or registering the power of attorney with the appropriate government office may be necessary depending on jurisdiction and the type of powers granted.
Pros and Cons of Guardianship and Power of Attorney
Guardianship provides court-appointed authority to manage personal and financial decisions for individuals unable to do so, ensuring legal oversight but often involving costly and time-consuming procedures. Power of attorney grants designated agents the ability to act on someone's behalf with greater flexibility and fewer legal constraints, yet it depends heavily on the trustworthiness of the agent and can lack court supervision. Both options serve to protect vulnerable individuals, but guardianship offers stronger legal protection while power of attorney provides easier implementation and control.
Choosing the Right Option: Factors to Consider
When choosing between guardianship and power of attorney, consider the individual's cognitive abilities and the level of control needed; guardianship suits those who cannot make decisions at all, while power of attorney applies to those who can delegate decisions temporarily or for specific matters. Evaluate the legal process and cost, as guardianship often requires court involvement and ongoing supervision, whereas power of attorney is less formal and more flexible. Assess personal preferences and existing relationships, ensuring the chosen representative is trustworthy and aligned with the principal's best interests and long-term care goals.
Guardianship Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com