Jurisdiction defines the legal authority a court or government body has to make decisions and enforce laws within a specific geographic area or over certain types of cases. Understanding jurisdiction is essential for determining where legal disputes should be resolved and which laws apply to your situation. Explore the rest of the article to learn how jurisdiction impacts your legal rights and responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
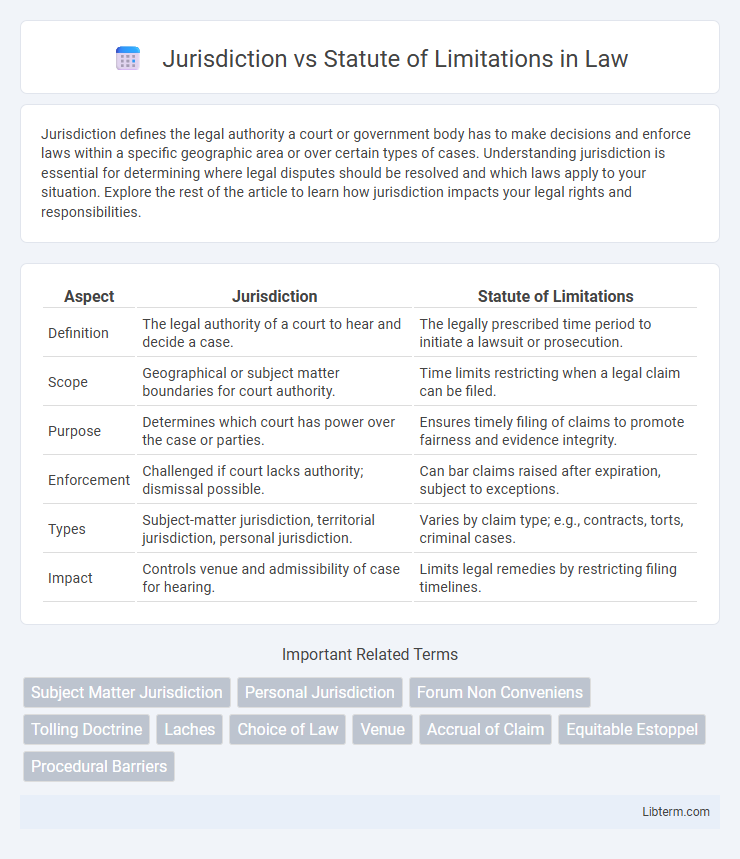
| Aspect | Jurisdiction | Statute of Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The legal authority of a court to hear and decide a case. | The legally prescribed time period to initiate a lawsuit or prosecution. |
| Scope | Geographical or subject matter boundaries for court authority. | Time limits restricting when a legal claim can be filed. |
| Purpose | Determines which court has power over the case or parties. | Ensures timely filing of claims to promote fairness and evidence integrity. |
| Enforcement | Challenged if court lacks authority; dismissal possible. | Can bar claims raised after expiration, subject to exceptions. |
| Types | Subject-matter jurisdiction, territorial jurisdiction, personal jurisdiction. | Varies by claim type; e.g., contracts, torts, criminal cases. |
| Impact | Controls venue and admissibility of case for hearing. | Limits legal remedies by restricting filing timelines. |
Understanding Jurisdiction: Legal Authority Defined
Jurisdiction refers to the legal authority granted to a court or governmental body to hear and decide cases within a specific geographic area or subject matter. It determines which court has the power to adjudicate disputes and enforce laws, ensuring that legal proceedings occur in the appropriate venue. Understanding jurisdiction is essential to avoid challenges related to the court's authority and to ensure proper administration of justice.
What Is a Statute of Limitations?
A statute of limitations refers to the legally prescribed time period within which a plaintiff must initiate a lawsuit or criminal prosecution, ensuring timely resolution and preventing indefinite threats of legal action. It varies by jurisdiction and case type, such as personal injury, contract disputes, or criminal offenses, typically ranging from one to several years. Jurisdiction determines the authority of a court to hear a case, while the statute of limitations sets the deadline to file that case within the appropriate jurisdiction.
Key Differences Between Jurisdiction and Statute of Limitations
Jurisdiction refers to a court's legal authority to hear and decide a case based on geographic area, subject matter, or parties involved, while statute of limitations sets the maximum time period within which a legal action can be initiated. Jurisdiction determines the court's ability to adjudicate a case, whereas the statute of limitations governs the timeliness and enforceability of claims. Understanding these distinctions is essential for correctly filing lawsuits and ensuring a court has both authority and procedural standing.
How Jurisdiction Impacts Legal Proceedings
Jurisdiction determines the authority of a court to hear and decide a case, directly impacting the legitimacy and enforceability of legal proceedings. Without proper jurisdiction, a court's rulings can be challenged and potentially invalidated, causing delays or dismissal of the case. Statute of limitations sets the deadline for filing a lawsuit, but jurisdiction establishes the foundational power to adjudicate the matter.
The Purpose of Statutes of Limitations in Law
Statutes of limitations establish a deadline for initiating legal actions to ensure timely and fair resolution of disputes. They protect defendants from defending against claims after evidence has deteriorated or memories have faded, preserving the integrity of the judicial process. These time limits promote legal certainty and encourage diligent prosecution of claims within a reasonable period.
Jurisdiction vs. Statute of Limitations: Common Misconceptions
Jurisdiction and statute of limitations are often confused but serve distinct legal functions; jurisdiction determines a court's authority to hear a case, while statute of limitations sets the time limit for filing a lawsuit. A common misconception is that missing the statute of limitations affects jurisdiction, but it actually impacts the timeliness and enforceability of a claim, not the court's power. Understanding this distinction helps in accurately assessing legal challenges and procedural defenses in litigation.
Factors Affecting Jurisdiction in Legal Cases
Jurisdiction in legal cases depends on factors including the geographic location where the dispute arose, the subject matter involved, and the parties' connections to the area. Courts assess personal jurisdiction based on the defendant's residency, physical presence, or consent to the forum, while subject matter jurisdiction hinges on the case type, such as criminal or civil matters. Understanding the distinctions between jurisdictional authority and the statute of limitations, which governs time limits on filing claims, is crucial for case admissibility.
Exceptions and Extensions to Statutes of Limitations
Exceptions and extensions to statutes of limitations often arise in cases involving fraud, minors, or discovery of harm after the fact, allowing claims to proceed beyond standard deadlines. Jurisdictional rules can affect these timelines by determining which court's laws apply, sometimes providing longer or shorter limitation periods based on the venue. Equitable tolling and specific legislative provisions may further extend the statute of limitations, especially in complex cases like medical malpractice or latent injuries.
Case Studies: Jurisdiction and Statute of Limitations in Practice
Case studies illustrate how jurisdiction determines the court's authority to hear a case, while the statute of limitations sets the timeframe within which a claim must be filed, often influencing case outcomes. For instance, in *Daimler AG v. Bauman*, the U.S. Supreme Court emphasized jurisdiction limits based on a defendant's contacts with the forum state, affecting plaintiffs' ability to sue outside their home jurisdiction. In contrast, the application of statutes of limitations, such as the two-year limit in personal injury claims under state law, frequently results in dismissal if the claim is not timely brought, underscoring the critical interplay between jurisdictional reach and time constraints.
Legal Strategies: Navigating Jurisdiction and Statute of Limitations
Legal strategies for navigating jurisdiction and statute of limitations require a precise understanding of the geographic and subject-matter scope where a court can hear a case, alongside the legally defined timeframe within which claims must be filed. Effective counsel evaluates these parameters to determine the most advantageous forum and timing, ensuring claims are not dismissed for lack of jurisdiction or expired limitation periods. Strategic litigation planning often involves filing actions in courts with favorable jurisdictional reach and monitoring critical deadlines dictated by statutes of limitations to preserve clients' rights.
Jurisdiction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com