A Judgment Debtor Receiver is appointed to manage and protect the assets of a debtor who has failed to satisfy a court judgment. This receiver ensures that the debtor's property is preserved and available for satisfying creditor claims in a lawful and efficient manner. Discover how a Judgment Debtor Receiver can impact your case and what steps you may need to take next by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
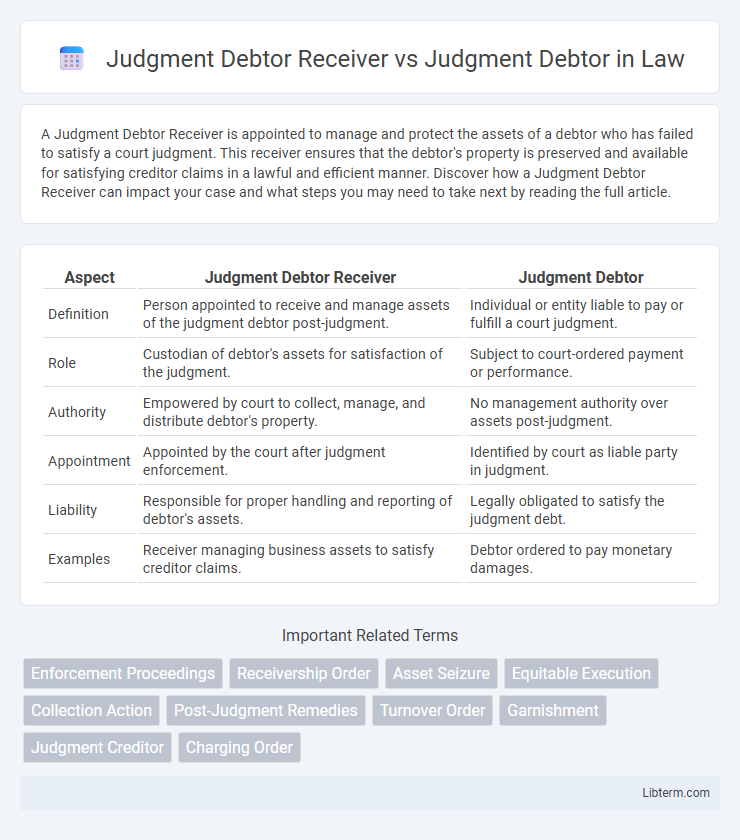
| Aspect | Judgment Debtor Receiver | Judgment Debtor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Person appointed to receive and manage assets of the judgment debtor post-judgment. | Individual or entity liable to pay or fulfill a court judgment. |
| Role | Custodian of debtor's assets for satisfaction of the judgment. | Subject to court-ordered payment or performance. |
| Authority | Empowered by court to collect, manage, and distribute debtor's property. | No management authority over assets post-judgment. |
| Appointment | Appointed by the court after judgment enforcement. | Identified by court as liable party in judgment. |
| Liability | Responsible for proper handling and reporting of debtor's assets. | Legally obligated to satisfy the judgment debt. |
| Examples | Receiver managing business assets to satisfy creditor claims. | Debtor ordered to pay monetary damages. |
Understanding the Judgment Debtor: Definition and Role
A Judgment Debtor is an individual or entity legally obligated to satisfy a court-issued monetary judgment. Their role involves repayment of the debt as mandated by the judgment, often leading to asset seizure or wage garnishment if non-compliance occurs. Understanding this definition is critical for distinguishing the Judgment Debtor from a Judgment Debtor Receiver, who is appointed to manage or liquidate the debtor's assets to fulfill the judgment.
Who Is a Judgment Debtor Receiver?
A Judgment Debtor Receiver is an individual or entity appointed by the court to take control of a judgment debtor's assets or business operations to satisfy a debt owed to a judgment creditor. Unlike the judgment debtor, who is the party obligated to pay the debt, the receiver acts as a neutral third party managing or liquidating assets to ensure fair distribution to creditors. The appointment of a Judgment Debtor Receiver typically occurs in complex cases where direct collection efforts against the judgment debtor have proven ineffective.
Legal Basis for Appointing a Judgment Debtor Receiver
The legal basis for appointing a Judgment Debtor Receiver lies in the court's authority to enforce a money judgment by taking control of the debtor's property or business operations to satisfy the judgment. This appointment is governed by specific procedural rules under civil procedure codes, which require that the judgment debtor has failed to comply with the monetary judgment, justifying the need for a receiver to protect the creditor's interests. The receiver acts as a neutral party, managing or liquidating assets to ensure payment, and their appointment must be explicitly authorized by a court order following proof of the debtor's inability or refusal to pay.
Key Differences: Judgment Debtor Receiver vs Judgment Debtor
A Judgment Debtor is an individual or entity required to satisfy a court judgment by paying a debt or performing an obligation, while a Judgment Debtor Receiver is a court-appointed official tasked with managing or liquidating the debtor's assets to fulfill the judgment. The key difference lies in their roles: the Judgment Debtor owes the debt, whereas the Judgment Debtor Receiver acts under court authority to oversee asset distribution. This distinction ensures effective enforcement of judgments through direct debtor responsibility versus third-party asset management.
Powers and Limitations of a Judgment Debtor Receiver
A Judgment Debtor Receiver possesses the authority to take control of a judgment debtor's assets, manage, and sell property to satisfy a court judgment, effectively acting as an intermediary between the judgment creditor and debtor. Their powers often include collecting rents, operating the business, and maintaining property, but they face limitations such as adherence to court orders, restrictions on asset disposal without approval, and the obligation to act in the best interest of all parties involved. Unlike the judgment debtor, who retains ownership and control subject to court enforcement, the receiver's role is to ensure compliance with the judgment while maintaining transparency and accountability in asset management.
Rights and Responsibilities of the Judgment Debtor
The judgment debtor retains the right to redeem their property before the receiver completes the sale, ensuring a chance to satisfy the debt voluntarily. Responsibilities include providing accurate financial information and cooperating with the receiver to facilitate asset evaluation and disposition. Failure to comply may result in court sanctions or continued possession relinquishment to the judgment debtor receiver for debt recovery.
Process of Appointing a Judgment Debtor Receiver
The process of appointing a judgment debtor receiver involves the creditor petitioning the court after obtaining a judgment against the debtor, demonstrating the debtor's failure to satisfy the judgment voluntarily. The court then evaluates evidence of the debtor's non-compliance, financial status, and potential asset concealment before issuing an order to appoint the receiver. Once appointed, the judgment debtor receiver gains authority to manage, collect, and liquidate the debtor's assets to satisfy the judgment, operating independently from the judgment debtor's control.
Impact on Asset Management and Recovery
Judgment Debtor Receivers significantly enhance asset management and recovery by assuming control over the judgment debtor's assets, ensuring efficient administration and preservation of value during enforcement. Unlike judgment debtors, who maintain ownership and risk dissipating assets, receivers operate under court authority to protect and maximize asset recovery for creditors. This judicial oversight minimizes loss and accelerates creditor repayment by directly managing the debtor's property and financial affairs.
Common Legal Challenges and Resolutions
Judgment Debtor Receivers frequently face legal challenges surrounding asset identification and valuation, which complicate the enforcement of court judgments against the Judgment Debtor. Disputes often arise over the receiver's authority to manage or liquidate assets, requiring judicial clarification to resolve conflicts between parties. Courts typically address these issues by issuing detailed orders that define the receiver's powers and establish procedural safeguards to protect the rights of all stakeholders.
Practical Implications for Creditors and Debtors
A Judgment Debtor Receiver manages the debtor's assets to satisfy court judgments, ensuring creditors receive repayment through asset liquidation or revenue collection. Judgment Debtors retain control over their assets but face legal constraints restricting their ability to dispose of property or evade debt obligations. Creditors benefit from the appointment of a receiver as it provides a structured enforcement mechanism, while debtors may experience reduced asset control and increased scrutiny of financial activities.
Judgment Debtor Receiver Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com