A non-solicitation agreement protects businesses by preventing former employees or partners from enticing clients or staff away, thereby safeguarding valuable relationships and confidential information. Such agreements are crucial in maintaining competitive advantage and ensuring that proprietary information remains secure. Explore the rest of the article to understand how a non-solicitation agreement can specifically benefit your business and the key elements it should include.
Table of Comparison
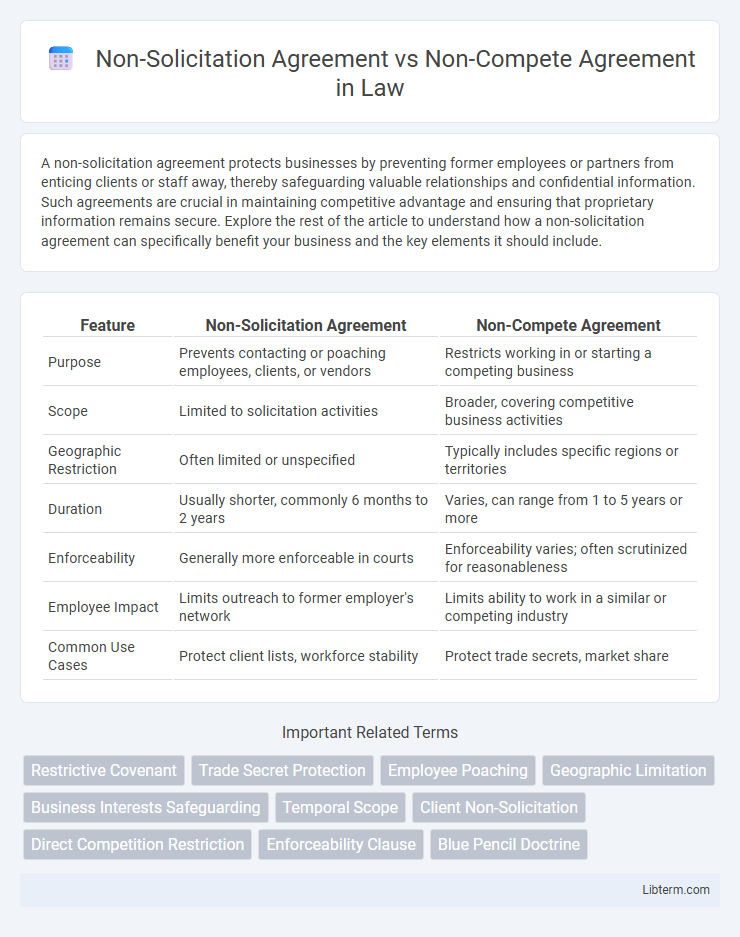
| Feature | Non-Solicitation Agreement | Non-Compete Agreement |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents contacting or poaching employees, clients, or vendors | Restricts working in or starting a competing business |
| Scope | Limited to solicitation activities | Broader, covering competitive business activities |
| Geographic Restriction | Often limited or unspecified | Typically includes specific regions or territories |
| Duration | Usually shorter, commonly 6 months to 2 years | Varies, can range from 1 to 5 years or more |
| Enforceability | Generally more enforceable in courts | Enforceability varies; often scrutinized for reasonableness |
| Employee Impact | Limits outreach to former employer's network | Limits ability to work in a similar or competing industry |
| Common Use Cases | Protect client lists, workforce stability | Protect trade secrets, market share |
Understanding Non-Solicitation Agreements
Non-Solicitation Agreements specifically prevent former employees or business partners from soliciting clients, customers, or employees of the company for a defined period, ensuring protection of business relationships without restricting broader employment opportunities. These agreements focus on maintaining existing business contacts rather than limiting an individual's ability to work in the same industry, unlike Non-Compete Agreements which impose broader restrictions on competing with the employer. Understanding the scope and enforceability of Non-Solicitation Agreements is crucial for businesses aiming to safeguard client relationships while minimizing legal challenges.
What is a Non-Compete Agreement?
A Non-Compete Agreement is a legally binding contract that restricts an employee from joining or starting a competing business within a specific geographic area and time frame after leaving their current employer. It aims to protect trade secrets, confidential information, and business interests by limiting competition and preventing unfair advantage. Companies often use non-compete agreements to safeguard proprietary knowledge and maintain their market position.
Key Differences Between Non-Solicitation and Non-Compete
Non-solicitation agreements restrict employees from contacting or poaching clients, customers, or employees of their former employer for a defined period, focusing primarily on relationship preservation rather than market competition. Non-compete agreements impose broader restrictions by prohibiting employees from engaging in similar business activities or working for competitors within a specific geographic area and time frame, aiming to limit market competition and protect trade secrets. Key differences include the scope of restrictions--non-solicitation targets direct solicitation behaviors, whereas non-compete limits employment or business activities altogether.
Purpose and Scope of Each Agreement
Non-Solicitation Agreements primarily prevent employees or contractors from poaching clients, customers, or employees after leaving a company, ensuring protection of business relationships and workforce stability. Non-Compete Agreements restrict former employees from working with competitors or starting competing businesses within a specific geographic area and timeframe, aiming to safeguard trade secrets and competitive advantage. The scope of Non-Solicitation Agreements is narrower, focusing on direct solicitation, while Non-Compete Agreements impose broader work limitations to minimize market competition.
Legal Enforceability of Non-Solicitation vs Non-Compete
Non-solicitation agreements typically have higher legal enforceability compared to non-compete agreements because they narrowly restrict direct solicitation of employees or clients without broadly limiting professional opportunities. Courts often scrutinize non-compete agreements more strictly, emphasizing reasonableness in duration, geographic scope, and the necessity to protect legitimate business interests. Enforceability varies widely by jurisdiction, with some states like California largely prohibiting non-compete clauses while favoring non-solicitation agreements as a less restrictive means of protecting trade secrets and business relationships.
Typical Clauses in Non-Solicitation Agreements
Typical clauses in non-solicitation agreements include restrictions on soliciting employees, clients, or customers of the employer for a specified time after termination. These agreements often define the scope, geographic area, and duration of non-solicitation to protect business relationships without overly limiting the former employee's future employment opportunities. Unlike non-compete agreements that restrict working in competing businesses, non-solicitation clauses specifically target the prevention of unfair recruitment or client poaching.
Common Provisions in Non-Compete Agreements
Non-compete agreements commonly include provisions defining the geographic scope, duration, and restricted activities to prevent former employees from working with direct competitors or starting a competing business within a specified area and timeframe. These agreements often feature clauses addressing confidentiality obligations, consideration for signing, and consequences of breach, such as injunctive relief or monetary damages. Courts typically scrutinize the reasonableness of these provisions to balance employer protection with employee mobility and public interest.
Pros and Cons for Employers and Employees
Non-Solicitation Agreements protect employers by preventing former employees from poaching clients or staff, promoting business stability, but can limit employees' freedom to engage in similar professional networks. Non-Compete Agreements offer strong protection against direct competition but may hinder employee mobility and career growth due to geographic or time restrictions. Employers gain competitive advantage through both agreements, while employees face potential limitations on future job opportunities and entrepreneurship.
How Courts Interpret Restrictive Covenants
Courts interpret non-solicitation agreements more favorably than non-compete agreements, often upholding them as reasonable restrictions aimed at protecting legitimate business interests like client relationships. Judicial scrutiny of non-compete clauses tends to be stricter due to their broader impact on an individual's ability to work, frequently requiring precise geographic and temporal limits to ensure enforceability. Courts balance the employer's need to safeguard trade secrets against the employee's right to earn a livelihood when deciding the validity of restrictive covenants.
Best Practices When Drafting Restrictive Agreements
When drafting restrictive agreements, clearly define the scope, duration, and geographic limitations to ensure enforceability and avoid overly broad restrictions. Tailor non-solicitation agreements to focus specifically on preventing the solicitation of employees or clients without restricting legitimate business activities, while non-compete agreements should limit competitive behaviors only to what is necessary to protect legitimate business interests. Consult current jurisdictional laws to align agreements with legal standards and incorporate reasonable considerations to balance protection with fairness for all parties involved.
Non-Solicitation Agreement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com