Eviction is the legal process through which a landlord removes a tenant from a rental property, often due to non-payment of rent or violation of lease terms. Understanding your rights and the specific procedures involved is crucial to protect your interests during an eviction. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to navigate eviction effectively and safeguard your living situation.
Table of Comparison
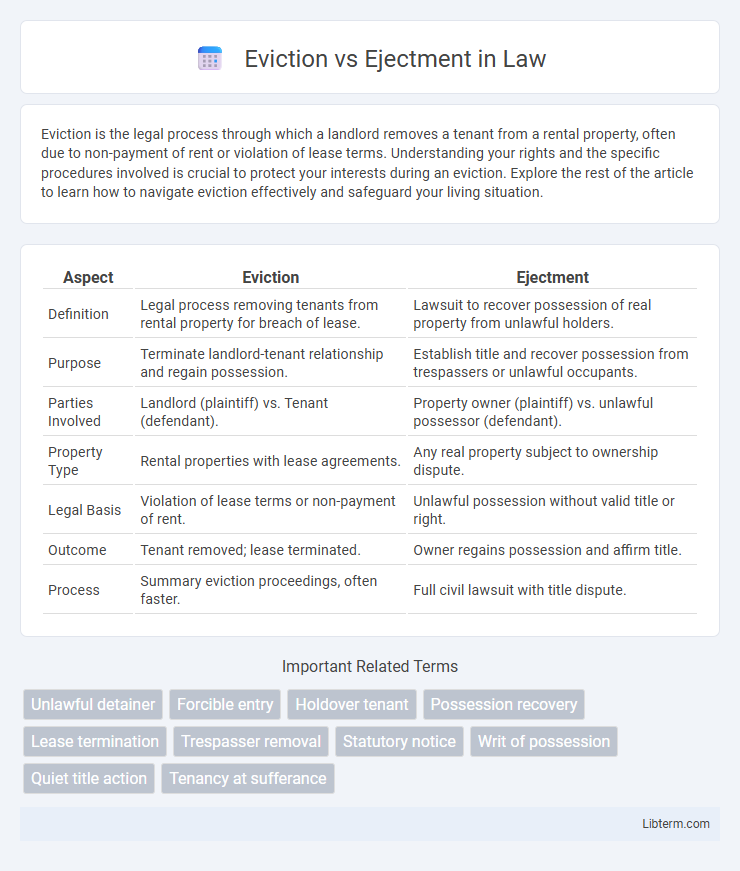
| Aspect | Eviction | Ejectment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal process removing tenants from rental property for breach of lease. | Lawsuit to recover possession of real property from unlawful holders. |
| Purpose | Terminate landlord-tenant relationship and regain possession. | Establish title and recover possession from trespassers or unlawful occupants. |
| Parties Involved | Landlord (plaintiff) vs. Tenant (defendant). | Property owner (plaintiff) vs. unlawful possessor (defendant). |
| Property Type | Rental properties with lease agreements. | Any real property subject to ownership dispute. |
| Legal Basis | Violation of lease terms or non-payment of rent. | Unlawful possession without valid title or right. |
| Outcome | Tenant removed; lease terminated. | Owner regains possession and affirm title. |
| Process | Summary eviction proceedings, often faster. | Full civil lawsuit with title dispute. |
Understanding Eviction: Definition and Legal Basis
Eviction is the legal process by which a landlord removes a tenant from a property due to breach of lease terms or nonpayment of rent, grounded in property and landlord-tenant law. This procedure requires adherence to state-specific statutes, including proper notice periods and court orders, ensuring the tenant's rights are protected throughout. Understanding eviction involves recognizing its basis in contractual agreements and statutory regulations that govern occupancy and tenancy rights.
What is Ejectment? Key Differences Explained
Ejectment is a legal action aimed at recovering possession of real property wrongfully occupied by another party, typically involving the removal of a tenant or trespasser without a lease agreement. Unlike eviction, which enforces the termination of a landlord-tenant relationship based on lease violations or nonpayment of rent, ejectment addresses disputes over rightful ownership or possession without an existing tenancy. Key differences include the basis for the claim--eviction stems from lease breaches, while ejectment arises from ownership or possession rights--and the types of parties involved, with eviction focusing on landlord and tenant, and ejectment involving property owners and unauthorized occupants.
Common Grounds for Eviction
Common grounds for eviction include non-payment of rent, lease violations, property damage, illegal activities, and failure to vacate after lease expiration. Eviction processes enforce tenants to leave rental premises through legal procedures, protecting landlord rights. Understanding these grounds helps prevent disputes and ensures compliance with landlord-tenant laws.
Typical Scenarios Requiring Ejectment
Typical scenarios requiring ejectment often involve disputes where a tenant or trespasser refuses to vacate property despite lacking a valid lease or ownership right, such as unauthorized occupants remaining after lease termination or unlawful possession following a property sale. Landlords or property owners resort to ejectment actions to remove squatters, holdover tenants without legal claim, or former owners who no longer have title rights. Unlike eviction, which generally addresses breaches of lease terms, ejectment focuses on restoring possession due to defective or absent property interest.
Legal Procedures: Eviction vs Ejectment
Eviction is a legal process used by landlords to remove tenants from rental properties due to lease violations or nonpayment of rent, typically initiated through a court-issued eviction notice. Ejectment involves a property owner's legal action to recover possession of real property from someone wrongfully occupying it, often requiring proof of ownership in a civil lawsuit. Eviction follows tenancy laws with specific procedural steps like notice periods and court hearings, while ejectment requires establishing property title and unjust possession in a more complex judicial proceeding.
Rights of Landlords and Occupants in Each Process
Eviction primarily protects landlords' rights to regain possession of rental property when tenants violate lease terms, focusing on unlawful detainer actions and requiring due process to remove occupants. Ejectment addresses property ownership disputes, allowing rightful owners to reclaim possession from wrongdoers, emphasizing title and possession claims rather than lease violations. Occupants in eviction cases have defenses based on tenancy agreements, while in ejectment, occupants must prove legal right to possess to avoid removal.
Court Involvement and Documentation Required
Eviction involves a formal legal process initiated by landlords to remove tenants for lease violations, requiring court filings such as eviction notices and complaints. Ejectment addresses the removal of individuals unlawfully occupying property without tenancy rights, demanding more complex documentation like title deeds and proof of ownership to establish rightful possession. Court involvement in eviction cases follows established tenant protection laws, while ejectment actions often necessitate proving historic ownership and may proceed through higher courts.
Timelines and Outcomes for Both Actions
Eviction proceedings typically follow a strict timeline starting with a notice to vacate, often ranging from 3 to 30 days, followed by a court hearing and potential removal within weeks if the landlord prevails. Ejectment actions, used to recover possession of real property wrongfully occupied, involve a longer process that may take several months due to complex legal requirements and often result in a court order for possession rather than immediate removal. Outcomes for eviction usually lead to tenant removal and potential damage claims, whereas ejectment resolves property title disputes, giving the rightful owner legal possession.
Preventing Legal Issues: Best Practices for Property Owners
Eviction and ejectment are critical legal processes property owners must understand to prevent costly disputes and ensure compliance with tenant laws. Implementing clear lease agreements, maintaining detailed records of tenant interactions, and following proper notice procedures reduce the risk of wrongful eviction claims or delayed property recovery. Consulting local landlord-tenant laws and engaging legal counsel early protects property owners from potential litigation in eviction and ejectment cases.
Frequently Asked Questions on Eviction and Ejectment
Eviction refers to the legal process by which a landlord removes a tenant from rental property for reasons such as nonpayment of rent or lease violations, while ejectment involves reclaiming possession of real property from someone unlawfully occupying it without any tenancy agreement. Frequently asked questions on eviction include inquiries about required notice periods, tenant rights during eviction, and the eviction timeline, whereas questions on ejectment often focus on proving unlawful possession, filing correct legal actions, and the differences between ejectment and eviction procedures. Understanding these distinctions helps landlords and property owners navigate property disputes and enforce their rights effectively.
Eviction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com