Territorial jurisdiction defines the geographical limits within which a court has the authority to hear and decide cases. It ensures that legal disputes are handled in the appropriate location based on where the events occurred or where the parties reside. Explore the rest of the article to understand how territorial jurisdiction impacts your legal rights and court proceedings.
Table of Comparison
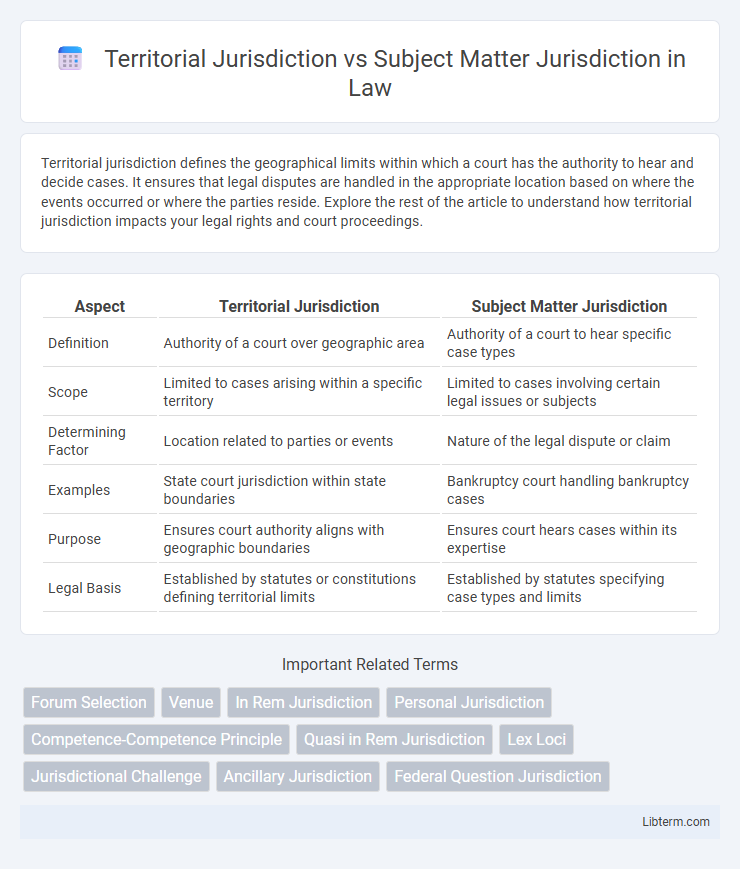
| Aspect | Territorial Jurisdiction | Subject Matter Jurisdiction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Authority of a court over geographic area | Authority of a court to hear specific case types |
| Scope | Limited to cases arising within a specific territory | Limited to cases involving certain legal issues or subjects |
| Determining Factor | Location related to parties or events | Nature of the legal dispute or claim |
| Examples | State court jurisdiction within state boundaries | Bankruptcy court handling bankruptcy cases |
| Purpose | Ensures court authority aligns with geographic boundaries | Ensures court hears cases within its expertise |
| Legal Basis | Established by statutes or constitutions defining territorial limits | Established by statutes specifying case types and limits |
Introduction to Jurisdiction
Territorial jurisdiction refers to a court's authority to hear cases within a specific geographic area, determined by state, county, or district boundaries. Subject matter jurisdiction defines a court's power to adjudicate particular types of cases, such as criminal, civil, or family law matters. Understanding these distinct jurisdiction types is essential for ensuring cases are filed in the proper court, preventing jurisdictional conflicts or dismissals.
Definition of Territorial Jurisdiction
Territorial jurisdiction refers to the legal authority granted to a court or governmental body to hear cases and enforce laws within a specific geographic area, such as a state, county, or district. It determines the spatial boundaries where a court can operate and exercise its power over persons, property, and events located within that area. Understanding territorial jurisdiction is essential for ensuring cases are heard in the appropriate venue according to geographic limits established by law.
Definition of Subject Matter Jurisdiction
Subject matter jurisdiction refers to a court's authority to hear cases of a specific type or cases relating to particular subject matter, such as criminal, civil, family, or bankruptcy law. Territorial jurisdiction, in contrast, pertains to a court's power to adjudicate cases within a defined geographic area or territory. Understanding subject matter jurisdiction is crucial because a court lacking this authority must dismiss the case regardless of territorial considerations.
Key Differences Between Territorial and Subject Matter Jurisdiction
Territorial jurisdiction refers to a court's authority to hear cases arising within a specific geographic area, while subject matter jurisdiction involves a court's power to adjudicate particular types of disputes or legal issues. Key differences include that territorial jurisdiction limits a court's authority based on location, ensuring cases are tried in the jurisdiction where the events occurred or the parties reside, whereas subject matter jurisdiction restricts courts to specific categories such as criminal, civil, or family law cases. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for determining the proper venue and court system capable of legally resolving a dispute.
Legal Basis for Territorial Jurisdiction
Territorial jurisdiction is legally grounded in the principle that a court's authority extends only within the geographic boundaries of its territorial limits, often defined by statutes or constitutional provisions. This jurisdiction enables courts to adjudicate matters involving persons, property, or events occurring within that specific area, ensuring respect for sovereignty and orderly administration of justice. Subject matter jurisdiction, in contrast, arises from the nature of the case or the legal issues presented, independent of geographic constraints, focusing solely on the court's competence to hear particular types of disputes.
Legal Basis for Subject Matter Jurisdiction
Subject matter jurisdiction derives from statutory authorization, defining a court's authority to hear specific types of cases such as criminal, civil, or family law matters, based on legal provisions established by legislatures. Territorial jurisdiction, in contrast, is determined by geographic boundaries delineated by law, specifying where a court's authority applies within a defined area. Understanding the legal basis for subject matter jurisdiction is critical for ensuring courts adjudicate only cases within their legislatively sanctioned scope, maintaining judicial validity.
Importance in Civil and Criminal Cases
Territorial jurisdiction determines the geographic area where a court has authority to hear a case, which is essential for ensuring that disputes are resolved within the appropriate location and legal system. Subject matter jurisdiction defines the court's power to hear particular types of cases, such as civil or criminal matters, and is critical for the court's legal competence to adjudicate specific issues. Correct application of both jurisdictions ensures fair trial procedures and prevents jurisdictional conflicts in civil and criminal law.
Jurisdictional Challenges and Conflicts
Territorial jurisdiction and subject matter jurisdiction are fundamental concepts that often lead to jurisdictional challenges and conflicts in legal disputes. Territorial jurisdiction refers to a court's authority over events, persons, or property within a specific geographic area, whereas subject matter jurisdiction concerns the court's power to adjudicate particular types of cases, such as criminal, civil, or family law matters. Conflicts arise when questions emerge about whether a court has the proper geographic authority or legal competency to hear a case, often resulting in motions to dismiss or transfer based on jurisdictional grounds.
Landmark Cases Illustrating Jurisdictional Issues
Landmark cases such as International Shoe Co. v. Washington clarified the principles of territorial jurisdiction by establishing minimum contacts standards for personal jurisdiction. In contrast, subject matter jurisdiction issues were addressed in cases like Marbury v. Madison, which defined the authority of courts to hear specific types of cases. These decisions play a crucial role in delineating the boundaries of court power over parties and legal issues, ensuring proper application of jurisdictional principles.
Conclusion: Significance in Legal Proceedings
Territorial jurisdiction determines the geographical area within which a court has the authority to hear a case, while subject matter jurisdiction defines the types of cases a court can adjudicate based on the legal issues involved. Understanding the distinction ensures that legal proceedings occur in the proper court, which is essential for the enforcement of judgments and the protection of defendants' rights. Incorrect jurisdiction can lead to dismissal of cases, wasted resources, and delayed justice, highlighting its critical role in effective legal system functioning.
Territorial Jurisdiction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com