Interpretation involves analyzing and explaining the meaning behind various forms of information, such as texts, data, or artistic expressions, to uncover deeper insights. It plays a crucial role in understanding context, intent, and significance across different fields, from literature to data science. Discover how enhancing your interpretation skills can transform your perspective by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
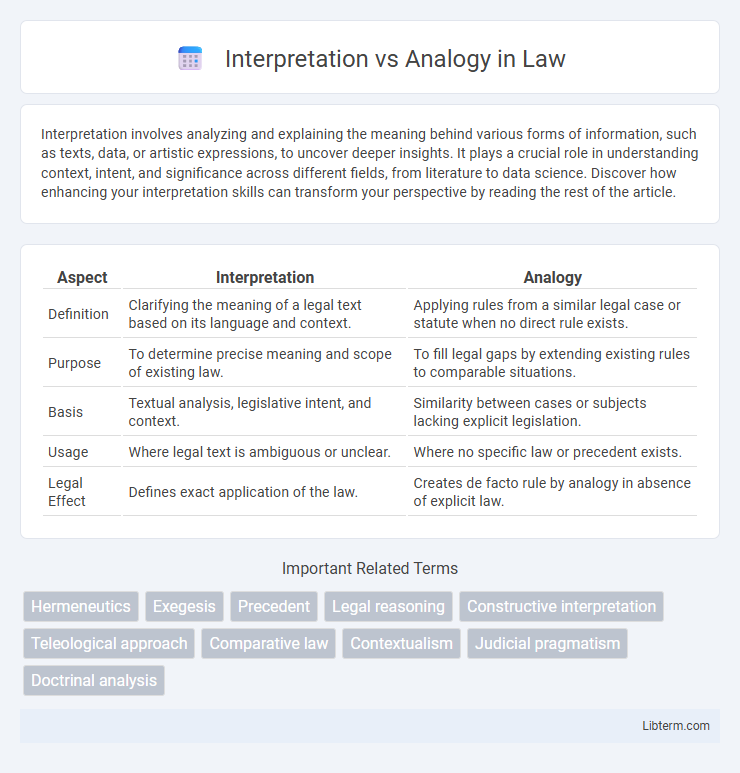
| Aspect | Interpretation | Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Clarifying the meaning of a legal text based on its language and context. | Applying rules from a similar legal case or statute when no direct rule exists. |
| Purpose | To determine precise meaning and scope of existing law. | To fill legal gaps by extending existing rules to comparable situations. |
| Basis | Textual analysis, legislative intent, and context. | Similarity between cases or subjects lacking explicit legislation. |
| Usage | Where legal text is ambiguous or unclear. | Where no specific law or precedent exists. |
| Legal Effect | Defines exact application of the law. | Creates de facto rule by analogy in absence of explicit law. |
Understanding Interpretation and Analogy
Interpretation involves explaining the meaning of a specific text, event, or concept by analyzing its context and underlying significance, while analogy draws a comparison between two different things to highlight similarities and aid understanding. Understanding interpretation requires recognizing the intent, symbolism, and nuances within the original material, whereas analogy leverages familiar concepts to clarify unfamiliar or complex ideas. Mastery of both skills enhances critical thinking by bridging gaps between known and unknown knowledge domains.
Defining Interpretation: A Semantic Perspective
Interpretation involves assigning meaning to a text or symbol based on contextual understanding and semantic analysis, emphasizing the intrinsic significance rather than superficial resemblance. It requires decoding intentions, cultural nuances, and linguistic subtleties to reveal deeper insights beyond literal expression. Unlike analogy, which highlights similarity between different concepts, interpretation centers on extracting precise meaning from a specific source.
What is Analogy? Clarifying the Concept
Analogy is a cognitive process of identifying similarities between two different concepts or objects to explain or clarify unfamiliar ideas. It involves mapping the relationships and attributes from a known domain onto a less familiar one, facilitating comprehension through comparative reasoning. Understanding analogy enhances problem-solving and communication by bridging gaps between abstract or complex topics and concrete, relatable examples.
Key Differences Between Interpretation and Analogy
Interpretation involves explaining the meaning or significance of information, text, or data based on context and evidence, whereas analogy draws a comparison between two different entities to highlight similarities for better understanding. Interpretation requires analyzing original content to infer deeper insights, while analogy simplifies complex concepts by relating them to familiar experiences. Key differences include their purpose--interpretation seeks clarity and explanation, whereas analogy aids comprehension through relational similarity.
Historical Contexts of Interpretation vs Analogy
Interpretation in historical contexts involves analyzing original texts or events to understand their meaning within the specific time and culture they originated, emphasizing direct evidence and contextual accuracy. Analogy draws parallels between historical events or texts and contemporary situations, using similarities to infer meaning or lessons, often bridging gaps in understanding where direct evidence is limited. Scholars maintain strict differentiation between interpretation's detailed exegesis and analogy's comparative reasoning to preserve historical integrity and avoid anachronism.
Applications in Linguistics and Philosophy
Interpretation in linguistics involves analyzing semantic meaning within language contexts, while analogy in philosophy serves to draw parallels between different concepts for better understanding. Linguistic interpretation applies to translating texts and deciphering idiomatic expressions, whereas philosophical analogy facilitates ethical reasoning and conceptual clarification. Both methods enhance comprehension by linking known information to new or complex ideas.
Interpretation vs Analogy in Legal Reasoning
Interpretation in legal reasoning involves explaining or clarifying the meaning of statutes, contracts, or legal texts based on language, context, and legislative intent. Analogy applies prior legal principles from similar cases to new situations lacking direct precedent, serving as a tool to bridge gaps in the law. While interpretation seeks to uncover original or intended meanings, analogy extends and adapts existing rules to novel circumstances, ensuring legal consistency and fairness.
Cognitive Processes: How We Interpret and Analogize
Interpretation involves decoding specific meanings from information by applying context, prior knowledge, and mental frameworks to understand unique content. Analogy relies on cognitive mapping between familiar and novel domains, enabling problem-solving and learning through recognizing structural similarities. Both processes engage mental representations but differ as interpretation extracts meaning from one context while analogy transfers understanding across contexts.
Common Misconceptions and Overlaps
Interpretation involves extracting meaning directly from a text or situation, while analogy draws comparisons between two different concepts to highlight similarities. A common misconception is that analogy serves as a definitive explanation rather than a tool for understanding complexity, leading to confusion between inference and illustrative comparison. Overlaps occur when analogies are mistaken for interpretations, obscuring the line between derived meaning and illustrative reasoning in analysis.
Implications for Critical Thinking and Communication
Interpretation involves analyzing meaning based on evidence, encouraging critical thinking by requiring evaluation of context and intent, while analogy draws comparisons between similar concepts to simplify complex ideas and enhance understanding. The implications for critical thinking include fostering deeper analysis through interpretation versus promoting relational reasoning via analogy. In communication, effective use of interpretation clarifies intent, whereas analogy bridges knowledge gaps by connecting unfamiliar information to known concepts.
Interpretation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com