Judicial corruption undermines the fairness and impartiality of legal systems, eroding public trust and enabling injustice. It often manifests through bribery, manipulation of case outcomes, or undue influence from powerful entities. Discover how judicial corruption affects societies and what measures can safeguard your rights by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
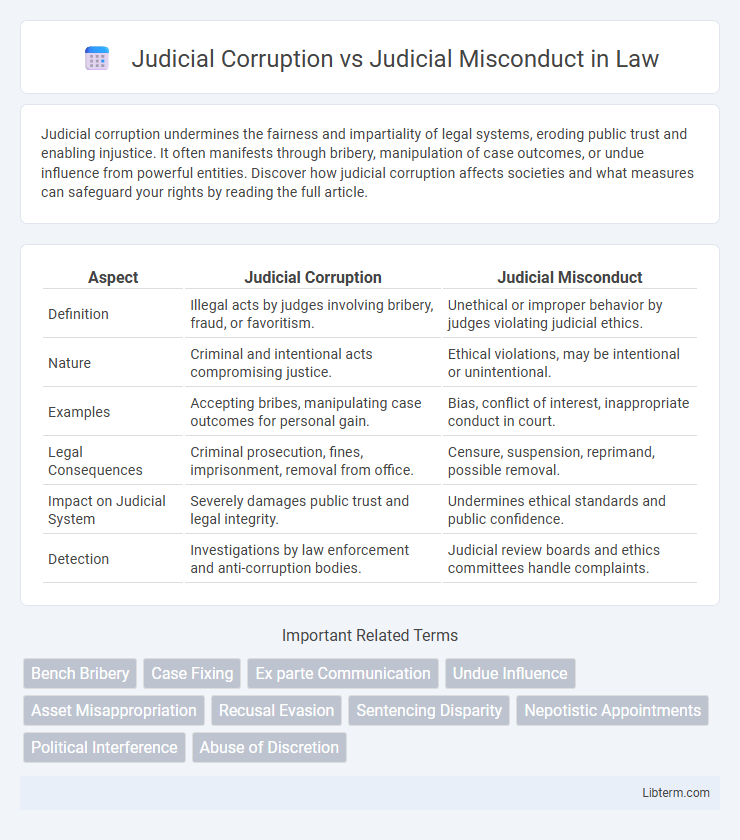
| Aspect | Judicial Corruption | Judicial Misconduct |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Illegal acts by judges involving bribery, fraud, or favoritism. | Unethical or improper behavior by judges violating judicial ethics. |
| Nature | Criminal and intentional acts compromising justice. | Ethical violations, may be intentional or unintentional. |
| Examples | Accepting bribes, manipulating case outcomes for personal gain. | Bias, conflict of interest, inappropriate conduct in court. |
| Legal Consequences | Criminal prosecution, fines, imprisonment, removal from office. | Censure, suspension, reprimand, possible removal. |
| Impact on Judicial System | Severely damages public trust and legal integrity. | Undermines ethical standards and public confidence. |
| Detection | Investigations by law enforcement and anti-corruption bodies. | Judicial review boards and ethics committees handle complaints. |
Understanding Judicial Corruption and Judicial Misconduct
Judicial corruption involves the abuse of judicial power for personal gain, including bribery, fraud, or other unethical acts compromising the integrity of the justice system. Judicial misconduct refers to improper behavior by judges, such as bias, conflicts of interest, or violations of legal ethics, which undermines public trust but may not involve criminal activity. Understanding the distinction is crucial for addressing accountability, as corruption denotes criminal offenses while misconduct pertains to ethical violations within judicial conduct standards.
Key Differences Between Judicial Corruption and Misconduct
Judicial corruption involves illegal actions by judges such as bribery, fraud, or accepting kickbacks to influence case outcomes, which directly undermines the integrity of the judicial system. Judicial misconduct refers to unethical or inappropriate behavior by judges, including biases, conflicts of interest, or procedural violations that do not necessarily involve criminal activity but erode public trust. The key difference lies in corruption's criminal element aimed at personal gain, while misconduct encompasses breaches of judicial ethics affecting fairness and impartiality.
Common Forms of Judicial Corruption
Common forms of judicial corruption include bribery, where judges accept money or favors in exchange for favorable rulings, and favoritism, involving biased decisions benefiting particular parties. Other prevalent types are manipulation of case outcomes and unauthorized ex parte communications that undermine the integrity of the judicial process. These corrupt practices directly erode public trust in the judiciary and hinder the fair administration of justice.
Typical Examples of Judicial Misconduct
Typical examples of judicial misconduct include conflicts of interest, bias, abuse of judicial power, and failure to uphold impartiality and ethical standards. Judges may engage in inappropriate behavior such as accepting gifts, showing favoritism, or making decisions influenced by personal relationships rather than facts and law. These actions undermine public trust and violate judicial codes of conduct without necessarily involving criminal acts characteristic of judicial corruption.
Legal Definitions: Corruption vs Misconduct in the Judiciary
Judicial corruption refers to the act of judges engaging in bribery, favoritism, or other unethical behaviors that compromise the impartiality and integrity of the legal system. Judicial misconduct encompasses a broader range of inappropriate actions, including unethical behavior, abuse of authority, and violations of judicial codes of conduct that may not necessarily involve corrupt intent. Legally, corruption is often prosecuted as a criminal offense involving illegal financial or personal gain, while misconduct is typically addressed through disciplinary procedures and sanctions within the judiciary.
Causes and Motivations Behind Judicial Corruption
Judicial corruption arises from personal gain motives such as bribery, nepotism, and influence peddling, undermining the integrity of the legal system. Unlike judicial misconduct, which often involves procedural errors or ethical lapses without illicit intent, corruption is driven by financial incentives and power abuse. Root causes include weak oversight, lack of transparency, inadequate enforcement of judicial ethics, and systemic vulnerabilities that allow corrupt practices to flourish.
Impact of Misconduct and Corruption on Judicial Integrity
Judicial corruption, involving bribery and illicit gains, severely undermines public trust and the rule of law, leading to biased verdicts and compromised justice. Judicial misconduct, such as ethical violations and abuse of authority, erodes judicial integrity by damaging the credibility and impartiality of the judiciary. Both corruption and misconduct diminish confidence in legal systems, hinder fair dispute resolution, and weaken democratic governance.
Mechanisms for Addressing Judicial Corruption
Mechanisms for addressing judicial corruption include independent judicial oversight bodies, transparent investigation procedures, and stringent disciplinary actions such as removal or suspension of corrupt judges. Whistleblower protections and confidential reporting channels enable the exposure of corrupt practices without fear of retaliation. International cooperation and anti-corruption frameworks further reinforce accountability by promoting best practices and monitoring judicial integrity.
Preventive Measures Against Judicial Misconduct
Preventive measures against judicial misconduct emphasize robust ethics training, transparent disciplinary procedures, and enhanced accountability through independent oversight bodies. Implementing regular performance evaluations and fostering a culture of integrity within the judiciary significantly reduce the incidence of unethical behavior. Technology-driven monitoring systems also help detect early signs of misconduct, ensuring timely interventions and preserving public trust in the legal system.
Strengthening Accountability in the Judicial System
Judicial corruption involves the abuse of judicial power for personal gain, compromising the integrity of legal decisions, while judicial misconduct includes unethical or improper behavior that undermines public trust without necessarily involving corruption. Strengthening accountability in the judicial system requires implementing rigorous oversight mechanisms such as independent judicial review boards and transparent disciplinary procedures to detect and deter both corruption and misconduct. Incorporating technology-driven case management and whistleblower protection programs enhances the monitoring of judicial behavior, promoting a culture of integrity and impartiality.
Judicial Corruption Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com