Partnerships drive innovation and growth by combining the strengths and resources of two or more entities. Establishing a clear agreement ensures aligned goals and smooth collaboration, maximizing the potential for mutual success. Discover how to build and maintain successful partnerships that can elevate your business by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
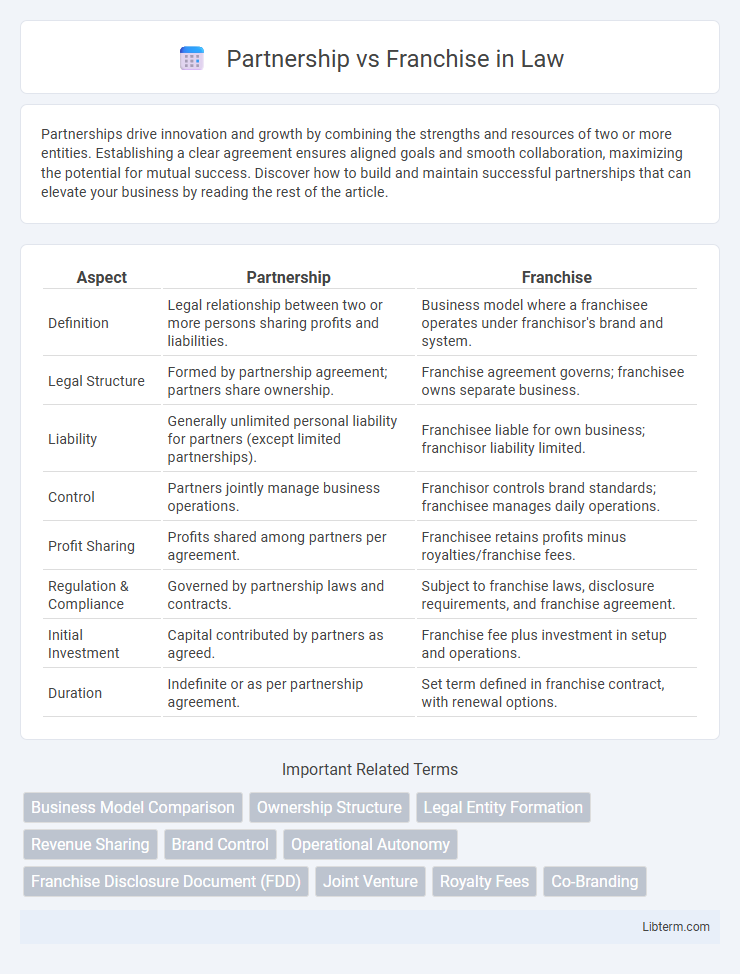
| Aspect | Partnership | Franchise |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal relationship between two or more persons sharing profits and liabilities. | Business model where a franchisee operates under franchisor's brand and system. |
| Legal Structure | Formed by partnership agreement; partners share ownership. | Franchise agreement governs; franchisee owns separate business. |
| Liability | Generally unlimited personal liability for partners (except limited partnerships). | Franchisee liable for own business; franchisor liability limited. |
| Control | Partners jointly manage business operations. | Franchisor controls brand standards; franchisee manages daily operations. |
| Profit Sharing | Profits shared among partners per agreement. | Franchisee retains profits minus royalties/franchise fees. |
| Regulation & Compliance | Governed by partnership laws and contracts. | Subject to franchise laws, disclosure requirements, and franchise agreement. |
| Initial Investment | Capital contributed by partners as agreed. | Franchise fee plus investment in setup and operations. |
| Duration | Indefinite or as per partnership agreement. | Set term defined in franchise contract, with renewal options. |
Understanding Partnerships and Franchises
Partnerships involve two or more individuals or entities sharing ownership, profits, and responsibilities in a business, with flexible management and liability structures based on agreements. Franchises operate under a licensing agreement where the franchisee uses the franchisor's brand, business model, and proprietary systems in exchange for fees and adherence to standardized operations. Understanding these distinctions helps businesses choose a growth strategy that aligns with their goals, risk tolerance, and control preferences.
Key Differences Between Partnerships and Franchises
Partnerships involve shared ownership and decision-making among two or more individuals who contribute capital, skills, and resources to operate a business collaboratively. Franchises operate under a licensing agreement where the franchisee adopts the franchisor's brand, business model, and operational guidelines in exchange for fees and royalties. Key differences include control structure, with partnerships allowing equal management input while franchises enforce standardized systems, and financial obligations, where partnerships share profits directly, whereas franchisees pay ongoing royalties and marketing fees.
Legal Structures: Partnership vs Franchise
Partnerships involve two or more individuals who share ownership, liability, and management responsibilities based on a partnership agreement, offering flexibility but exposing partners to joint liability. Franchises operate under a legal agreement where the franchisor grants the franchisee the right to use its trademark, business model, and ongoing support, creating a distinct legal relationship with defined obligations and reduced operational autonomy. The legal structure of a franchise often provides stronger brand protection and standardized operations compared to the more informal and variable arrangements seen in partnerships.
Ownership and Control Dynamics
Partnerships involve shared ownership where partners collectively make decisions and share profits, allowing for flexible control dynamics tailored to the partners' agreements. Franchises operate under a franchisee-owner model where the franchisor retains significant control over operations, brand standards, and marketing, while the franchisee manages day-to-day business activities. Ownership in partnerships is joint and often equal, whereas franchise ownership is individual but bound by contractual obligations to the franchisor's strict operational guidelines.
Financial Commitment and Investment
Partnerships typically require lower initial financial commitment as costs and investments are shared among partners, reducing individual risk. Franchises demand significant upfront fees and ongoing royalty payments, reflecting brand value and support services provided by the franchisor. Investment in partnerships varies based on agreed contributions, while franchises have structured financial requirements defined by franchise agreements.
Revenue Sharing and Profit Distribution
In a partnership, revenue sharing and profit distribution are typically flexible and agreed upon based on each partner's contribution, allowing for customized allocation according to investment, roles, or performance. Franchise agreements usually involve fixed royalty fees or a percentage of gross sales paid to the franchisor, with profits primarily retained by the franchisee after these deductions. This structure creates a clear division where franchisors earn steady income from royalties, while franchisees assume operational risks and profit potential.
Risk and Liability Considerations
Partnerships involve shared liability where all partners are personally responsible for business debts and legal actions, increasing individual financial risk. Franchises typically limit liability through the franchise agreement, protecting the franchisee from broader corporate risks but requiring adherence to franchisor policies. Understanding these risk and liability differences is crucial for entrepreneurs choosing between partnership agreements and franchise contracts.
Flexibility and Operational Autonomy
Partnerships offer greater flexibility and operational autonomy, allowing partners to make decisions collaboratively and adapt business strategies quickly without rigid corporate constraints. Franchises operate under strict guidelines set by the franchisor, limiting flexibility but providing a proven business model with established branding. The ability to customize operations significantly differs, with partnerships enabling tailored approaches while franchises require adherence to standardized procedures.
Branding and Support Systems
Partnerships allow shared branding decisions with flexible support systems tailored to mutual goals, fostering a collaborative identity. Franchises offer standardized branding with established support systems, ensuring consistency and operational efficiency across all locations. The choice impacts brand control and the level of ongoing support available to business operators.
Choosing the Best Model for Your Business
A partnership offers shared control, flexible management, and profit-sharing among partners, making it ideal for businesses seeking collaborative decision-making and personalized operations. Franchising provides a proven business model, brand recognition, and support from the franchisor, suitable for entrepreneurs aiming for rapid expansion and established market presence. Choosing the best model depends on factors like desired control level, investment capacity, risk tolerance, and long-term business goals.
Partnership Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com