Registration processes vary widely across different platforms and services, requiring accurate information to ensure seamless access and security. Understanding key steps involved, from data entry to verification, can streamline your experience and prevent common errors. Discover how to navigate successful registration in the following article.
Table of Comparison
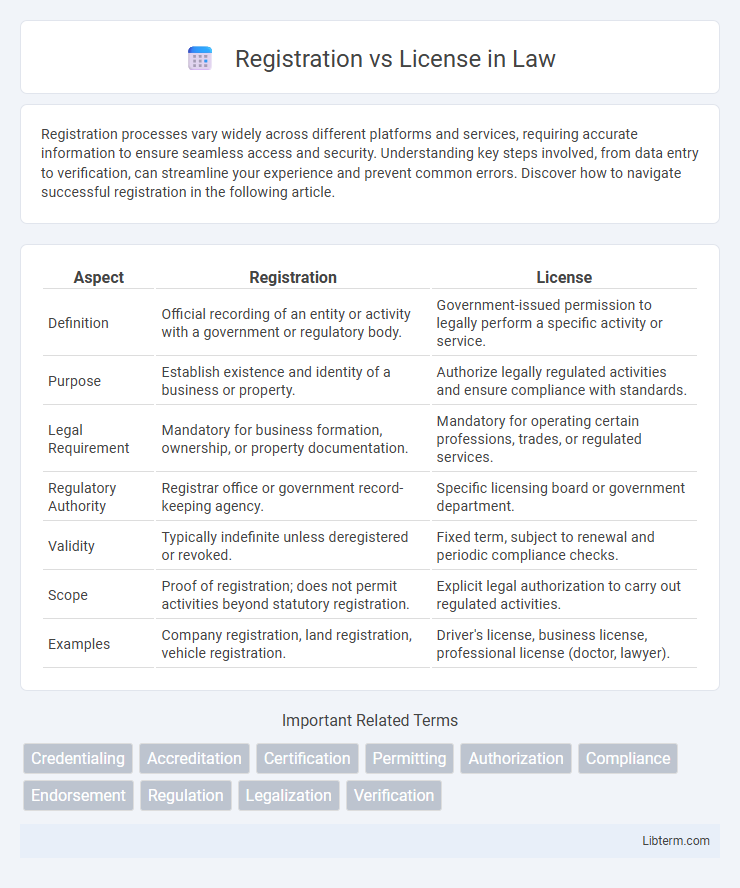
| Aspect | Registration | License |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official recording of an entity or activity with a government or regulatory body. | Government-issued permission to legally perform a specific activity or service. |
| Purpose | Establish existence and identity of a business or property. | Authorize legally regulated activities and ensure compliance with standards. |
| Legal Requirement | Mandatory for business formation, ownership, or property documentation. | Mandatory for operating certain professions, trades, or regulated services. |
| Regulatory Authority | Registrar office or government record-keeping agency. | Specific licensing board or government department. |
| Validity | Typically indefinite unless deregistered or revoked. | Fixed term, subject to renewal and periodic compliance checks. |
| Scope | Proof of registration; does not permit activities beyond statutory registration. | Explicit legal authorization to carry out regulated activities. |
| Examples | Company registration, land registration, vehicle registration. | Driver's license, business license, professional license (doctor, lawyer). |
Understanding Registration and Licensing
Registration involves formally recording information about a business or product with a government authority to establish its existence and legal standing. Licensing grants permission from a regulatory body to legally operate, often requiring compliance with specific standards or qualifications. Understanding the distinction between registration and licensing is crucial for ensuring legal compliance and operational legitimacy in various industries.
Key Differences Between Registration and License
Registration involves officially recording an entity or asset with a government or regulatory body, primarily serving as proof of existence or ownership, while a license grants legal permission to perform specific activities or operations. Registration typically requires meeting basic criteria and paying fees, whereas obtaining a license demands compliance with detailed standards, qualifications, or examinations to ensure competency and legal authorization. The key difference lies in registration being a formal acknowledgment, whereas a license is an active permit to engage in regulated conduct.
Registration: Definition and Purpose
Registration is the formal process of recording an entity, product, or service with a relevant government authority to establish its official existence and compliance with legal standards. It serves the purpose of ensuring traceability, accountability, and regulation by maintaining a public record that enables monitoring and enforcement of industry-specific rules. Unlike licenses, registration does not usually grant permission to engage in activities but confirms legal recognition and adherence to prescribed requirements.
License: Definition and Purpose
A license is an official authorization issued by a governmental or regulatory body granting permission to engage in a specific activity, such as operating a business or practicing a profession. Its primary purpose is to ensure compliance with established standards, protect public safety, and regulate market practices. Unlike registration, which is typically a formal recording process, a license often requires meeting specific qualifications and ongoing adherence to legal requirements.
Legal Requirements for Registration
Legal requirements for registration typically involve submitting detailed ownership information, proof of identity, and payment of prescribed fees to a government authority, establishing official recognition of an asset or entity. Registration serves as a foundational legal process to validate possession, enforce rights, and enable regulatory compliance, differing from licensing which grants permission to perform specific activities. Failure to fulfill registration requirements can result in penalties, legal disputes, or loss of legal protection under applicable laws.
Legal Requirements for Licensing
Licensing requires businesses to meet specific legal conditions set by local, state, or federal authorities, ensuring compliance with industry regulations and public safety standards. Registration typically involves recording business information with government agencies without the stringent legal checks mandatory in licensing processes. Legal requirements for licensing may include background checks, proof of qualifications, inspections, and ongoing renewals, all designed to authorize and regulate the operation of certain professions or commercial activities.
Cost Comparison: Registration vs License
Registration typically involves a one-time or annual fee that is lower than licensing costs, making it a more cost-effective option for basic compliance or initial business setup. Licensing often requires higher fees and periodic renewals, reflecting the added regulatory oversight, specialized permissions, or industry-specific qualifications it entails. Businesses should evaluate these cost differences in relation to their operational needs, as licensing expenses might be justified by the legal protections and market access it provides compared to simple registration.
Renewal Processes: Registration vs Licensing
Registration renewal typically requires submitting updated information and paying fees to maintain compliance within a specified period, ensuring continued legal recognition of a business or vehicle. Licensing renewal often involves fulfilling ongoing requirements such as training, background checks, or inspections to retain the privilege to operate in regulated industries. Both processes demand timely action to avoid penalties or suspension, but licensing renewals generally entail more rigorous verification steps compared to straightforward registration updates.
Common Industries Requiring Registration or Licensing
Common industries requiring registration or licensing include healthcare, construction, finance, and food service. Healthcare professionals such as doctors and nurses must obtain licenses to ensure compliance with medical standards, while construction firms register to meet safety and regulatory requirements. Financial institutions and food service businesses secure licenses to operate legally and maintain consumer trust.
Choosing Between Registration and License
Choosing between registration and license depends on regulatory requirements and the nature of the activity involved. Registration typically involves formally recording an entity or product with a government body, while a license grants legal permission to engage in specific activities. Businesses should assess legal obligations, the scope of operations, and compliance costs when deciding between registration and obtaining a license.
Registration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com